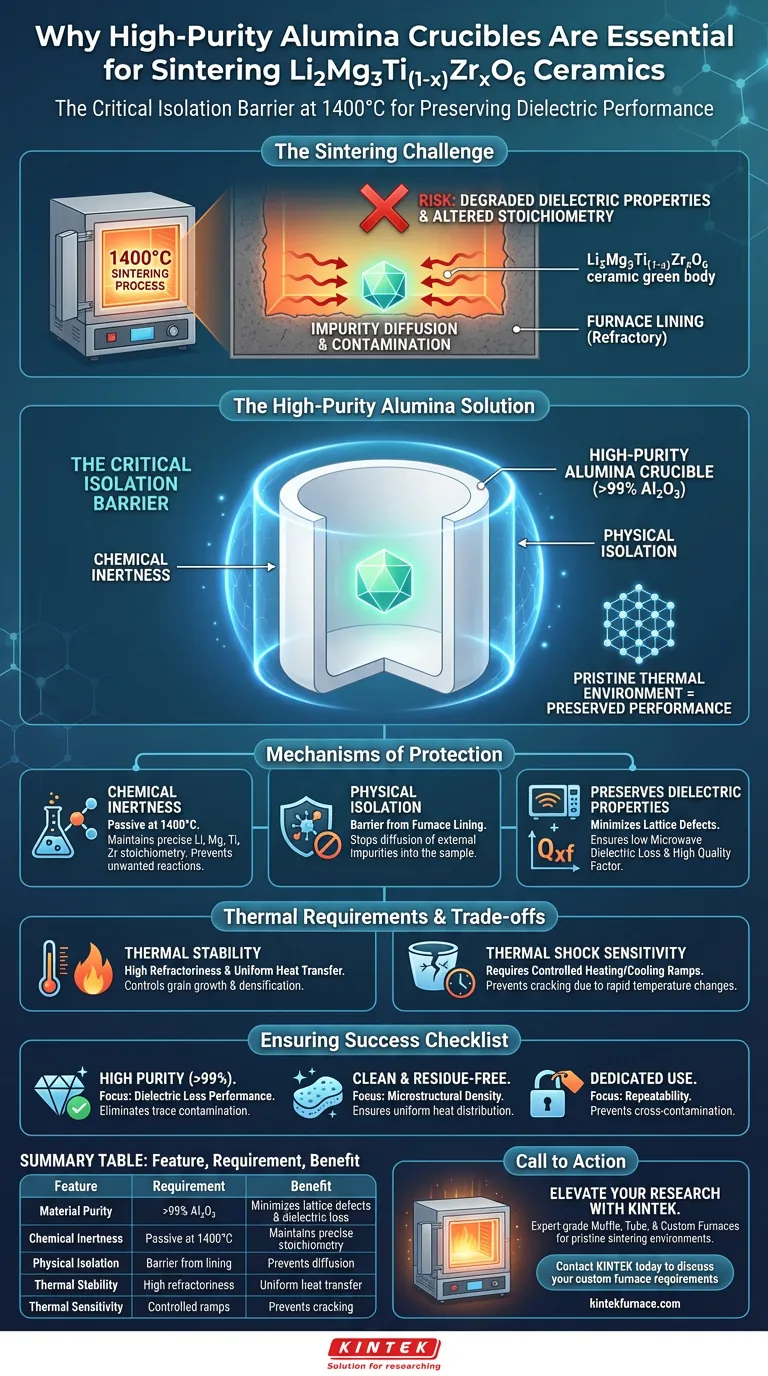
High-purity alumina crucibles are the critical isolation barrier required to sinter Li2Mg3Ti(1-x)ZrxO6 ceramics successfully. These vessels act as a safeguard during the 1400°C heating process, physically preventing the reactive ceramic green bodies from contacting the furnace lining. This isolation is essential to stop external impurities from altering the material's composition, which would directly degrade its microwave dielectric loss performance.
Sintering advanced ceramics requires a pristine thermal environment, not just high heat. High-purity alumina crucibles provide the necessary chemical inertness to isolate the sample from the furnace, preventing contamination that would destroy the delicate dielectric properties of the final product.

The Mechanism of Protection
Chemical Inertness at High Temperatures
The primary function of the alumina crucible is to remain chemically passive. At sintering temperatures reaching 1400°C, many materials become reactive.
High-purity alumina does not react with the precursor powders of Li2Mg3Ti(1-x)ZrxO6. This ensures that the stoichiometry—the precise ratio of elements like Lithium, Magnesium, and Titanium—remains exactly as calculated during the synthesis phase.
Isolating the Furnace Lining
Furnace linings are often made of refractory materials that can degrade or outgas at high temperatures. Without a crucible, the ceramic green body would be in direct contact with these linings.
