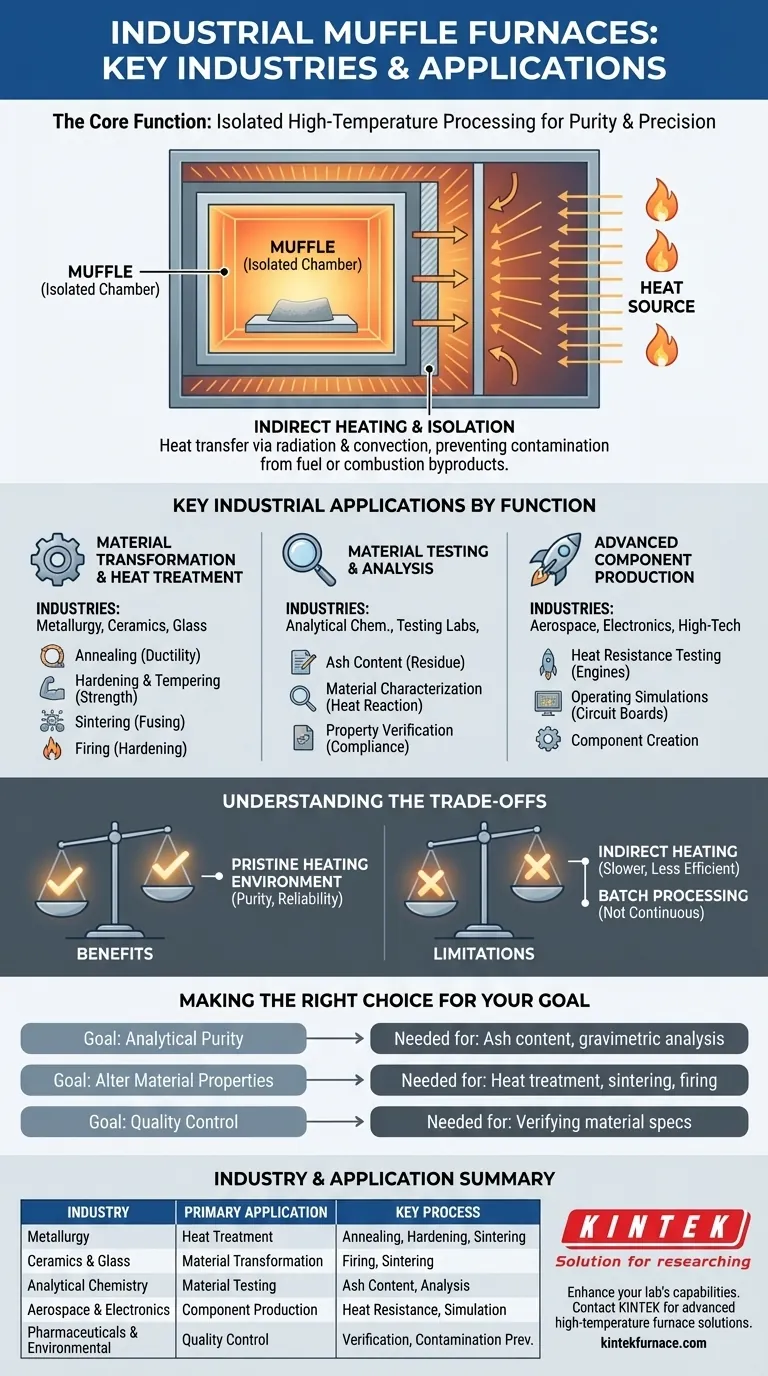
At a high level, industrial muffle furnaces are cornerstones in metallurgy, materials science, ceramics, and analytical chemistry. Their use, however, extends across a surprisingly diverse range of sectors, including aerospace, electronics, pharmaceuticals, and environmental testing, where precise, high-temperature processing is a critical requirement.
The widespread adoption of the muffle furnace is not tied to any single industry, but to a universal need: the ability to heat a material to a high temperature within a controlled environment, completely isolated from contaminants like fuel or combustion byproducts. This core function is what makes it an indispensable tool.

The Core Function: Isolated High-Temperature Processing
To understand why so many industries rely on this equipment, you must first understand its fundamental design principle. The "muffle" is the key.
What is a Muffle Furnace?
A muffle furnace is essentially a high-temperature oven with an inner chamber—the muffle—that is shielded from the external heating elements.
