At its core, dimensional accuracy is critical for an alumina ceramic furnace tube because it dictates whether the tube can be installed correctly and perform its function without failing. A tube with precise dimensions fits properly into the furnace assembly, forms a reliable seal, and avoids creating localized stress points that lead to mechanical or thermal fracture.
While alumina is chosen for its exceptional heat and chemical resistance, these material properties are rendered useless if the component does not fit. Dimensional inaccuracy is the leading cause of installation failure and premature cracking in high-temperature ceramic systems.

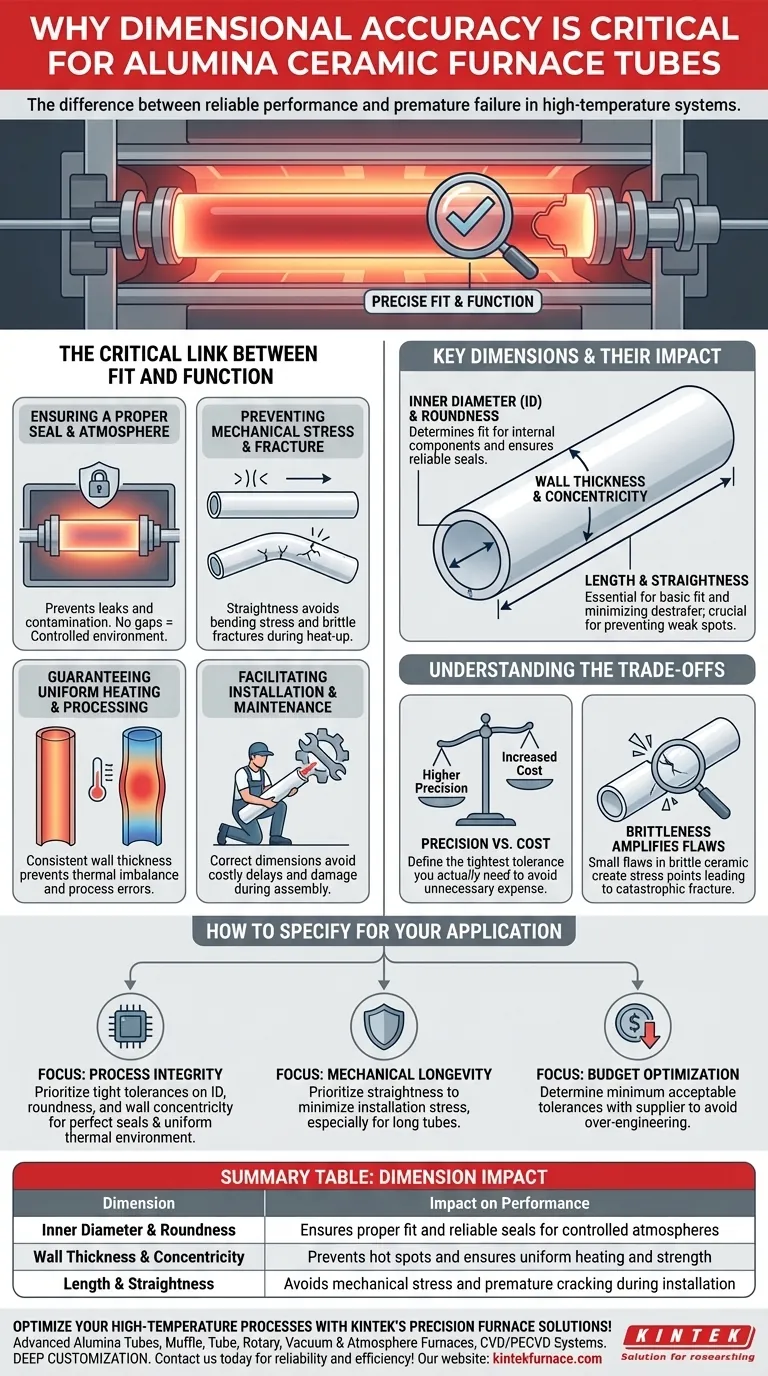
The Critical Link Between Fit and Function
The specified dimensions of a furnace tube are not arbitrary numbers; they are engineering requirements that directly impact the safety and reliability of the entire high-temperature process.
