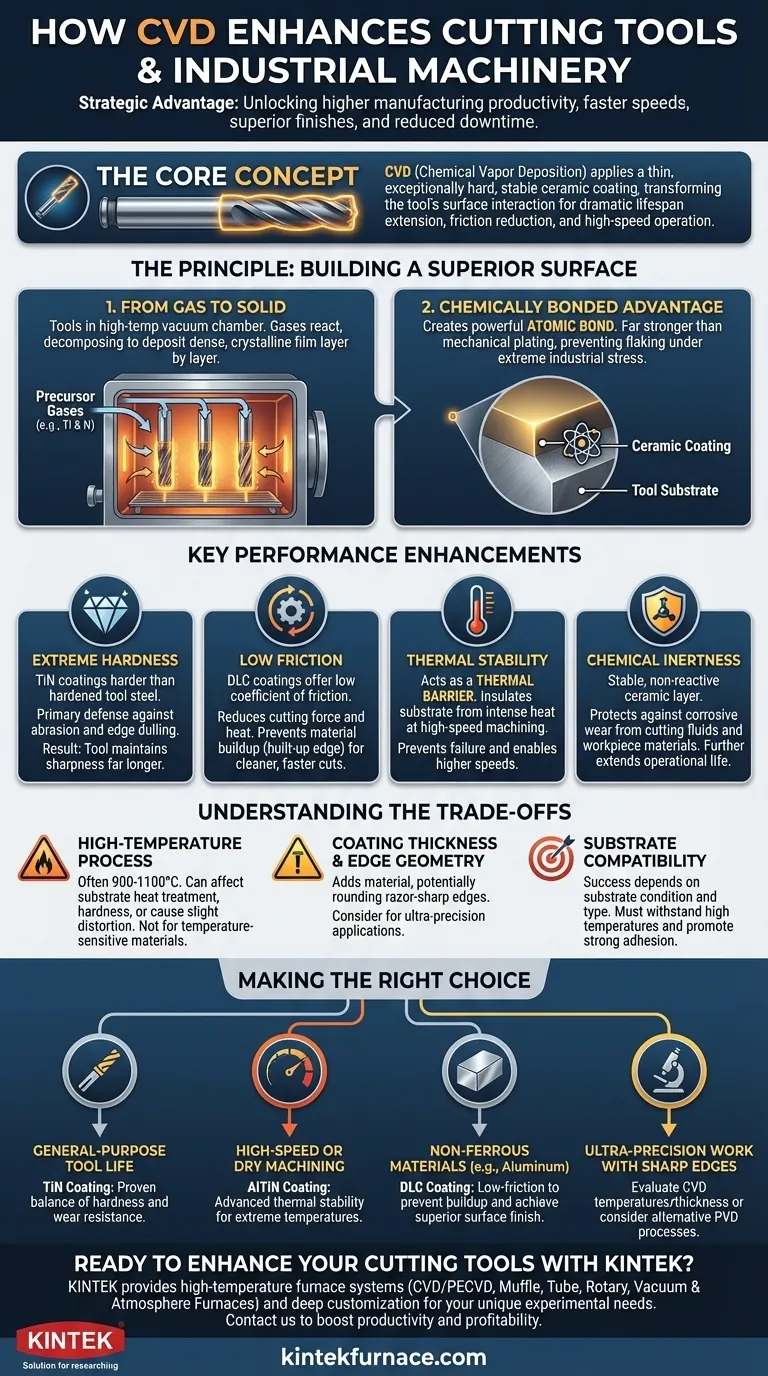
At its core, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) enhances cutting tools by applying a thin, exceptionally hard, and stable ceramic coating onto their surface. This microscopic layer fundamentally changes the tool's interaction with the workpiece, leading to a dramatic extension of its lifespan, a significant reduction in friction, and the ability to operate at higher speeds and temperatures.
While often viewed as a way to simply make tools last longer, the true strategic advantage of CVD is its ability to unlock higher levels of manufacturing productivity. It enables faster cutting speeds, superior surface finishes, and reduced operational downtime, directly impacting profitability.
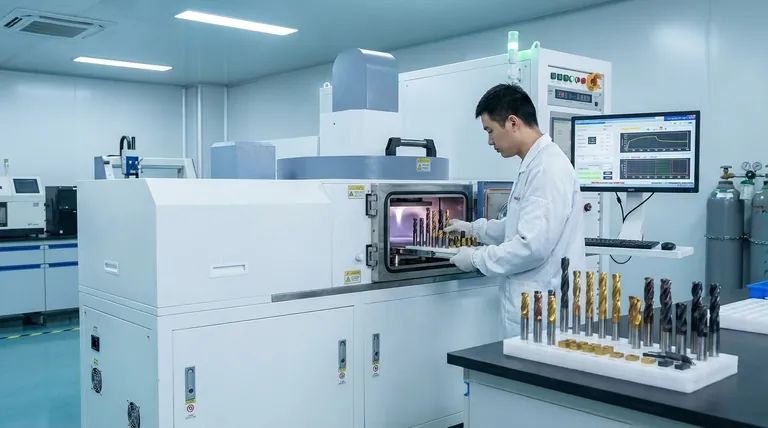

The Principle: How CVD Builds a Superior Surface
CVD is not a simple paint or plating process. It involves a chemical reaction that creates a new, atomically bonded surface layer on the tool, making it incredibly durable.
