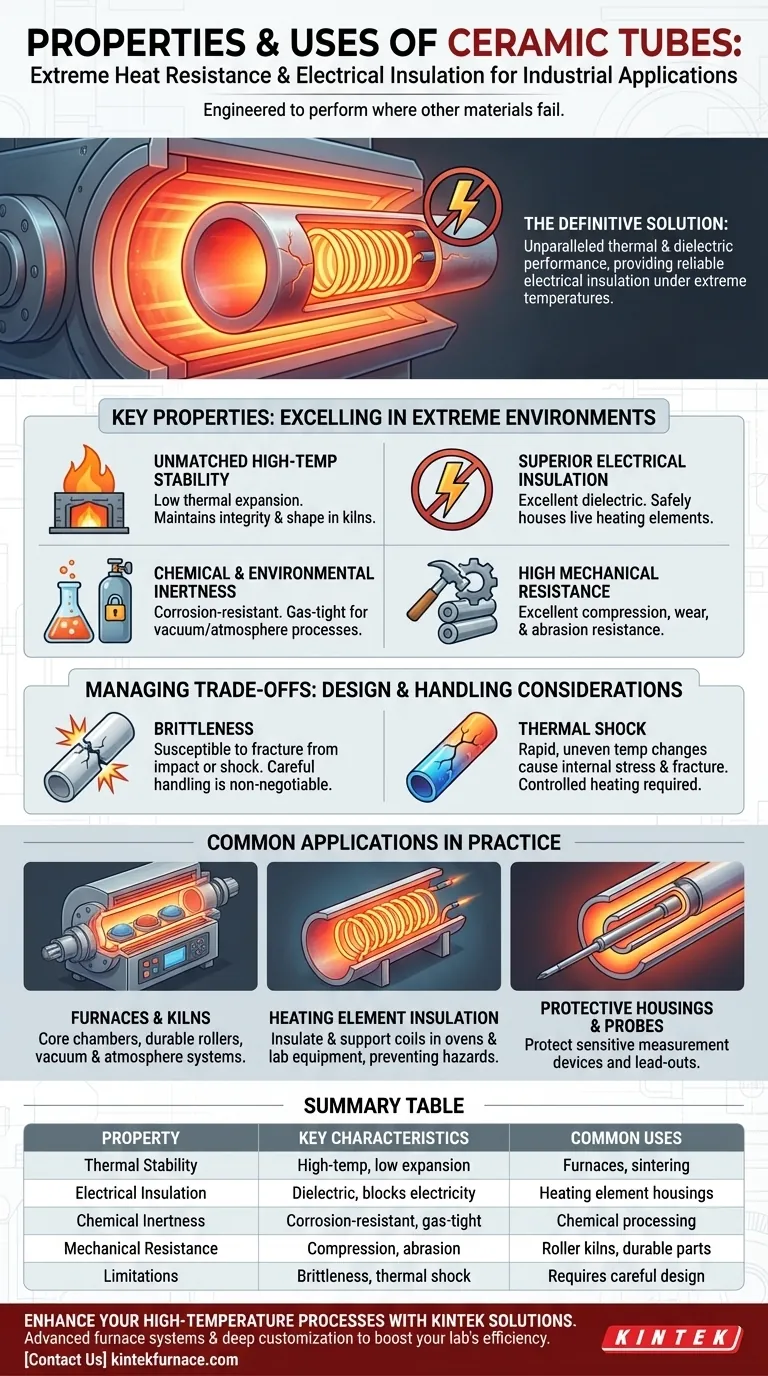
In essence, ceramic tubes are specialized components engineered to perform in environments where most other materials fail. They are primarily defined by their exceptional resistance to extreme heat and their inability to conduct electricity, making them indispensable for high-temperature industrial processes and electrical applications.
The core challenge in many advanced engineering applications is finding a material that can simultaneously withstand extreme temperatures and provide reliable electrical insulation. Ceramic tubes are the definitive solution, offering unparalleled thermal and dielectric performance, provided their inherent brittleness is managed through careful design and handling.
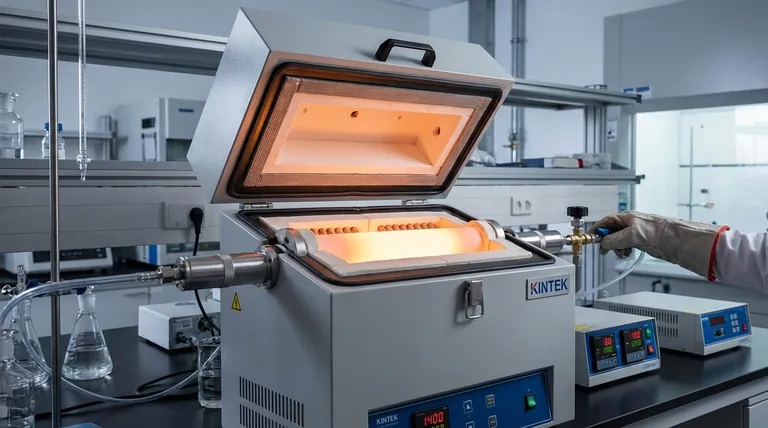

Why Ceramic Tubes Excel in Extreme Environments
The value of ceramic tubes comes from a unique combination of thermal, electrical, and mechanical properties. Understanding these is key to leveraging them effectively.
