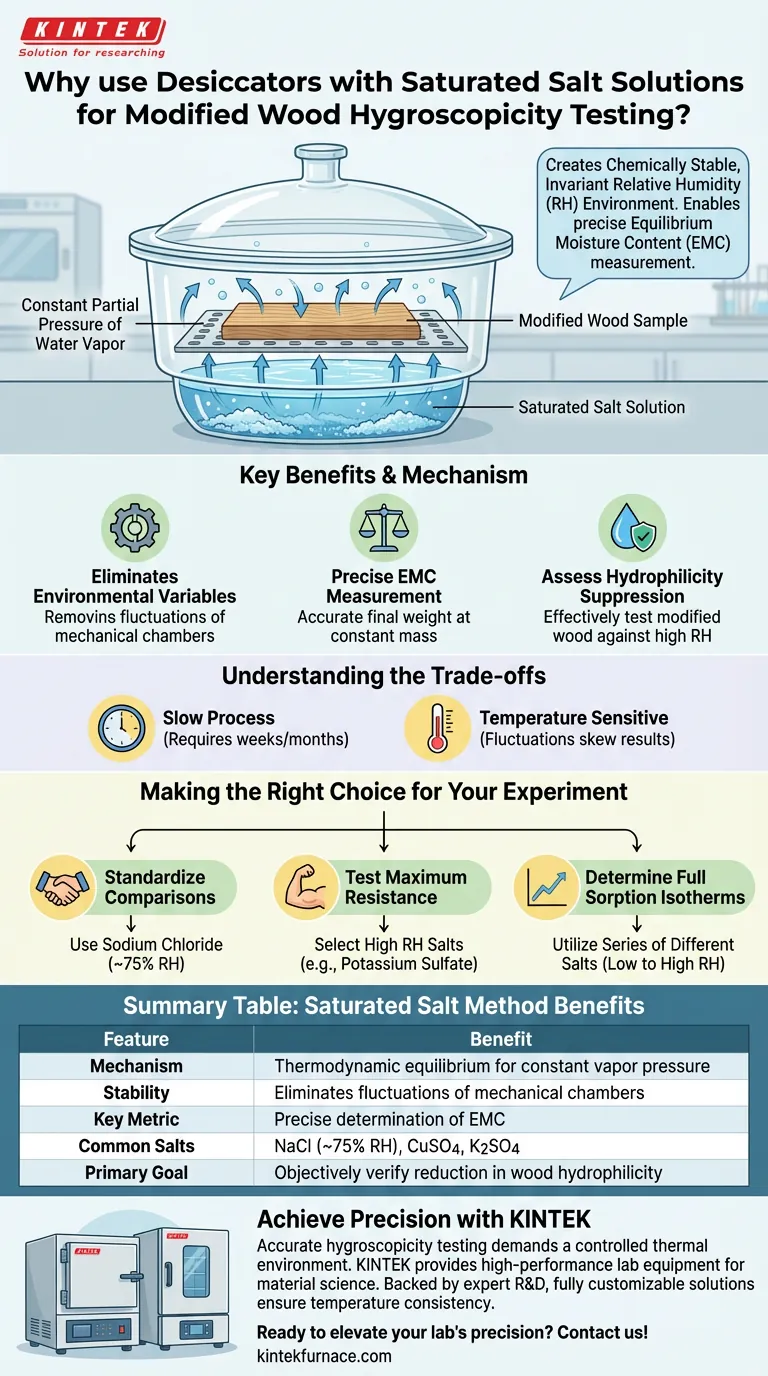
Desiccators containing saturated salt solutions are utilized to generate chemically stable, invariant relative humidity environments that are essential for standardized wood science testing. This method allows researchers to expose modified wood to precise moisture conditions—such as 75% or 98% humidity—to accurately determine its hygroscopic properties without the fluctuations inherent in mechanical climate chambers.
The core function of saturated salt solutions is to create a constant partial pressure of water vapor within a sealed system. This enables the precise measurement of Equilibrium Moisture Content (EMC), providing the objective data needed to verify if a modification process has successfully reduced the wood's natural affinity for water.

The Mechanism of Humidity Control
Creating a Stable Atmosphere
Saturated salt solutions are used because they naturally maintain a specific relative humidity (RH) based on their chemical properties.
When a salt like sodium chloride or copper sulfate pentahydrate is saturated in water within a sealed desiccator, it establishes a thermodynamic equilibrium.
