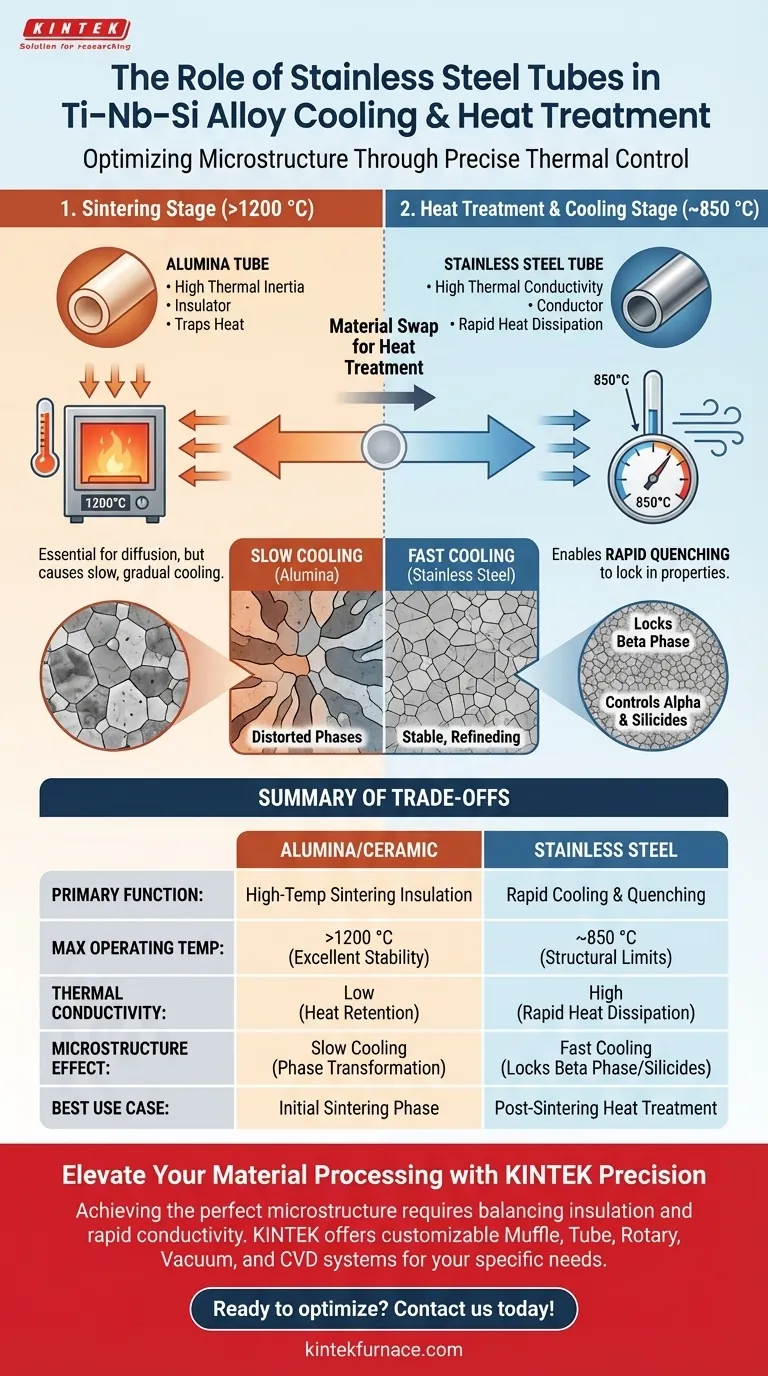
Stainless steel tubes are selected specifically for their high thermal conductivity, which allows for rapid heat dissipation during the cooling phase. Unlike ceramic alternatives that retain heat, stainless steel enables a fast cooling rate (quenching) when subjected to external ventilation, which is critical for locking in specific material properties.
The use of stainless steel is a strategic choice to control the alloy's microstructure. By facilitating rapid cooling from heat treatment temperatures (such as 850 °C), it regulates the stability of the beta phase and controls the precipitation kinetics of the alpha phase and silicides.

The Role of Thermal Conductivity
Overcoming Thermal Inertia
During the initial sintering process, materials like alumina (ceramic) are used because they are excellent insulators. They hold heat to ensure stability at extreme temperatures (up to 1200 °C).
However, this insulation becomes a liability when you need to cool the material down. Alumina tubes trap heat, leading to a slow, gradual cooling process.
