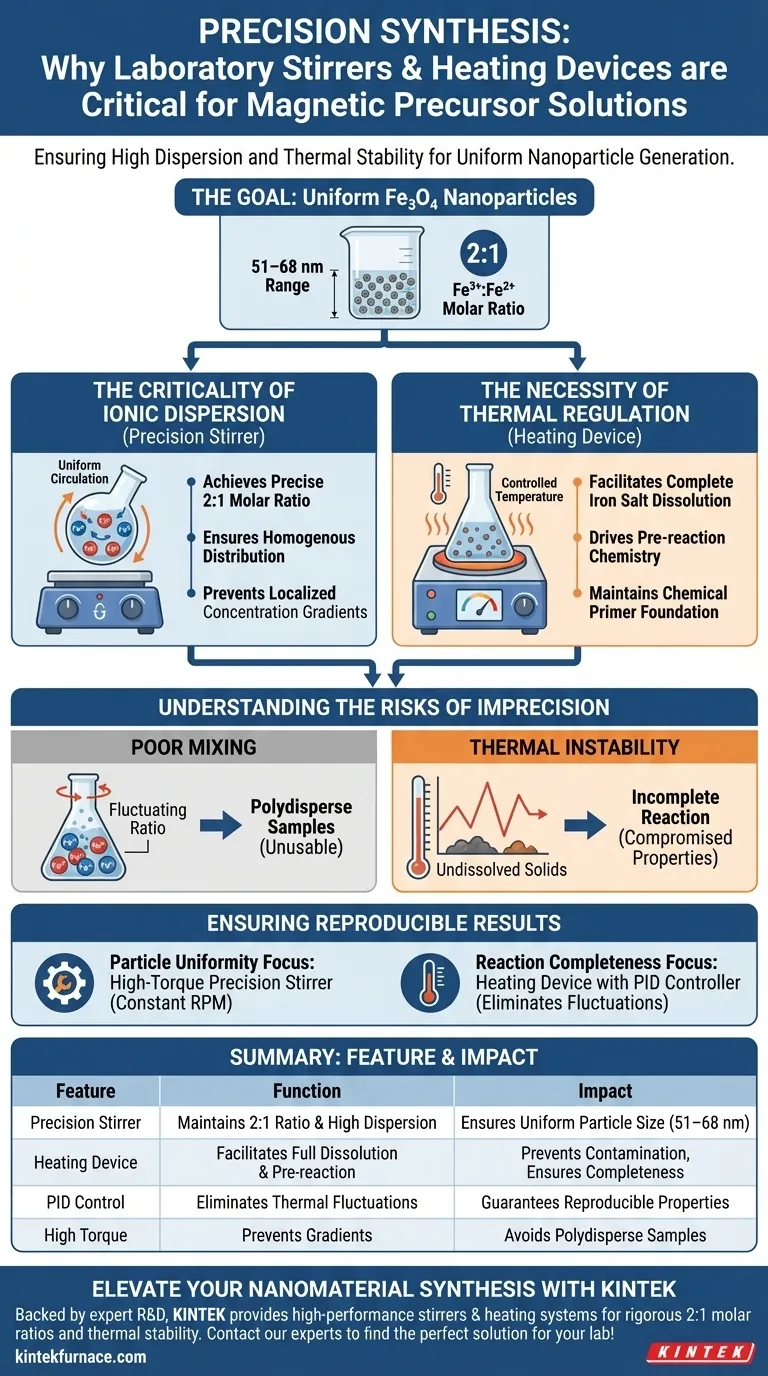
Laboratory precision stirrers and heating devices act as the critical control mechanisms for synthesizing magnetic precursor solutions. They function in tandem to ensure the high dispersion of ferric (Fe3+) and ferrous (Fe2+) ions while maintaining the precise thermal environment required for full molecular dissolution. Without this strict regulation, the chemical foundation necessary for uniform nanoparticle generation cannot be established.
Success in synthesizing magnetic nanoparticles is defined by uniformity. Precision equipment ensures the specific 2:1 molar ratio and thermal stability required to produce Fe3O4 nanoparticles with consistent sizes ranging from 51 to 68 nm.
The Criticality of Ionic Dispersion
Achieving the Correct Molar Ratio
For magnetic precursor solutions, simply adding ingredients is insufficient. You must achieve a precise 2:1 molar ratio of ferric ions (Fe3+) to ferrous ions (Fe2+).
