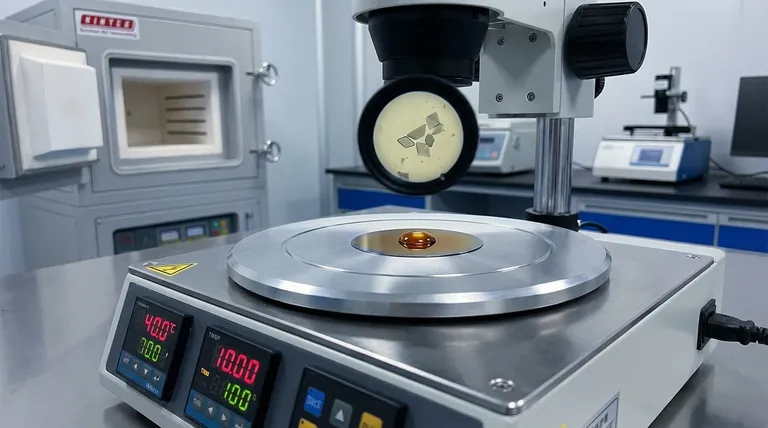
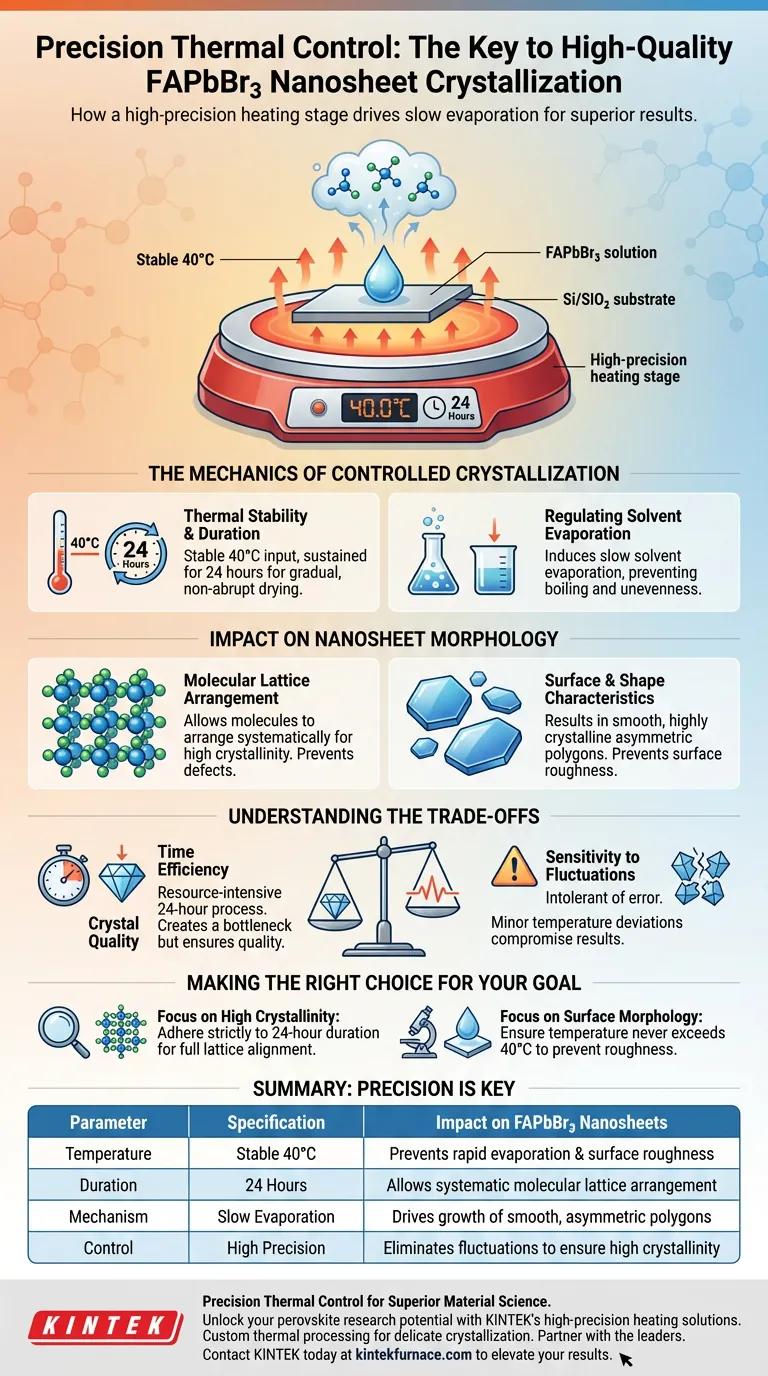
A high-precision heating stage acts as a rigorous control mechanism for solvent evaporation. By maintaining a stable, low temperature of 40°C over a continuous 24-hour period, it facilitates the slow drying of FAPbBr3 solutions on Si/SiO2 substrates. This controlled thermal environment is the primary driver for achieving specific morphological and structural properties in the final nanosheets.