Facilitating the Quench Effect
Stainless steel acts as a thermal conductor rather than an insulator. By replacing the alumina tube with a stainless steel one for post-sintering heat treatments, operators can rapidly extract heat from the system.
This exchange allows external ventilation systems to effectively "quench" the alloy, dropping its temperature at a rate that ceramic tubes simply cannot support.
Controlling Microstructure
Regulating Phase Stability
The speed at which Ti–Nb–Si alloys are cooled directly impacts their internal structure. Rapid cooling is required to regulate the stability of the beta phase of the titanium.
Without the rapid heat extraction provided by the stainless steel tube, the beta phase may decompose or transform in undesirable ways, altering the alloy's mechanical properties.
Managing Precipitation Kinetics
Cooling rates also dictate how other elements within the alloy solidify and grow. The quenching effect helps control the precipitation of the alpha phase and silicides.
Precise control over these kinetics prevents the formation of coarse or uneven precipitates, ensuring the final material meets the necessary metallurgical quality standards.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Temperature Limitations
While stainless steel is superior for cooling, it cannot withstand the extreme temperatures of the initial sintering phase.
Primary sintering often occurs at 1200 °C or higher to facilitate diffusion and alloying. At these temperatures, stainless steel would lose structural integrity or melt.
The Necessity of Material Swapping
This creates a necessary operational trade-off: Alumina must be used for the high-temperature sintering carrier to provide structural strength and a sealed vacuum environment.
Stainless steel is introduced only during the lower-temperature heat treatment stages (around 850 °C) where rapid cooling becomes the priority over extreme heat resistance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct tube material depends entirely on where you are in the processing cycle.
- If your primary focus is High-Temperature Sintering (1200 °C+): Use Alumina or Quartz tubes to ensure structural stability, thermal insulation, and protection against oxidation during prolonged high-heat cycles.
- If your primary focus is Heat Treatment and Quenching (~850 °C): Use Stainless Steel tubes to leverage high thermal conductivity for rapid cooling and precise control over phase stability and precipitation.
Ultimately, successful processing of Ti–Nb–Si alloys requires utilizing ceramic stability for atom diffusion and metallic conductivity for microstructural locking.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Alumina/Ceramic Tubes | Stainless Steel Tubes |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | High-temperature sintering insulation | Rapid cooling and quenching |
| Max Operating Temp | >1200 °C (Excellent stability) | ~850 °C (Structural limits) |
| Thermal Conductivity | Low (Heat retention) | High (Rapid heat dissipation) |
| Microstructure Effect | Slow cooling (Phase transformation) | Fast cooling (Locks beta phase/silicides) |
| Best Use Case | Initial sintering phase | Post-sintering heat treatment |
Elevate Your Material Processing with KINTEK Precision
Achieving the perfect microstructure in Ti–Nb–Si alloys requires the right balance of thermal insulation and rapid conductivity. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of lab high-temp furnaces, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet your specific cooling and sintering requirements.
Whether you need the high-heat resistance of alumina or the rapid quenching capabilities of specialized metallic configurations, our engineering team is ready to deliver the exact solution for your research or production needs.
Ready to optimize your thermal processing? Contact us today to discuss your custom furnace requirements!
Visual Guide
References
- Douglas Daniel de Carvalho, Cristiano Binder. Effect of Nb and Si Content on Phase Stability, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Sintered Ti–Nb–Si Alloys. DOI: 10.3390/met15010034
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of specialized sealing ferrules in heating experiments? Ensure Hermetic Isolation and Purity
- How do a three-stub tuner and a sliding short contribute to microwave carbothermic reduction? Maximize Energy Efficiency
- What is the function of ceramic balls within a box furnace? Improve Coke Graphitization & System Safety
- What is the role of a high-temperature ceramic boat during phosphidation? Ensure Pure and Stable Chemical Synthesis
- How does the purity of alumina ceramic tubes compare to quartz ceramic tubes? Discover Key Differences for Your Lab
- What roles do high-purity graphite molds play in the SPS of copper sulfide? Enhance Your Thermoelectric Material Quality
- What is the role of vacuum pressure impregnation equipment in full-cell saturation tests? Ensure Precise ASE Analysis
- How do sealed boxes and backfill materials function during high-temperature powder metallurgy sintering?



