Precision stirrers circulate the aqueous solution to ensure these ions are distributed evenly throughout the vessel.
High-Level Dispersion
The goal of stirring is to prevent localized concentration gradients.
High dispersion ensures that every part of the solution interacts uniformly. This homogeneity is the prerequisite for the ammonia precipitation method used to generate the final particles.
The Necessity of Thermal Regulation
Facilitating Complete Dissolution
Iron salt molecules require specific thermal energy levels to dissolve fully into the solution.
Heating devices provide the constant, controlled temperature needed to break down these salts. This prevents undissolved solids from contaminating the precursor phase.
Driving the Pre-reaction
Beyond simple dissolution, heat drives the necessary pre-reaction chemistry.
By maintaining a specific temperature, the device ensures the solution is chemically primed. This creates the "foundation" mentioned in scientific literature for the successful formation of Fe3O4 nanoparticles.
Understanding the Risks of Imprecision
The Consequence of Poor Mixing
If the stirring is inconsistent, the 2:1 molar ratio will fluctuate within the container.
This leads to significant variations in particle size. Instead of a tight range (51–68 nm), you may produce polydisperse samples that are unusable for precision applications.
The Impact of Thermal Instability
If the heating device fluctuates or fails to maintain the set point, the iron salts may not fully dissolve.
This results in an incomplete reaction. The final magnetic properties of the nanoparticles will likely be compromised due to a flawed structural foundation.
Ensuring Reproducible Results
To maximize the quality of your magnetic precursor solutions, align your equipment choices with your specific synthesis goals:
- If your primary focus is Particle Uniformity: Prioritize a high-torque precision stirrer that maintains constant RPM to guarantee the homogenous dispersion of the 2:1 ionic ratio.
- If your primary focus is Reaction Completeness: Ensure your heating device has a PID controller to eliminate thermal fluctuations that could inhibit full salt dissolution.
Precision in the precursor stage is the only way to guarantee predictability in the final magnetic nanomaterial.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in Synthesis | Impact on Final Nanoparticles |
|---|---|---|
| Precision Stirrer | Maintains 2:1 Fe3+/Fe2+ molar ratio & high dispersion | Ensures uniform particle size (51–68 nm) |
| Heating Device | Facilitates full salt dissolution & drives pre-reaction | Prevents contamination & ensures chemical completeness |
| PID Control | Eliminates thermal fluctuations | Guarantees reproducible magnetic properties |
| High Torque | Prevents localized concentration gradients | Avoids polydisperse, unusable samples |
Elevate Your Nanomaterial Synthesis with KINTEK
Achieving the perfect magnetic precursor requires more than just basic mixing—it demands absolute precision. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK provides the high-performance stirrers and heating systems needed to maintain the rigorous 2:1 molar ratios and thermal stability your research depends on.
From customizable CVD systems to precision lab furnaces and thermal devices, our equipment is designed to help you produce consistent, high-quality nanoparticles every time. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your lab!
Visual Guide
References
- Róger Moya, Karla J. Merazzo. Magnetic and Physical-Mechanical Properties of Wood Particleboards Composite (MWPC) Fabricated with FE3o4 Nanoparticles and Three Plantation Wood. DOI: 10.22382/wfs-2023-19
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering and Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why must alloy samples be sealed in vacuum-evacuated fused silica containers during diffusion annealing processes?
- What is the primary function of a constant temperature drying oven? Master S53P4 Bioactive Glass Gel Integrity
- What processes is the circulating water multifunctional vacuum pump suitable for? Ideal for Clean, Economical Lab Vacuum Needs
- What are the advantages of using borosilicate glass for the upper atmosphere control chamber? Protect Your Vacuum Seals
- What functions do carbon black and carbon fiber felt serve as insulation? Maximize Efficiency in 3000°C Furnaces
- Why is toluene used as a grinding aid in wet ball milling? Master Fine Metal Powder Synthesis with PCAs
- What is the function of a forced air drying oven in zeolite preparation? Protect Pore Integrity and Ensure Uniformity
- How does the design of high-purity alumina capillaries influence bubble formation? Optimize Surface Tension Accuracy



