The alumina crucible provides physical isolation, ensuring the sample only touches a chemically stable surface. This prevents the diffusion of foreign atoms from the furnace insulation into the ceramic matrix.
Preserving Dielectric Properties
For microwave ceramics, purity is the defining factor for performance. The presence of external impurities creates defects in the crystal lattice.
These defects significantly increase microwave dielectric loss. By preventing these impurities from entering the sample, the alumina crucible directly contributes to maintaining a high Quality Factor (Qxf) and stable dielectric constant.
Thermal Stability Requirements
Withstanding the Sintering Window
The sintering process for these ceramics requires sustained temperatures of approximately 1400°C. The containment vessel must possess superior refractoriness to maintain its structural integrity under this thermal load.
Uniform Heat Transfer
While acting as a barrier to matter, the crucible must effectively transfer energy. The thermal stability of alumina ensures that the heat from the furnace is transferred to the green body without the crucible warping or degrading.
This stability allows for the precise control of grain growth and densification, which are driven by diffusion mechanisms dependent on a uniform temperature field.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Limits of Inertness
While high-purity alumina is excellent for Li2Mg3Ti(1-x)ZrxO6, it is not universally inert. It is chosen specifically because it resists corrosion from this specific oxide system.
In other contexts, such as with extremely reactive molten salts or specific reducing atmospheres, even alumina can degrade or leach components. Therefore, its "inertness" should always be viewed as relative to the specific material being sintered.
Thermal Shock Sensitivity
Alumina ceramics are generally dense and brittle. While they handle high steady-state temperatures well, they can be susceptible to thermal shock if heating or cooling rates are too aggressive.
Rapid temperature changes can cause the crucible to crack, potentially ruining the sample. This necessitates careful programming of the furnace's heating and cooling ramps.
Ensuring Experimental Success
To maximize the quality of your Li2Mg3Ti(1-x)ZrxO6 ceramics, consider the following based on your specific goals:
- If your primary focus is Dielectric Loss Performance: Ensure the crucible is certified high-purity (>99% Al2O3) to eliminate any risk of trace contamination affecting the lattice.
- If your primary focus is Microstructural Density: Verify that the crucible is clean and free of residue from previous runs to ensure uniform heat distribution and consistent grain growth.
- If your primary focus is Repeatability: Use a dedicated crucible for this specific composition to prevent cross-contamination from other experimental materials.
Ultimately, the crucible is not just a container; it is an active component of the quality control process that defines the final electronic properties of your ceramic.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Requirement for Sintering | Benefit to Ceramic Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Material Purity | >99% Al2O3 | Minimizes lattice defects and dielectric loss |
| Chemical Inertness | Passive at 1400°C | Maintains precise stoichiometry of Li, Mg, and Ti |
| Physical Isolation | Barrier from furnace lining | Prevents diffusion of foreign atoms into the sample |
| Thermal Stability | High refractoriness | Ensures uniform heat transfer and grain growth control |
| Thermal Sensitivity | Controlled ramp rates | Prevents crucible cracking and sample damage |
Elevate Your Advanced Ceramic Research with KINTEK
Precise dielectric performance starts with a pristine thermal environment. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, along with specialized lab high-temp furnaces—all fully customizable to meet your unique sintering needs.
Don't let impurities compromise your microwave ceramics. Our expert-grade equipment and high-purity containment solutions ensure the integrity of your materials from green body to final densification.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom furnace requirements and achieve the superior Quality Factor your research demands.
Visual Guide
References
- Weihua Li, Haiguang Zhao. Highly bright solid-state carbon dots for efficient anticounterfeiting. DOI: 10.1039/d3ra07235e
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Chairside Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Furnace with Transformer for Ceramic Restorations
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Magnesium Extraction and Purification Condensing Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- Why are alumina ceramic tubes preferred for high-temperature furnaces? Ensure Stability and Control Up to 1800°C
- What is the role of a laboratory oven in the pre-treatment of Date Palm Stones? Enhance Torrefaction & Grinding Efficiency
- Why is a laboratory pellet press used to compress powders? Optimize Conductivity for Flash Joule Heating
- Alumina vs. Platinum Crucibles for Lithium Titanate (LTO) Synthesis: Which is Right for You?
- How do a precision hydraulic press and high-strength stainless steel molds facilitate boron carbide green body forming?
- What is the function of a vacuum pump in tantalum capacitor recycling? Optimize Purity and Speed
- What is the purpose of configuring a hot gas filter within a Catalytic Hydropyrolysis (CHP) process? Ensure Reactor Life
- What is the role of a high-temperature ceramic boat during phosphidation? Ensure Pure and Stable Chemical Synthesis

















