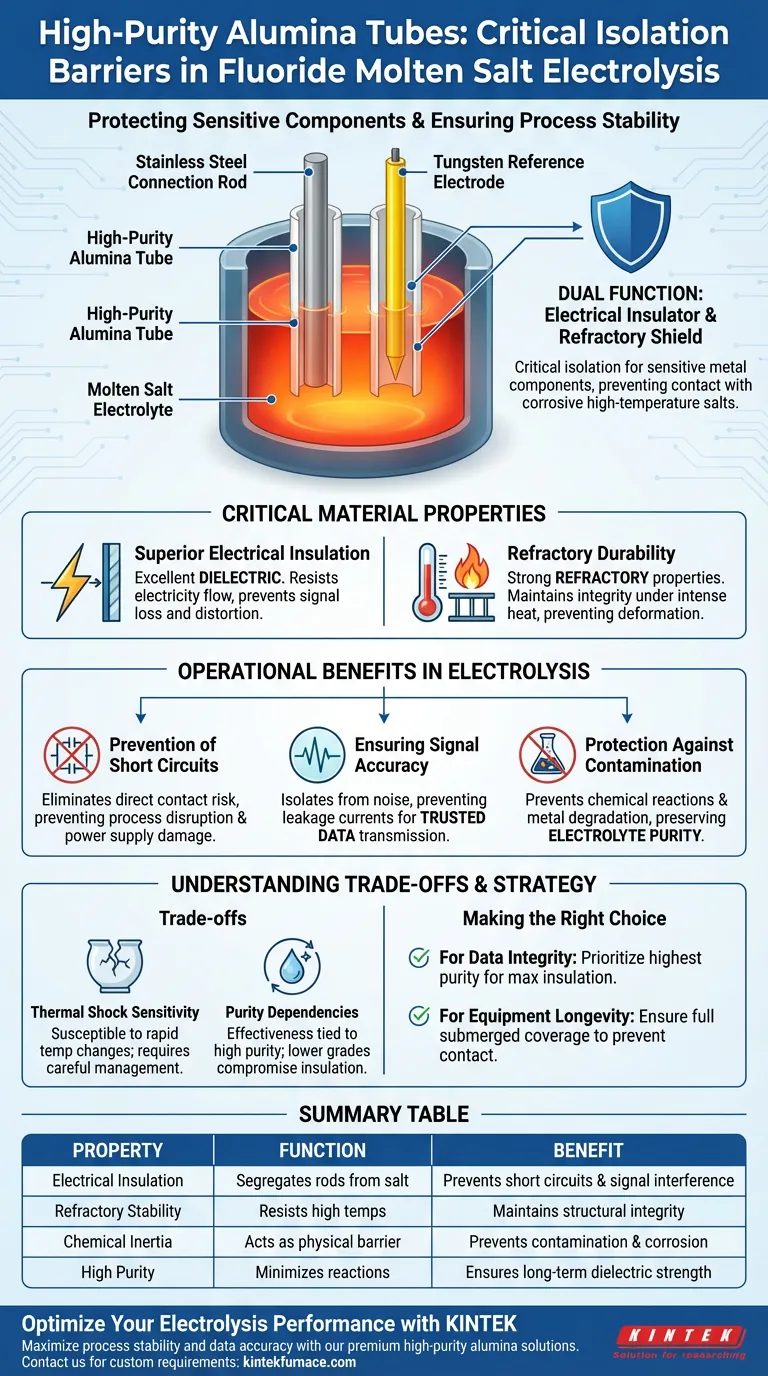
High-purity Alumina Tubes act as critical isolation barriers within the harsh environment of fluoride molten salt electrolysis. These tubes are primarily selected to sheath sensitive metal components—specifically stainless steel connection rods and tungsten reference electrodes—effectively separating them from corrosive high-temperature salts.
The core value of high-purity alumina lies in its dual function as both a refractory shield and an electrical insulator. By physically segregating conductive metals from the electrolyte, it prevents short circuits and contamination, ensuring precise data collection and prolonged equipment life.

The Critical Role of Material Properties
To understand why Alumina is the standard, one must look at the specific demands of the electrolysis environment.
Superior Electrical Insulation
In an electrolytic process, controlling the flow of current is paramount. Alumina is an excellent dielectric, meaning it resists the flow of electricity.
By acting as an insulating sleeve, the tube ensures that electrical signals are not lost or distorted through contact with the conductive molten salt. This isolation is vital for maintaining the integrity of the electrical circuit within the cell.
