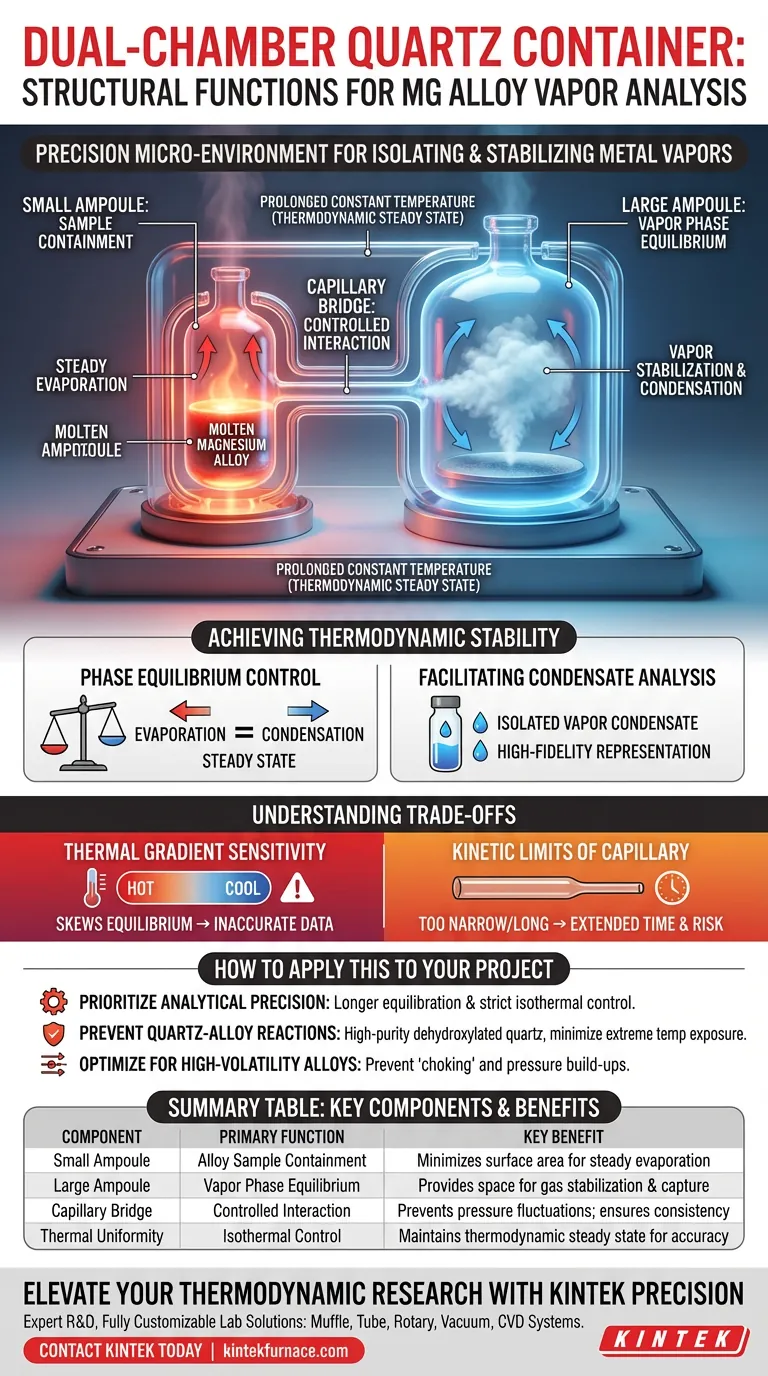
The dual-chamber quartz glass container serves as a precision micro-environment for isolating and stabilizing metal vapors. Its primary function is to facilitate a controlled chemical equilibrium between a liquid magnesium alloy and its gaseous phase. This structural arrangement allows for the accurate capture of vapor composition through condensation, ensuring that the resulting sample is representative of the alloy's thermodynamic state.
This design uses a segregated two-chamber system connected by a capillary to decouple the liquid alloy source from the equilibrium vapor, ensuring that chemical equilibrium is fully established before analysis.

Functional Components of the Dual-Chamber Design
The Small Ampoule: Sample Containment
The smaller ampoule is specifically engineered to hold the solid or liquid magnesium alloy sample. By restricting the alloy to this smaller volume, the design minimizes the surface area of the liquid phase exposed to the broader system, which helps maintain a steady evaporation rate.
