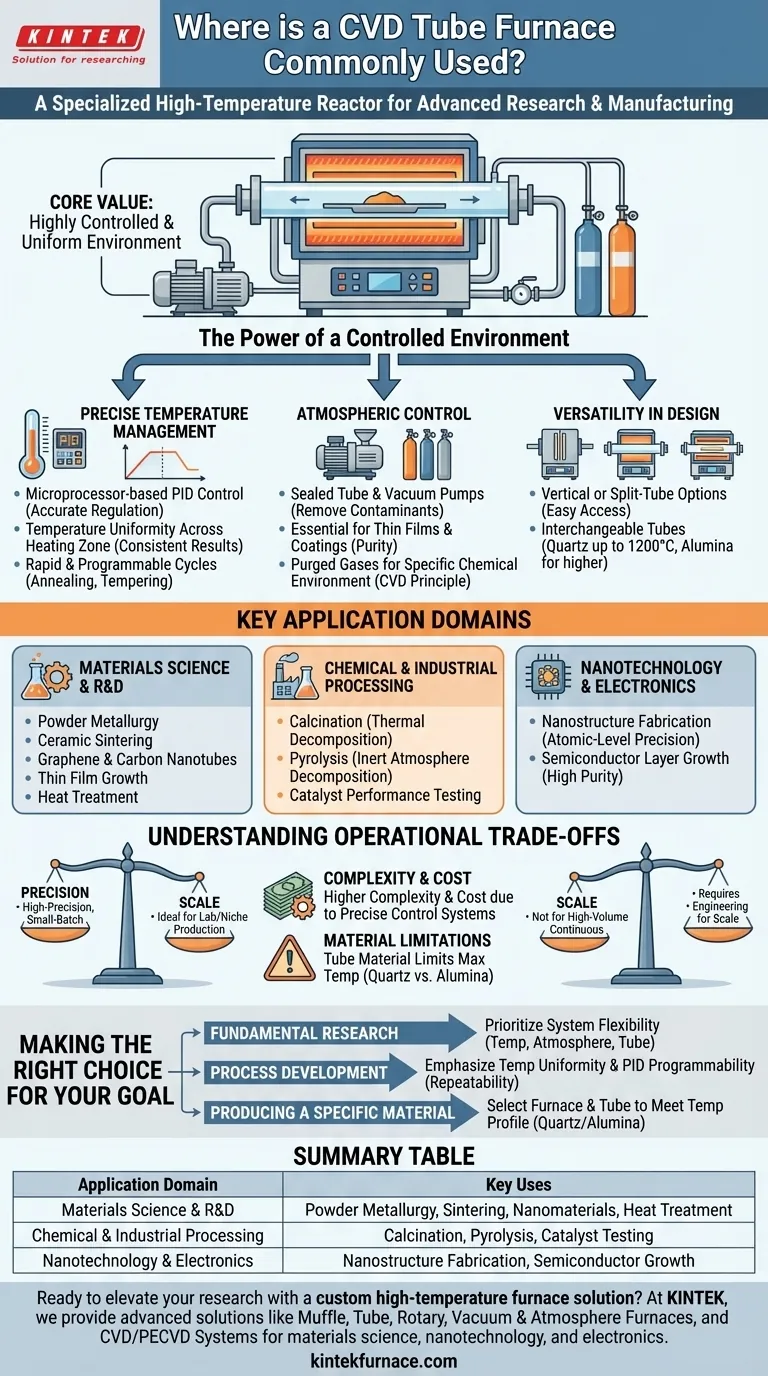
At its core, a Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) tube furnace is a specialized high-temperature reactor used in advanced research and manufacturing settings. You will find them in university laboratories, government research institutes, and the R&D or specialized production departments of industrial enterprises focused on materials science, nanotechnology, and electronics.
The primary value of a CVD tube furnace is not just its ability to generate heat, but its power to create a highly controlled and uniform environment. This precision is what makes it indispensable for synthesizing advanced materials and conducting repeatable scientific experiments.

The Power of a Controlled Environment
The widespread use of CVD tube furnaces stems from their ability to precisely manage the critical variables of material synthesis. Unlike a simple oven, a tube furnace is an integrated system designed for control.
Precise Temperature Management
A microprocessor-based PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) control system is the furnace's brain. This allows for extremely accurate temperature regulation.