Refractory Durability
Fluoride molten salts operate at extremely high temperatures that would degrade many standard materials. Alumina possesses strong refractory properties, allowing it to maintain structural integrity under intense heat.
This thermal resistance ensures the protective sleeve does not soften, deform, or melt during operation, providing a reliable physical barrier for the internal components.
Operational Benefits in Electrolysis
The application of these tubes directly impacts the efficiency and accuracy of the electrolysis process.
Prevention of Short Circuits
The primary danger in this setup is the unintended flow of electricity between the metal components and the salt bath.
The Alumina sleeve prevents direct contact between the stainless steel or tungsten and the electrolyte. This eliminates the risk of short circuits that could disrupt the process or damage the power supply.
Ensuring Signal Accuracy
For reference electrodes, such as those made of tungsten, signal clarity is essential for monitoring the process.
By isolating the rod from the "noise" of the corrosive bath and preventing leakage currents, the Alumina tube ensures accurate signal transmission. This allows operators to trust the data coming from the cell.
Protection Against Contamination
Direct contact between metal rods and corrosive salts leads to chemical reactions that degrade the metal.
This degradation releases impurities into the molten salt, altering its chemistry. The Alumina barrier prevents this chemical contamination, preserving the purity of the electrolyte and the quality of the final product.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While high-purity Alumina is the material of choice, it is not without operational considerations.
Thermal Shock Sensitivity
Like most ceramics, Alumina can be susceptible to thermal shock. Rapid changes in temperature—such as inserting a cold tube directly into molten salt—can cause cracking.
Operators must manage temperature gradients carefully during startup and shutdown to prevent immediate mechanical failure of the sleeve.
Purity Dependencies
The effectiveness of the tube is directly tied to its purity level. The reference specifically highlights "high-purity" Alumina.
Lower-grade alumina may contain impurities that reduce its electrical resistance or react with the fluoride salts. Using sub-standard tubes can compromise the insulation barrier, leading to the exact shorts and contamination the system is designed to avoid.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When designing or maintaining an electrolysis setup, focus on these implementation strategies:
- If your primary focus is Data Integrity: Prioritize the highest available purity of Alumina to maximize electrical insulation and minimize signal interference.
- If your primary focus is Equipment Longevity: Ensure the Alumina sleeve covers the entire submerged length of the connection rods to prevent any point of contact with corrosive salts.
Ultimately, the use of high-purity Alumina is an investment in process stability, safeguarding both your expensive instrumentation and the chemical purity of your electrolyte.
Summary Table:
| Property | Function in Electrolysis | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Insulation | Segregates metal rods from conductive salt | Prevents short circuits and signal interference |
| Refractory Stability | Resists high operating temperatures | Maintains structural integrity under intense heat |
| Chemical Inertia | Acts as a physical barrier | Prevents electrolyte contamination and rod corrosion |
| High Purity | Minimizes trace element reactions | Ensures long-term dielectric strength and material life |
Optimize Your Electrolysis Performance with KINTEK
Maximize your process stability and data accuracy with our premium high-purity alumina solutions. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK provides high-performance components tailored for the most demanding environments.
Whether you require specialized protective sleeves or fully customizable Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, or CVD systems, our lab high-temperature furnaces are engineered to meet your unique research and production needs. Don't let contamination or equipment failure stall your progress—partner with the experts in thermal technology.
Contact KINTEK Today to Discuss Your Custom Requirements
Visual Guide
References
- Kamaljeet Singh, Guðrún Sævarsdóttir. Overpotential on Oxygen-Evolving Platinum and Ni-Fe-Cu Anode for Low-Temperature Molten Fluoride Electrolytes. DOI: 10.1007/s11837-024-06425-5
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Magnesium Extraction and Purification Condensing Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
People Also Ask
- Why are desiccators containing saturated salt solutions used when evaluating the hygroscopicity of modified wood?
- What are the technical considerations for selecting a graphite crucible? Expert Insights for Molten Salt Electrolysis
- What is the role of providing a uniform heating environment? Achieve Perfect Deep Eutectic Solvent Formation
- What roles do high-purity graphite dies play in SPS of Ti-6Al-4V? Mastering Efficient Composite Sintering
- What is the primary function of graphitized quartz glass tubes in the synthesis of Bi2Se3-Nd2Se3 alloys?
- What is the role of a vacuum pass-box and a high-capacity vacuum pump? Ensuring Safety in Battery Recycling
- What are the specific functions of the grinder and laboratory oven during sugarcane-based activated carbon preparation?
- How does a high-precision heating stage contribute to the drying and crystallization of FAPbBr3 nanosheets?



