The Large Ampoule: Vapor Phase Equilibrium
The larger ampoule functions as a dedicated equilibrium chamber where the vapor phase expands and stabilizes. This increased volume provides sufficient space for the gas phase to reach a state of full chemical equilibrium with the liquid source under constant temperature conditions.
The Capillary Bridge: Controlled Interaction
The two chambers are interconnected by a narrow capillary. This bridge serves as a restricted pathway that allows for the slow migration of atoms between chambers, preventing rapid pressure fluctuations and ensuring that the vapor in the larger chamber remains consistent with the liquid's equilibrium pressure.
Achieving Thermodynamic Stability
Phase Equilibrium Control
The primary structural goal of this container is to facilitate prolonged constant temperature conditions. This environment is essential for ensuring that the transition between the alloy's liquid phase and the gas phase reaches a "steady state," where the rate of evaporation equals the rate of condensation.
Facilitating Condensate Analysis
Once equilibrium is reached, the design allows for the precise collection of the resulting condensate. Because the vapor has been isolated in the larger chamber, the condensed material provides a high-fidelity representation of the vapor's composition without contamination from the bulk liquid alloy.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Thermal Gradient Sensitivity
The effectiveness of the dual-chamber design is highly dependent on thermal uniformity. If a temperature gradient exists between the small and large ampoules, the vapor will migrate toward the cooler zone, potentially skewing the equilibrium and leading to inaccurate compositional data.
Kinetic Limits of the Capillary
While the capillary is vital for controlled equilibrium, it introduces kinetic resistance. If the capillary is too narrow or too long, the time required to reach full chemical equilibrium may be significantly extended, increasing the risk of quartz degradation or sample oxidation over long durations.
How to Apply This to Your Project
To ensure the highest accuracy when using dual-chamber quartz containers for magnesium alloy analysis, consider your specific experimental constraints:
- If your primary focus is analytical precision: Prioritize a longer equilibration time at a strictly controlled isothermal temperature to ensure the vapor in the large ampoule is perfectly representative.
- If your primary focus is preventing quartz-alloy reactions: Use high-purity, dehydroxylated quartz glass and minimize the total time the small ampoule is exposed to extreme temperatures.
- If your primary focus is high-volatility alloys: Ensure the capillary diameter is optimized to prevent "choking" of the vapor flow, which can lead to localized pressure build-ups.
By leveraging the structural separation of the liquid and vapor phases, you can transform a complex thermodynamic challenge into a manageable and repeatable analytical process.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Function | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Small Ampoule | Alloy Sample Containment | Minimizes surface area for steady evaporation |
| Large Ampoule | Vapor Phase Equilibrium | Provides space for gas stabilization and capture |
| Capillary Bridge | Controlled Interaction | Prevents pressure fluctuations; ensures consistency |
| Thermal Uniformity | Isothermal Control | Maintains thermodynamic steady state for accuracy |
Elevate Your Thermodynamic Research with KINTEK Precision
Precise material analysis requires high-performance equipment that can withstand extreme conditions. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of lab solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems. Whether you are working with magnesium alloys or complex vapor phase equilibria, our high-temperature furnaces are fully customizable to meet your unique research needs.
Ready to achieve superior thermal stability?
Contact KINTEK Today to discuss your custom furnace requirements with our technical team.
Visual Guide
References
- В. Н. Володин, Alexey Trebukhov. On the Problem of the Distillation Separation of Secondary Alloys of Magnesium with Zinc and Magnesium with Cadmium. DOI: 10.3390/met14060671
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station CVD Machine
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role do graphite molds play in the Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS)? Enhance Alumina Composite Performance
- Can alumina ceramic furnace tubes be reused? Maximize Cost Savings and Safety
- Why are desiccators containing saturated salt solutions used when evaluating the hygroscopicity of modified wood?
- Why is an additional large alumina outer crucible required? Ensure Safety and Equipment Longevity in Steel Research
- Why are laboratory precision stirrers and heating devices essential for synthesizing magnetic precursor solutions?
- Why is dimensional accuracy important for alumina ceramic furnace tubes? Ensure Reliable High-Temp Performance
- Why is an alundum crucible necessary for the melting and casting of FeAl alloys? Ensure Maximum Purity and Stability
- What is the specific function of the water circulation cooler in zirconium sponge processing? Key for Purity & Safety



















