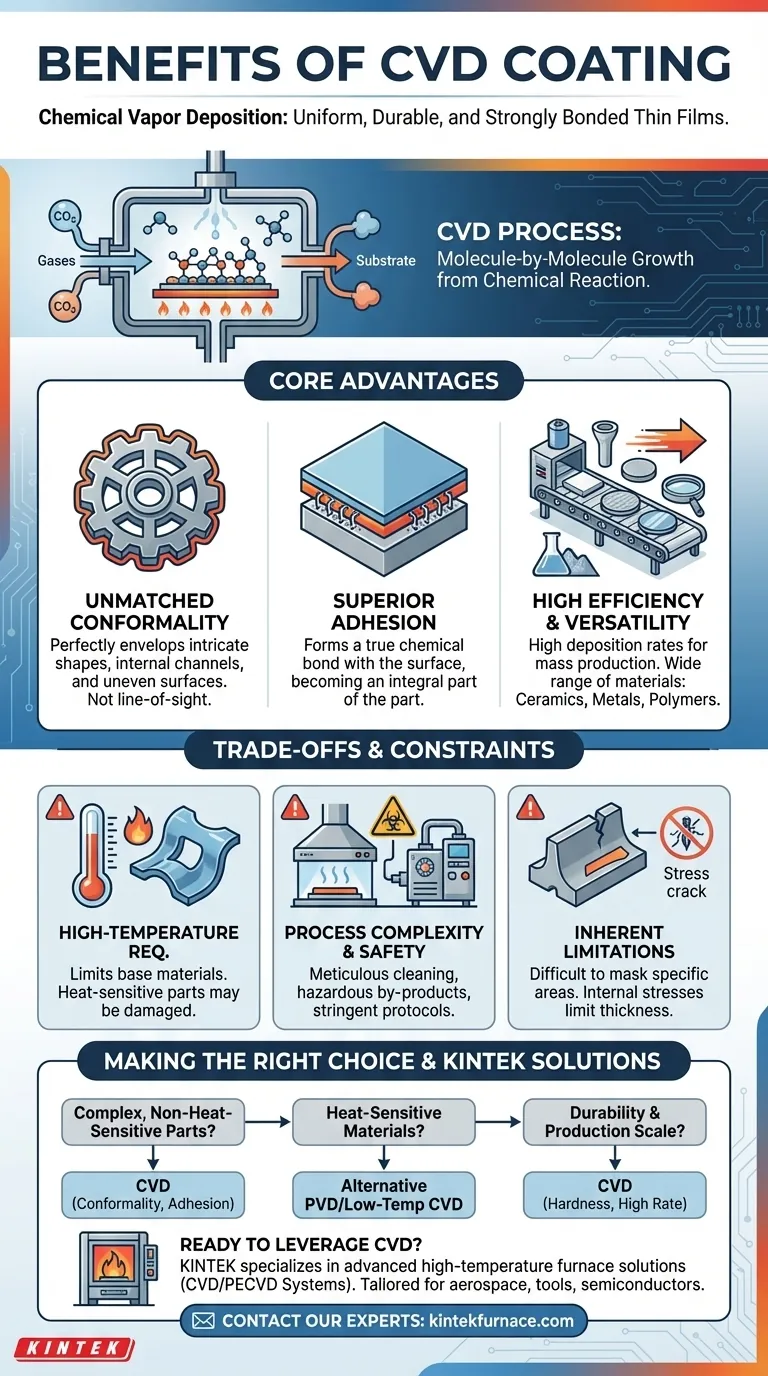
At its core, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a process designed to produce highly uniform, durable, and strongly bonded thin films. Its primary benefits include unmatched conformality on complex surfaces, superior adhesion to the base material, and high deposition rates suitable for mass production, allowing for the application of a diverse range of materials from ceramics to metals.
The defining advantage of CVD lies in its chemical reaction-based method. Unlike line-of-sight processes, CVD "grows" a coating molecule by molecule, allowing it to perfectly envelop intricate shapes and form a powerful chemical bond with the surface.