This system ensures temperature uniformity across the entire heating zone, which is critical for consistent results in processes like sintering or crystal growth.
It also enables rapid, programmable heating and cooling cycles, saving time and energy while allowing for complex thermal processing like annealing and tempering.
Atmospheric Control
The furnace's sealed tube is the key to controlling the chemical environment. Using vacuum pumps connected via stainless steel flanges, operators can remove ambient air and contaminants.
This vacuum capability is essential for creating thin films and coatings, where purity is paramount.
Gases can then be purged into the tube, allowing for reactions in a specific, controlled atmosphere. This is the fundamental principle of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), where precursor gases react at high temperatures to deposit a solid material onto a substrate.
Versatility in Design
Furnaces come in various configurations, such as vertical or split-tube, to accommodate different experimental setups and ease of access to the sample.
The furnace tubes themselves are interchangeable. Quartz tubes are used for processes up to around 1200°C, while alumina tubes are required for higher temperatures, providing flexibility for a wide range of material requirements.
Key Application Domains
The precise control offered by CVD tube furnaces makes them a cornerstone technology in several high-tech fields.
Materials Science and R&D
This is the most common application area. Researchers use these furnaces for developing advanced materials from the ground up.
Specific uses include powder metallurgy, ceramic sintering, and producing novel materials like graphene, carbon nanotubes, and other nanomaterials. It is also used for growing thin films and strengthening materials through heat treatment.
Chemical and Industrial Processing
In the chemical industry, tube furnaces are used for processes that require controlled heating of substances in a specific atmosphere.
This includes the calcination (thermal decomposition) of raw materials, pyrolysis (decomposition in an inert atmosphere), and testing the performance of catalysts at high temperatures.
Nanotechnology and Electronics
The fabrication of modern electronics and nanostructures depends on atomic-level precision.
CVD tube furnaces provide the thermal control needed to fabricate nanostructures and grow the highly pure crystalline layers used in semiconductor components.
Understanding the Operational Trade-offs
While powerful, these furnaces are specialized tools with inherent trade-offs that are important to understand.
Precision vs. Scale
CVD tube furnaces excel at high-precision, small-batch operations typical in a laboratory or for niche production. They are not designed for high-volume, continuous manufacturing without significant engineering and cost.
Complexity and Cost
The systems required for precise control—PID controllers, vacuum pumps, gas flow controllers, and specialized tube materials—make these furnaces more complex and costly to acquire and operate than standard industrial ovens.
Material Limitations
The maximum operating temperature is strictly limited by the material of the furnace tube. Exceeding the thermal limit of a quartz tube, for instance, will cause it to fail, compromising the experiment and potentially damaging the furnace.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting or using a CVD tube furnace requires matching its capabilities to your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is fundamental research: Prioritize a system with maximum flexibility in temperature range, atmospheric control, and tube interchangeability.
- If your primary focus is process development: Emphasize temperature uniformity and PID controller programmability to ensure process repeatability and optimization.
- If your primary focus is producing a specific material: Select the furnace and tube material (e.g., quartz or alumina) that safely and efficiently meets the required temperature profile for that synthesis.
Ultimately, the CVD tube furnace is the instrument of choice wherever the creation of materials demands absolute control over the thermal and chemical environment.
Summary Table:
| Application Domain | Key Uses |
|---|---|
| Materials Science & R&D | Powder metallurgy, ceramic sintering, graphene/carbon nanotube synthesis, heat treatment |
| Chemical & Industrial Processing | Calcination, pyrolysis, catalyst testing |
| Nanotechnology & Electronics | Nanostructure fabrication, semiconductor layer growth |
Ready to elevate your research with a custom high-temperature furnace solution? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs in materials science, nanotechnology, and electronics. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's performance and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- What makes a CVD Tube Furnace essential for material science and nanotechnology? Unlock Precision in Material Synthesis
- Why are CVD tube furnace sintering systems indispensable for 2D material research and production? Unlock Atomic-Scale Precision
- Which industries and research fields benefit from CVD tube furnace sintering systems for 2D materials? Unlock Next-Gen Tech Innovations
- What types of atmosphere control does a CVD Tube Furnace support? Master Vacuum and Gas Control for Precision
- What temperature ranges can a CVD Tube Furnace achieve with different tube materials? Unlock High-Temp Precision for Your Lab



