Ensuring a Proper Seal and Atmosphere
A furnace tube must form a tight seal with end caps or flanges to maintain a controlled atmosphere. If the inner or outer diameter is incorrect, or if the tube is not perfectly round, gaps will form.
These gaps lead to leaks, compromising the process by allowing contamination from the outside air or loss of expensive process gases.
Preventing Mechanical Stress and Fracture
Alumina ceramic is very strong under compression but is brittle and has poor resistance to bending forces and thermal shock. Poor dimensional accuracy is a primary source of this destructive mechanical stress.
If a tube is not perfectly straight, forcing it into a rigid furnace body creates immense bending stress. This stored mechanical energy makes the tube extremely vulnerable to fracturing when thermal stress is added during heat-up.
Guaranteeing Uniform Heating and Processing
Many applications require a perfectly uniform temperature zone inside the tube. This is only possible if the wall thickness is consistent.
An inconsistent wall, a result of poor concentricity, will create hot and cold spots along the tube's length. This thermal imbalance can ruin sensitive processes like crystal growth or semiconductor wafer annealing.
Facilitating Installation and Maintenance
From a practical standpoint, a tube with correct dimensions simply fits. This avoids costly delays during assembly and prevents technicians from damaging the brittle tube while trying to force it into place.
Key Dimensions and Their Specific Impact
Each dimension serves a distinct purpose. Understanding them allows you to specify a tube correctly for your application's unique demands.
Inner Diameter (ID) and Roundness
The ID determines what can fit inside the tube, such as sample boats or thermocouples. Roundness is essential for creating a reliable seal with internal components or end flanges.
Wall Thickness and Concentricity
Wall thickness dictates the tube's overall mechanical strength and insulation properties. Concentricity—the uniformity of that wall thickness around the entire circumference—is crucial for preventing weak spots and ensuring even heat transfer.
Length and Straightness
Length is a basic fit requirement. Straightness, however, is a critical engineering parameter. A lack of straightness is a primary driver of the destructive bending stresses that cause premature failure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Specifying a component is always an exercise in balancing ideal performance with practical constraints.
Precision vs. Cost
Achieving higher dimensional accuracy requires more advanced manufacturing and grinding processes, which significantly increases cost. It is critical to define the tightest tolerance you actually need for your application to function.
Over-specifying dimensions that are not critical to your process (e.g., demanding extreme straightness for a short, freely-hanging tube) adds unnecessary expense.
Brittleness Amplifies Flaws
The inherent nature of alumina ceramic means it does not bend or yield under stress—it cracks. This is why a small dimensional flaw is so dangerous.
A slight deviation in straightness or roundness might be irrelevant for a metal tube, but in a brittle ceramic, it creates a stress concentration point that can easily become the origin of a catastrophic fracture during heating or cooling.
How to Specify for Your Application
Use your primary goal to guide your specification focus.
- If your primary focus is process integrity (e.g., semiconductor manufacturing): Prioritize tight tolerances on inner diameter, roundness, and wall concentricity to ensure a perfect seal and uniform thermal environment.
- If your primary focus is mechanical longevity and safety: Prioritize straightness above all else to minimize installation stress, especially for long tubes that are rigidly supported.
- If your primary focus is budget optimization: Work with a reputable supplier to analyze your furnace design and determine the minimum acceptable tolerances required, avoiding the cost of over-engineering.
Ultimately, specifying the correct dimensions is the foundation for a reliable and successful high-temperature operation.
Summary Table:
| Dimension | Impact on Performance |
|---|---|
| Inner Diameter & Roundness | Ensures proper fit and reliable seals for controlled atmospheres |
| Wall Thickness & Concentricity | Prevents hot spots and ensures uniform heating and strength |
| Length & Straightness | Avoids mechanical stress and premature cracking during installation |
Optimize your high-temperature processes with KINTEK's precision furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide advanced alumina ceramic tubes and a full product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—with deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your lab's reliability and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability



















