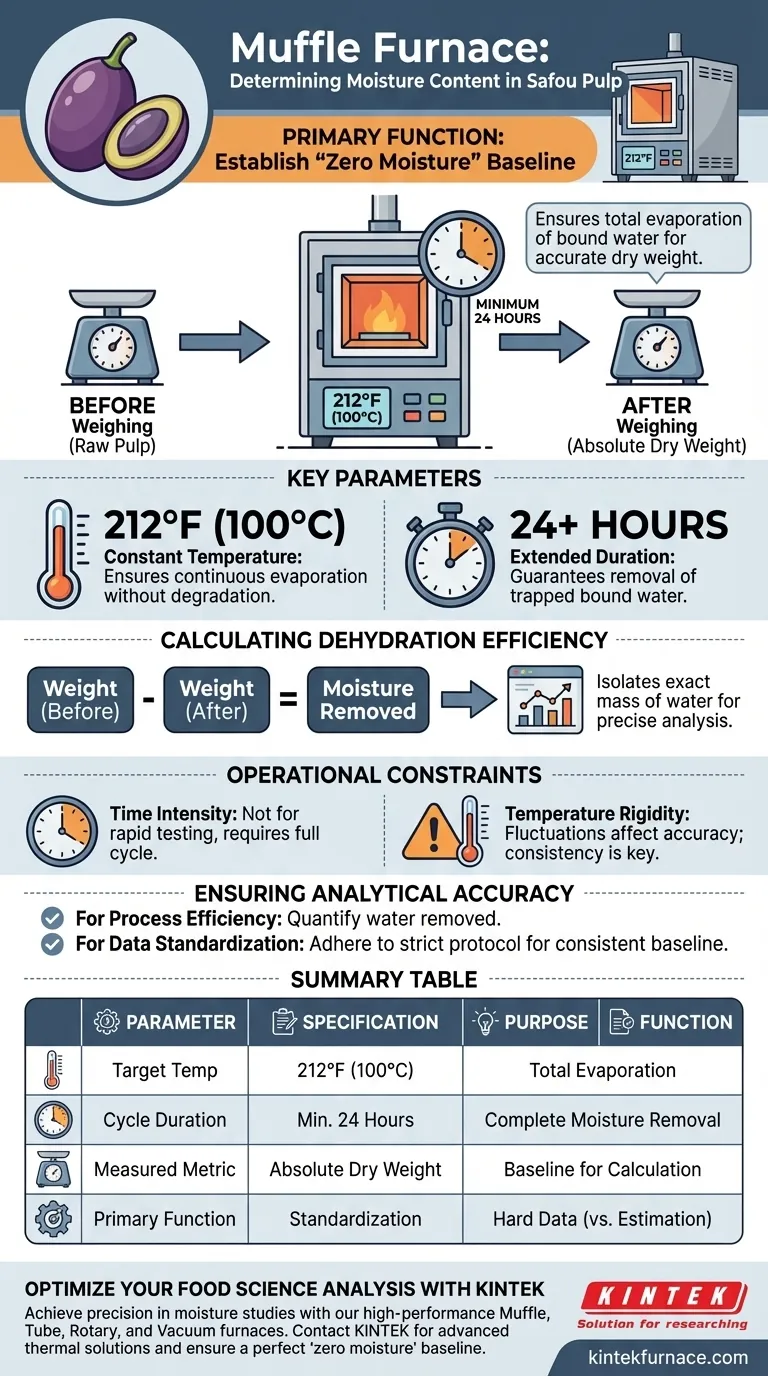
The primary function of a Muffle Furnace in the analysis of Safou pulp is to completely eliminate bound water to establish a "zero moisture" baseline. By subjecting the samples to a constant temperature of 212°F (100°C) for a minimum duration of 24 hours, the furnace ensures the raw material reaches its accurate dry weight.
The Muffle Furnace acts as the standardizing tool for moisture analysis. By defining the absolute dry weight of the Safou pulp, it allows for the precise calculation of dehydration efficiency based on hard data rather than estimation.