Unmatched High-Temperature Stability
Ceramic materials, particularly alumina, are fundamentally stable at very high temperatures. They maintain their structural integrity and properties in environments like industrial furnaces and kilns where metals would warp or melt.
This stability is also linked to their low thermal expansion, meaning they do not significantly change in size or shape when heated. This predictability is critical for precision components.
Superior Electrical Insulation
Ceramics are excellent dielectric materials, meaning they are electrical insulators. They block the flow of electricity, even at high temperatures.
This property is crucial for applications involving heating elements. The tube can safely house a live electrical wire, allowing it to get incredibly hot without short-circuiting or creating an electrical hazard.
Chemical and Environmental Inertness
Ceramic tubes exhibit strong resistance to corrosion and chemical attack. This allows them to be used in processes involving reactive chemicals or harsh atmospheres.
Furthermore, they can be manufactured to be gas-tight. This makes them ideal for creating a controlled vacuum or a protective gas environment inside a high-temperature furnace, which is essential for many modern material processing and scientific applications.
High Mechanical Resistance
Despite being brittle, ceramics offer very high compression resistance and are extremely hard, leading to excellent wear and abrasion resistance.
In applications like roller kilns, where materials are constantly moving through hot zones, this durability ensures a long service life and prevents contamination from worn-out components.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Brittleness and Thermal Shock
While incredibly capable, ceramic tubes are not indestructible. Their primary limitation is a lack of ductility, which must be accounted for in design and handling.
The Challenge of Brittleness
Unlike metals, ceramics do not bend or deform under stress; they fracture. This means they are highly susceptible to failure from impact or sharp mechanical shock.
Careful handling is non-negotiable. Dropping a ceramic tube or subjecting it to sudden vibration or impact will likely cause it to crack or shatter.
Thermal Shock Considerations
While they are built for heat, rapid and uneven temperature changes can create internal stresses that lead to fracture—a phenomenon known as thermal shock.
Although high-purity ceramics like alumina have good thermal shock resistance, engineering controls are still necessary. Heating and cooling rates must be carefully managed to ensure the temperature across the tube remains as uniform as possible.
Common Applications in Practice
The properties of ceramic tubes make them the go-to solution in several key industrial and scientific fields.
High-Temperature Furnaces and Kilns
This is the most common application. Ceramic tubes form the core chamber of tube furnaces, act as durable rollers in roller hearth kilns, and create controlled environments in vacuum and atmosphere furnaces.
Insulating and Supporting Heating Elements
Ceramic tubes are widely used to electrically insulate heating coils in everything from industrial ovens to laboratory equipment. They provide the rigid structure needed to hold the element in place while preventing electrical current from escaping.
Protective Housings and Probes
Their ability to withstand heat and insulate makes them perfect for protecting sensitive measurement devices. This includes sheaths for thermocouples measuring temperature inside a furnace and lead-outs for routing electrical cables through hot zones.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right material requires matching its properties to your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is thermal stability in a controlled atmosphere: Ceramic tubes are the ideal choice for constructing furnace chambers for processes like sintering or chemical synthesis.
- If your primary focus is electrical insulation for a heating element: Ceramic tubes are the industry standard for safely containing and supporting coils in high-temperature heaters.
- If your application involves high vibration or risk of physical impact: You must either design robust mechanical protection for the ceramic tube or consider alternative materials if its thermal or electrical properties are not strictly required.
By understanding both their immense capabilities and their practical limitations, you can confidently engineer solutions that leverage the unique strengths of ceramic tubes.
Summary Table:
| Property | Key Characteristics | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Stability | High-temperature resistance, low thermal expansion | Tube furnaces, kilns, sintering processes |
| Electrical Insulation | Excellent dielectric, blocks electricity flow | Heating element housings, electrical safety |
| Chemical Inertness | Corrosion-resistant, gas-tight | Vacuum/atmosphere furnaces, chemical processing |
| Mechanical Resistance | High compression and abrasion resistance | Roller kilns, durable components |
| Limitations | Brittleness, thermal shock sensitivity | Requires careful handling and design |
Ready to enhance your high-temperature processes with reliable ceramic tube solutions? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace systems, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure we meet your unique experimental needs precisely. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can boost your lab's efficiency and performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What are the material requirements for furnace tubes? Optimize Performance and Safety in High-Temperature Labs
- What core process conditions does a tube furnace provide? Mastering Catalyst Precursor Treatment
- What is flash vacuum pyrolysis and how is a tube furnace utilized in this process? Unlock High-Temp Chemical Reactions
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing



