The quality of FAPbBr3 crystallization is directly tied to the stability of the evaporation rate. A high-precision stage eliminates thermal fluctuations, allowing molecules to arrange systematically into the crystal lattice to produce smooth, highly crystalline asymmetric polygons.

The Mechanics of Controlled Crystallization
Thermal Stability and Duration
The crystallization process for FAPbBr3 requires a sustained, low-energy input. The heating stage must provide a consistent 40°C heat source.
This temperature must be held without fluctuation for 24 hours. This extended duration ensures that the drying process is gradual rather than abrupt.
Regulating Solvent Evaporation
The primary function of this thermal setup is to induce slow solvent evaporation. Rapid evaporation often leads to disordered molecular structures.
By keeping the temperature low and constant, the stage prevents the solvent from boiling off or evaporating unevenly. This creates a quiescent environment ideal for orderly solid-state formation.
Impact on Nanosheet Morphology
Molecular Lattice Arrangement
The controlled environment allows FAPbBr3 molecules to organize naturally. Because the solvent leaves slowly, the molecules have time to arrange themselves according to the crystal lattice.
This strictly ordered arrangement is what defines "high crystallinity." Without this precision, the internal structure would likely contain defects or amorphous regions.
Surface and Shape Characteristics
The physical outcome of this process is distinct. The slow growth phase results in asymmetric polygonal nanosheets.
Furthermore, the steady heat prevents surface roughness. The resulting nanosheets are characterized by exceptionally smooth surfaces, indicating a uniform growth front during the drying phase.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Time Efficiency vs. Crystal Quality
The most significant trade-off in this method is time. Dedicating a high-precision stage to a single sample for 24 hours is a resource-intensive process.
If your project requires rapid throughput, this specific low-temperature method creates a bottleneck. However, attempting to speed up the process by increasing temperature would compromise the lattice structure.
Sensitivity to Fluctuations
Reliance on high precision means the process is intolerant of error. Even minor deviations from the 40°C setpoint could alter the evaporation rate.
If the stage fails to maintain stability, the result may be uneven crystallization or rough surface textures, rendering the 24-hour wait futile.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the utility of a high-precision heating stage for FAPbBr3, consider your specific end-goals:
- If your primary focus is High Crystallinity: strictly adhere to the 24-hour duration to allow full molecular lattice alignment.
- If your primary focus is Surface Morphology: Ensure the temperature never exceeds 40°C to prevent rapid evaporation and surface roughness.
Precision in thermal control is not just a variable; it is the defining factor between a disordered solid and a high-quality crystal.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Specification | Impact on FAPbBr3 Nanosheets |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Stable 40°C | Prevents rapid evaporation & surface roughness |
| Duration | 24 Hours | Allows systematic molecular lattice arrangement |
| Mechanism | Slow Evaporation | Drives the growth of smooth, asymmetric polygons |
| Control | High Precision | Eliminates fluctuations to ensure high crystallinity |
Precision Thermal Control for Superior Material Science
Unlock the full potential of your perovskite research with KINTEK. Our high-precision heating solutions provide the exact thermal stability required for delicate processes like the 24-hour crystallization of FAPbBr3 nanosheets.
Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of lab equipment including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all of which are fully customizable to meet your unique research specifications. Don't let thermal fluctuations compromise your crystal quality—partner with the leaders in high-temperature laboratory technology.
Ready to elevate your crystallization results? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom thermal processing needs!
Visual Guide
References
- Yao Liu, Yingkai Liu. High-response formamidine bromide lead hybrid cadmium sulfide photodetector. DOI: 10.3788/col202422.022502
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why are high-purity alumina crucibles used for containing molten high-silicon steel? Ensure Purity & Thermal Stability
- Why are high-purity alumina crucibles preferred over quartz crucibles at 1873 K? Ensure Precision at Extreme Heat
- Why use a graphite box for WS2 sulfurization? Essential for High-Quality Thin Film Synthesis
- What are the electrical properties of alumina tubes? Discover Superior Insulation for Extreme Conditions
- Why is a precision laboratory hydraulic press required for sulfide-based batteries? Achieve Critical Ion Conductivity
- What are the properties and uses of ceramic tubes? Unlock High-Temp, Insulating Solutions
- How are constant temperature water baths and drying ovens utilized to verify bonding quality? Master EN 314-1 Testing
- What are the structural functions of the dual-chamber quartz glass container? Optimize Magnesium Alloy Vapor Analysis



















