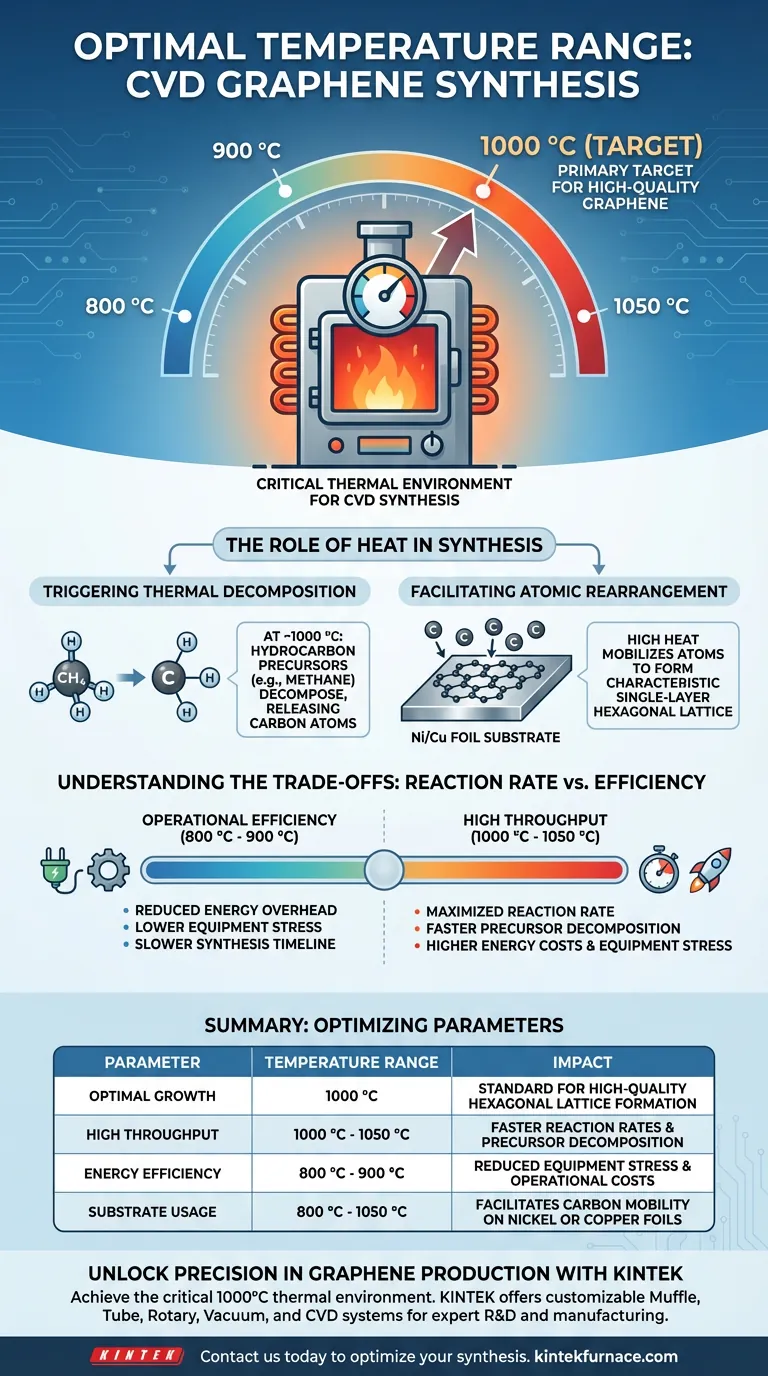
To achieve successful Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) synthesis of graphene, industrial high-temperature furnaces must generally operate within a range of 800 °C to 1050 °C, with a primary target often centered at approximately 1000 °C. This precise thermal environment is required to drive the chemical reactions necessary to form high-quality graphene layers on metal substrates.
While the operational window can span several hundred degrees, maintaining a temperature near 1000 °C is the standard thermodynamic condition required to effectively decompose hydrocarbon precursors and facilitate proper atomic lattice formation.

The Critical Role of Heat in Synthesis
Triggering Thermal Decomposition
The primary function of the furnace is to provide the energy needed to break chemical bonds.
Low-mass hydrocarbon precursors, such as methane, are introduced into the reaction zone.
At temperatures approaching 1000 °C, these precursors undergo thermal decomposition, releasing the carbon atoms necessary for growth.
Facilitating Atomic Rearrangement
Once the carbon atoms are released, they must organize into a specific structure.
The high heat allows these atoms to mobilize and rearrange themselves on the surface of transition metal foils, typically nickel or copper.
This rearrangement is what creates the characteristic single-layer, hexagonal lattice structure of high-quality graphene.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Reaction Rate vs. Energy Efficiency
There is a direct correlation between temperature and production speed.
Operating at the higher end of the spectrum (up to 1050 °C) significantly increases the rate of reaction, potentially boosting throughput.
However, this comes with a penalty of substantially higher energy consumption and operational costs.
Equipment Stress and Safety
Pushing the temperature limits poses increased risks to both personnel and machinery.
Higher temperatures accelerate the degradation of furnace components and require more robust safety protocols to manage the danger levels associated with extreme heat.
Balancing the need for speed against equipment longevity and safety is a critical operational decision.
Optimizing Your Furnace Parameters
To determine the exact set point for your specific application, consider your primary constraints:
- If your primary focus is Production Speed: Target the upper range (1000 °C – 1050 °C) to maximize the reaction rate and precursor decomposition, ensuring the fastest possible growth.
- If your primary focus is Operational Efficiency: Operate closer to the lower bound (800 °C – 900 °C) to reduce energy overhead and equipment stress, while accepting a slower synthesis timeline.
Ultimately, precise thermal control within this range is the defining factor in transitioning from raw gas to high-value nanomaterial.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Temperature Range | Impact on Synthesis |
|---|---|---|
| Optimal Growth | 1000 °C | Standard for high-quality hexagonal lattice formation |
| High Throughput | 1000 °C - 1050 °C | Faster reaction rates & precursor decomposition |
| Energy Efficiency | 800 °C - 900 °C | Reduced equipment stress & operational costs |
| Substrate Usage | 800 °C - 1050 °C | Facilitates carbon mobility on Nickel or Copper foils |
Unlock Precision in Graphene Production with KINTEK
Achieving the perfect 1000°C thermal environment is critical for high-quality graphene synthesis. At KINTEK, we empower researchers and industrial manufacturers with precision-engineered solutions. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all fully customizable to meet your unique high-temp lab requirements.
Ready to enhance your lab's efficiency and material quality? Contact us today to discuss how our customizable CVD systems can optimize your specific synthesis parameters!
Visual Guide
References
- Salam Hussein Alwan, Montather F. Ramadan. A Mini-Review on Graphene: Exploration of Synthesis Methods and Multifaceted Properties. DOI: 10.3390/engproc2023059226
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station CVD Machine
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why study beta-BiAsO2 epitaxial growth on SiO2? Unlock High-Performance Topological Device Development
- What is the function of the CVD exhaust system? Ensure Process Integrity and Equipment Longevity
- Why is a dual-zone tube furnace necessary for MnO2/CF phosphorization? Master CVD Synthesis with Precision Control
- What are the primary application areas of CVD technology? Unlock Advanced Thin-Film Solutions for Your Industry
- What are the benefits of CVD coating? Achieve Unmatched Conformality and Superior Adhesion
- What are the key components of a standard CVD system? Optimize Thin Film Deposition for Your Lab
- What does CVD stand for and what is its primary function? Discover High-Purity Thin Film Deposition
- How does CVD enhance cutting tools and industrial machinery? Boost Durability and Productivity



