Establishing a Zero Moisture Baseline
The Necessity of Total Evaporation
To accurately analyze moisture content, you cannot rely on surface dryness. You must determine the absolute dry weight of the raw material.
The Muffle Furnace facilitates this by maintaining a consistent thermal environment. It operates at 212°F (100°C) to ensure that water evaporation is continuous and complete.
The 24-Hour Rule
Removing "bound water"—moisture trapped within the cellular structure of the pulp—is not instantaneous.
The furnace must maintain this temperature for at least 24 hours. This extended duration guarantees that the final weight reflects the pulp solids only, with no residual moisture skewing the results.
Calculating Dehydration Efficiency
Comparative Weighing
The utility of the Muffle Furnace lies in the data generated after the heating cycle.
Analysts measure the weight of the Safou pulp before it enters the furnace and compare it to the weight after the 24-hour process.
Deriving the Metric
This differential allows for the calculation of dehydration efficiency.
By isolating the exact mass of the water removed, you can determine exactly how much moisture the raw pulp held versus its solid content.
Operational Constraints
Time Intensity
The most significant operational factor to consider is the time investment.
Because the process requires a minimum 24-hour cycle, it is not suitable for rapid, real-time testing. It is a rigorous method designed for accuracy over speed.
Temperature Rigidity
Success depends on strict adherence to the 100°C protocol.
Fluctuations below this temperature may leave residual moisture, while excessive heat could degrade the pulp solids. Consistency is the only way to ensure the baseline is valid.
Ensuring Analytical Accuracy
To get the most value from this process, align your methodology with your specific data requirements:
- If your primary focus is process efficiency: Use the pre- and post-heating weight differential to quantify exactly how much water is being removed during dehydration.
- If your primary focus is data standardization: Strictly adhere to the 24-hour minimum at 100°C to ensure every sample is measured against the same "zero moisture" baseline.
Reliable moisture analysis relies entirely on the precision with which you establish this dry weight foundation.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Specification | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Target Temperature | 212°F (100°C) | Ensures total evaporation of bound water without material degradation. |
| Cycle Duration | Minimum 24 Hours | Guarantees complete moisture removal from cellular pulp structures. |
| Measured Metric | Absolute Dry Weight | Serves as the baseline for calculating exact dehydration efficiency. |
| Primary Function | Standardization | Provides hard data for moisture analysis versus estimation. |
Optimize Your Food Science Analysis with KINTEK
Achieve uncompromising precision in your moisture content studies. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK provides high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, and Vacuum furnaces engineered to maintain the strict temperature rigidity required for Safou pulp analysis.
Whether you need standard laboratory units or fully customizable high-temperature systems, our equipment ensures a perfect 'zero moisture' baseline every time. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your unique lab needs and see how our advanced thermal solutions can enhance your dehydration efficiency data.
Visual Guide
References
- Daniel Allen Law. An Energy Analysis and Characterization of Safou (Dacryodes edulis) as Biofuel Feedstock. DOI: 10.71889/5fylantbak.29859674
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- How to keep samples in muffle furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe & Accurate Results
- What are the disadvantages of using a muffle furnace? Key Limitations and Better Alternatives
- How does a high-temperature laboratory muffle furnace affect material properties? Transform Anodic Oxide Films Fast
- Can a muffle furnace be used for pyrolysis? Unlock Precise Thermal Decomposition
- What are the benefits of using a muffle furnace? Achieve Precise, Contamination-Free Heating for Your Lab
- Why are muffle furnaces durable under rigorous industrial conditions? Discover Their Robust Design for Longevity
- What is the core role of a muffle furnace in Fe3O4/C synthesis? Optimize Your Magnetization Roasting Process
- What industries commonly use industrial muffle furnaces? Unlock Precision Heating for Diverse Sectors



