Imagine a box within a box. The outer box generates intense heat, while the inner box holds the material or sample. This design ensures the material is heated through radiation and convection, never coming into direct contact with the flame or electrical elements.
Why Isolation Matters
This separation is critical because it prevents contamination. In processes like chemical analysis or the heat treatment of sensitive alloys, any impurities from combustion can alter the results or compromise the final product's integrity.
The muffle creates a chemically clean environment, ensuring that the only thing affecting the sample is the heat itself.
Key Industrial Applications by Function
Instead of just listing industries, it's more insightful to group them by the common tasks they use muffle furnaces to accomplish.
Material Transformation and Heat Treatment
This category focuses on changing a material's physical properties. The furnace provides the precise thermal profiles needed for these transformations.
Industries include metallurgy, ceramics, and glass manufacturing for processes like:
- Annealing: Softening metals to improve ductility.
- Hardening & Tempering: Strengthening steel parts.
- Sintering: Fusing powdered materials (like ceramics or metals) together with heat.
- Firing: Hardening ceramic products after they have been shaped.
Material Testing and Analysis
This is about understanding a material's composition and behavior under thermal stress. Repeatability and purity are paramount.
Industries include analytical chemistry, materials testing labs, and quality control departments for tasks such as:
- Ash Content Determination: Burning off all organic material to measure the non-combustible residue, common in the food, coal, and chemical industries.
- Material Characterization: Analyzing how a material reacts to extreme heat.
- Property Verification: Ensuring a finished product meets its specified heat resistance or composition.
Advanced Component Production and Verification
In high-stakes industries, components must perform flawlessly under extreme conditions. Muffle furnaces are used to both create and test these parts.
Industries like aerospace and electronics use them for:
- Testing heat-resistant materials and coatings for engine or re-entry components.
- Simulating operating conditions for electronic circuit boards and other sensitive parts.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No technology is a universal solution. The design of a muffle furnace presents clear advantages but also inherent limitations.
The Benefit: Purity and Precision
The primary advantage is a pristine heating environment. This leads to highly reliable, repeatable, and uncontaminated results, which is non-negotiable for scientific analysis and high-performance manufacturing.
The Limitation: Indirect Heating
Because the heat source does not directly contact the workpiece, heat transfer can be slower and potentially less energy-efficient than in a direct-fired furnace. The process relies entirely on thermal radiation and convection within the chamber.
The Constraint: Batch Processing
Muffle furnaces are typically designed for batch work, not continuous industrial throughput. They are ideal for processing individual components, small lots, or samples in a laboratory or small-scale production setting.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Whether a muffle furnace is the correct tool depends entirely on your process requirements.
- If your primary focus is analytical purity: You need a muffle furnace to determine ash content, perform gravimetric analysis, or prepare samples without chemical contamination.
- If your primary focus is altering material properties: A muffle furnace is essential for heat-treating sensitive metals, firing technical ceramics, or sintering powdered parts where a controlled atmosphere is critical.
- If your primary focus is quality control and testing: A muffle furnace provides the stable, repeatable high-temperature environment needed to verify material specifications against a known standard.
Ultimately, understanding the principle of isolated heating is the key to leveraging a muffle furnace effectively across any application.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Primary Application | Key Process |
|---|---|---|
| Metallurgy | Heat Treatment | Annealing, Hardening, Sintering |
| Ceramics & Glass | Material Transformation | Firing, Sintering |
| Analytical Chemistry | Material Testing | Ash Content Determination, Analysis |
| Aerospace & Electronics | Component Production | Heat Resistance Testing, Simulation |
| Pharmaceuticals & Environmental | Quality Control | Property Verification, Contamination Prevention |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with a custom high-temperature furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we meet your unique experimental needs precisely. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can drive efficiency and purity in your processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a muffle furnace used to determine the ash content of biochar? Master Your Material Purity Analysis
- What is the primary use of a muffle furnace in the assembly of side-heated resistive gas sensors? Expert Annealing Guide
- Why are precision stirring and drying equipment necessary for photocatalytic materials? Master Microstructure Control
- What is the primary role of a muffle furnace in the annealing process of AlCrTiVNbx alloys? Enhance Alloy Strength
- How does a stainless steel reactor function within a muffle furnace for PET to graphene? Master Carbon Synthesis



