From Gas to Solid
The process involves placing the tools inside a high-temperature vacuum chamber. Precursor gases containing the elements of the desired coating (like titanium and nitrogen for TiN) are introduced. These gases react on the hot surface of the tool, decomposing and depositing a dense, crystalline film layer by layer.
A Chemically Bonded Advantage
This method creates a powerful atomic bond between the coating and the tool's base material (the substrate). This integration is far stronger than a mechanical bond, ensuring the coating does not flake or chip off even under the extreme pressures and vibrations of industrial machining.
Key Performance Enhancements Explained
The properties of the deposited layer translate directly into measurable improvements in cutting performance. Each characteristic solves a specific challenge in the machining process.
Extreme Hardness for Wear Resistance
CVD coatings like Titanium Nitride (TiN) are significantly harder than even hardened tool steel. This extreme hardness provides a primary defense against the two main forms of tool wear: abrasion from hard particles in the workpiece and gradual dulling of the cutting edge. The result is a tool that maintains its sharpness far longer.
Low Friction for Cleaner, Faster Cuts
Coatings such as Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) have a very low coefficient of friction. This lubricity reduces the force required to make a cut, which in turn minimizes heat generation. It also prevents chips of the workpiece material from welding onto the tool's cutting edge, a common failure mode known as "built-up edge."
Thermal Stability as a Heat Shield
High-speed machining generates intense heat at the cutting tip, which can soften the tool's underlying steel and cause it to fail. CVD coatings act as a thermal barrier, insulating the substrate from these extreme temperatures. This allows the tool to be run at much higher speeds without degrading.
Chemical Inertness for Material Protection
The deposited ceramic layer is chemically stable and non-reactive. This protects the tool from chemical reactions with cutting fluids or the workpiece material itself, preventing corrosive wear and further extending the tool's operational life.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, CVD is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is crucial for proper application.
The High-Temperature Process
The traditional CVD process requires very high temperatures (often 900-1100°C). This can affect the heat treatment of the underlying tool substrate, potentially altering its hardness or causing slight distortion. This makes it unsuitable for some temperature-sensitive tool materials.
Coating Thickness and Edge Geometry
CVD coatings, while thin, do add material to the tool. This can slightly round a razor-sharp cutting edge. For applications requiring extreme precision and the sharpest possible edges, this effect must be considered.
Substrate Compatibility
The success of the coating is highly dependent on the condition and type of the substrate material. The tool must be able to withstand the high process temperatures and have a surface that promotes strong adhesion of the coating.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct coating strategy requires aligning the coating's properties with the specific demands of the machining application.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose tool life extension: A standard TiN coating offers a proven, cost-effective balance of hardness and wear resistance for a wide range of materials.
- If your primary focus is high-speed or dry machining of steels: Advanced coatings like Aluminum Titanium Nitride (AlTiN) provide the necessary thermal stability to protect the tool at extreme temperatures.
- If your primary focus is machining non-ferrous materials like aluminum: Prioritize a low-friction DLC coating to prevent material buildup on the tool and achieve a superior surface finish.
- If your primary focus is ultra-precision work with sharp edges: Carefully evaluate whether the CVD process temperatures and added thickness are compatible with your tool's material and geometry, or consider alternative PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) processes.
By understanding these principles, you can leverage CVD not just to buy better tools, but to engineer a more efficient, productive, and profitable manufacturing operation.
Summary Table:
| Enhancement | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Extreme Hardness | Increases wear resistance and maintains cutting edge sharpness |
| Low Friction | Reduces heat and prevents material buildup for cleaner cuts |
| Thermal Stability | Allows operation at higher temperatures and speeds |
| Chemical Inertness | Protects against corrosion and extends tool life |
Ready to enhance your cutting tools with advanced CVD solutions? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide high-temperature furnace systems like CVD/PECVD, Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise solutions for your unique experimental needs, boosting productivity and profitability. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- How does plasma enhanced CVD work? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- How is silicon dioxide (SiO2) used in PECVD applications? Key Roles in Microfabrication
- What is the second benefit of deposition within a discharge in PECVD? Enhance Film Quality with Ion Bombardment
- What role does PECVD play in optical coatings? Essential for Low-Temp, High-Precision Film Deposition
- What is plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition application? Enable High-Performance Thin Films at Lower Temperatures



