This equilibrium forces the air inside the container to remain at a fixed humidity level, regardless of slight external variations, provided the temperature remains constant.
Eliminating Environmental Variables
In open-air testing or mechanical chambers, humidity can fluctuate due to sensor lag or airflow issues.
A sealed desiccator acts as a static micro-climate. By removing these variables, researchers ensure that any change in the wood’s mass is due solely to the wood's interaction with that specific humidity level, not experimental error.
Evaluating Wood Modification Effectiveness
Measuring Equilibrium Moisture Content (EMC)
The primary metric for hygroscopicity is Equilibrium Moisture Content (EMC).
Researchers place wood samples into the desiccator and wait until the samples reach a constant mass.
This state indicates that the moisture entering the wood balances the moisture leaving it. Accurately capturing this final weight is critical for calculating the EMC.
Assessing Hydrophilicity Suppression
The goal of thermal modification is to suppress the wood's hydrophilicity (its attraction to water).
By using salts that generate high humidity (e.g., 98%), researchers can subject the wood to "stress tests."
If the modified wood shows a significantly lower EMC compared to untreated wood under these identical, salt-controlled conditions, the thermal modification is deemed effective.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Factor of Time
While highly accurate, the saturated salt method is a slow process.
Reaching a true constant mass in a static environment relies on diffusion and can take weeks or even months, depending on the sample size and permeability.
Temperature Sensitivity
The precise humidity generated by a saturated salt is temperature-dependent.
If the laboratory temperature fluctuates, the equilibrium RH of the salt solution will shift, potentially skewing the EMC results. Strict temperature control of the room or incubator is required.
Making the Right Choice for Your Experiment
To ensure your data is valid and comparable to established literature, align your salt selection with your specific research goals.
- If your primary focus is standardizing comparisons: Use widely accepted salts like Sodium Chloride (~75% RH) to benchmark against existing studies on thermal modification.
- If your primary focus is testing maximum resistance: Select salts that generate near-saturation humidity (e.g., Potassium Sulfate or similar for high RH) to challenge the wood's moisture resistance limits.
- If your primary focus is determining full sorption isotherms: Utilize a series of different salt desiccators to plot the wood's behavior across the entire humidity range (low to high).
Precision in your humidity control is the only way to objectively quantify the performance of modified wood.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Saturated Salt Method Benefit |
|---|---|
| Mechanism | Thermodynamic equilibrium for constant partial vapor pressure |
| Stability | Eliminates fluctuations found in mechanical climate chambers |
| Key Metric | Precise determination of Equilibrium Moisture Content (EMC) |
| Common Salts | Sodium Chloride (~75% RH), Copper Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate |
| Primary Goal | Objectively verify reduction in wood hydrophilicity |
Achieve Precision in Wood Science Research with KINTEK
Accurate hygroscopicity testing requires more than just the right salt; it demands a perfectly controlled thermal environment. KINTEK provides high-performance laboratory equipment designed to meet the rigorous standards of material science.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, along with other specialized lab high-temp furnaces—all fully customizable to your unique research needs. Whether you are performing thermal modification or long-term EMC stabilization, our solutions ensure the temperature consistency your experiments demand.
Ready to elevate your lab's precision? Contact us today to discuss your custom furnace requirements!
Visual Guide
References
- Guntis Sosins, Jānis Zicāns. Water-Related Properties of Wood after Thermal Modification in Closed Process under Pressure in Nitrogen. DOI: 10.3390/f15010140
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station CVD Machine
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Magnesium Extraction and Purification Condensing Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the technical functions of condensation units and gas collection bags? Optimize Your Reduction Experiments
- How does the hardness of alumina ceramics compare to other materials? Discover Its Superior Wear Resistance
- What is a vacuum chamber good for? Mastering Material Processing with Environmental Control
- Why are lidded alumina crucibles required for LLZO sintering? Ensure High Ionic Conductivity and Phase Purity
- What is the specific function of a laboratory high-temperature furnace? Master Lost-PLA Burnout Success
- What is the significance of using ceramic balls of varying diameters? Optimize Reactor Flow and Filtration
- Are customization options available for alumina ceramic furnace tubes? Tailor Them for Your Lab's Needs
- Why is a graphite crucible used and the melt temperature maintained at 750°C for AA7150-Al2O3? Optimize Your Composite
