How CVD Delivers Superior Coating Properties
The benefits of CVD are a direct result of its unique deposition mechanism. The process involves introducing precursor gases into a chamber, which then react and decompose on a heated substrate to form the desired solid film.
Unmatched Conformality on Complex Geometries
Because CVD relies on a chemical gas reaction, it is not a "line-of-sight" process like Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD). The precursor gases flow around and into every feature of a component.
This allows the coating to form with exceptional uniformity, or conformality, on parts with intricate shapes, internal channels, or uneven surfaces.
Superior Adhesion Through Chemical Bonding
The high temperatures used in a typical CVD process facilitate a chemical reaction not just between the gases, but also with the substrate itself.
This creates a true chemical bond at the interface between the coating and the part. The result is superior adhesion, where the coating becomes an integral part of the surface rather than just a layer sitting on top.
High Efficiency and Material Versatility
CVD processes can often achieve higher deposition rates compared to other methods, making them highly efficient and cost-effective for mass production environments.
Furthermore, the technology is remarkably versatile. It can be used to deposit a wide array of materials, including hard ceramics for tools, pure metals for semiconductors, and advanced polymers for optics.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Constraints
While powerful, the CVD process has specific requirements and limitations that are critical to understand when evaluating it for your application.
The High-Temperature Requirement
Traditional CVD processes operate at elevated temperatures, often under vacuum. This heat is necessary to drive the chemical reaction.
This fundamental requirement limits the types of base materials that can be coated. Substrates that are sensitive to heat, such as many plastics or certain metal alloys, may be damaged or warped by the process.
Process Complexity and Safety
A successful CVD coating requires that the substrate surface be meticulously cleaned of all contaminants before the process begins.
Additionally, the chemical reactions can produce toxic or hazardous by-products. This necessitates stringent safety protocols, complex equipment, and robust waste management systems, which can increase operational costs.
Inherent Process Limitations
Due to the nature of the gas-phase reaction, it can be difficult to mask specific areas of a part that you do not want to be coated.
Furthermore, internal stresses can build up within the growing film, which often limits the maximum practical thickness of the coating.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct coating technology depends entirely on the specific demands of your component and production goals.
- If your primary focus is coating complex, non-heat-sensitive parts: CVD is an exceptional choice due to its unmatched conformality and chemically bonded adhesion.
- If your primary focus is coating heat-sensitive materials: You must explore lower-temperature alternatives like PVD or specialized CVD variations developed for substrates like plastics.
- If your primary focus is durability and production scale: CVD's ability to form hard, wear-resistant coatings with high deposition rates makes it a go-to choice for industries from aerospace to tool manufacturing.
Ultimately, choosing a coating is an engineering decision that balances the ideal properties with the practical constraints of the process.
Summary Table:
| Key Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Unmatched Conformality | Coats complex shapes, internal channels, and uneven surfaces with exceptional uniformity. |
| Superior Adhesion | Forms a powerful chemical bond with the substrate for integral, long-lasting performance. |
| High Deposition Rates | Efficient process suitable for mass production environments. |
| Material Versatility | Deposits a wide range of materials, from hard ceramics to pure metals and polymers. |
Ready to leverage the power of CVD for your components?
KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including our robust CVD/PECVD Systems. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide the precise thermal processing environment required for successful CVD coating.
Our systems are designed for industries demanding superior coating performance, such as aerospace, tool manufacturing, and semiconductors. With strong deep customization capabilities, we can tailor a furnace solution to your unique process requirements, ensuring optimal coating quality, adhesion, and efficiency.
Contact our experts today to discuss how a KINTEK CVD system can enhance your production capabilities and deliver the coating performance your components demand.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What types of atmosphere control does a CVD Tube Furnace support? Master Vacuum and Gas Control for Precision
- What role do CVD tube furnace sintering systems play in 2D material synthesis? Enabling High-Quality Atomic Layer Growth
- Why is the tube design important in CVD furnaces? Ensure Uniform Deposition for High-Quality Films
- Where is a CVD Tube Furnace commonly used? Essential for High-Tech Materials and Electronics
- What makes a CVD Tube Furnace essential for material science and nanotechnology? Unlock Precision in Material Synthesis



















