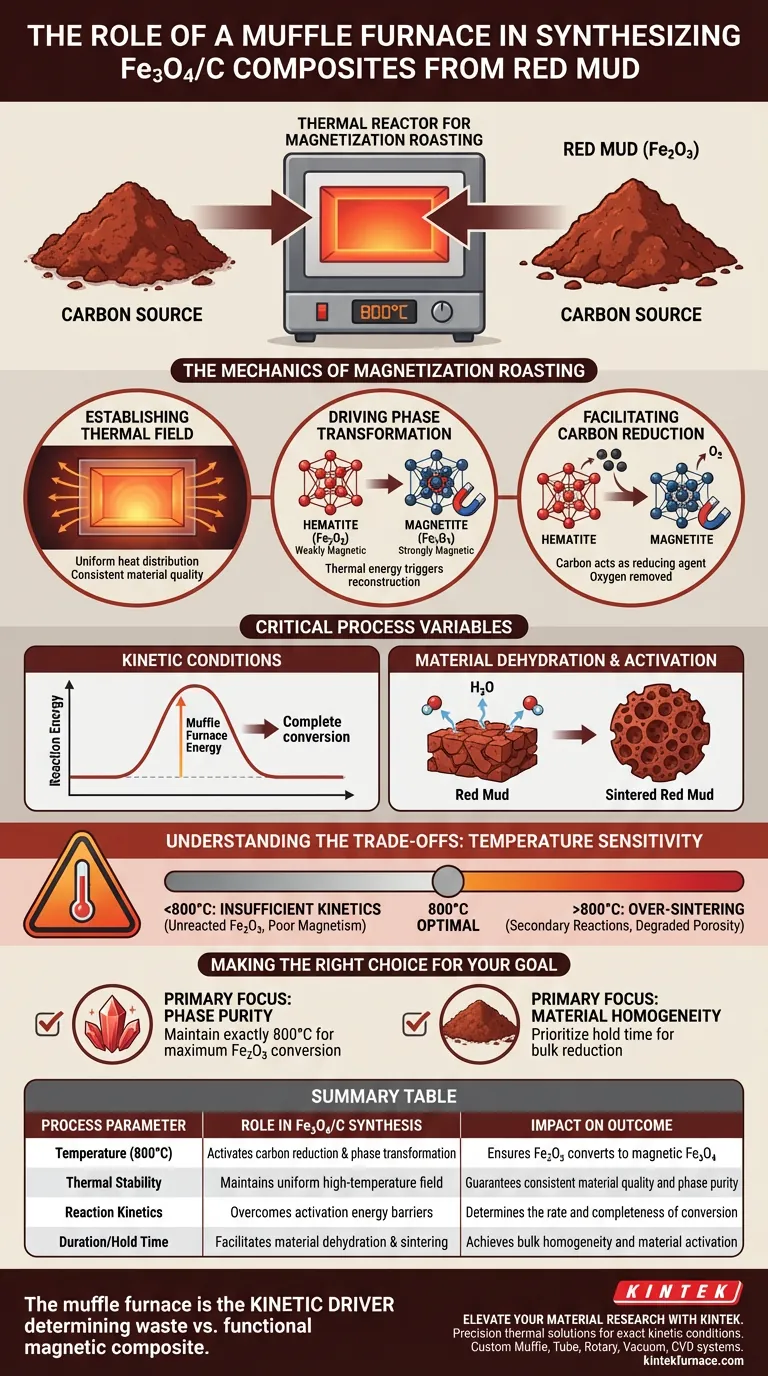
The muffle furnace acts as the primary thermal reactor for magnetization roasting. Its specific function in this synthesis is to provide and maintain a strictly controlled high-temperature environment—typically at 800°C—which is required to drive the chemical conversion of red mud into magnetic Fe3O4/C composites.
By establishing the necessary kinetic conditions, the muffle furnace facilitates the critical reduction reaction between carbon and hematite (Fe2O3), reconstructing the material into magnetic magnetite (Fe3O4).
The Mechanics of Magnetization Roasting
Establishing the Thermal Field
The synthesis of Fe3O4/C composites is not merely about heating; it is about precision.
The muffle furnace creates a stable, high-temperature thermal field (specifically around 800°C).
This stability ensures that the entire sample volume is subjected to uniform heat, which is essential for consistent material quality.
Driving Phase Transformation
The central chemical goal is phase reconstruction.
Red mud primarily contains hematite (Fe2O3), which is weakly magnetic.
The thermal energy provided by the furnace triggers the transformation of this hematite into magnetite (Fe3O4), a strongly magnetic material essential for the final composite's utility.
Facilitating Carbon Reduction
This transformation relies on a carbon reduction reaction.
The furnace maintains the temperature required to activate the carbon source mixed with the red mud.
At these specific temperatures, the carbon acts as a reducing agent, stripping oxygen from the hematite to form the desired magnetite structure.
Critical Process Variables
Kinetic Conditions
Chemical reactions require a specific energy threshold to occur at a useful rate.
The muffle furnace overcomes this activation energy barrier.
By holding the temperature constant for a set duration, it ensures the reaction kinetics are favorable for complete conversion rather than partial surface modification.
Material Dehydration and Activation
Before and during the phase change, the material undergoes dehydration.
The high thermal environment effectively removes combined water from the red mud matrix.
This results in "sintered red mud," a highly active state that is structurally prepared for the formation of the final composite.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Temperature Sensitivity
The muffle furnace provides control, but the process is highly sensitive to the set point.
If the temperature is too low (<800°C): The kinetic energy may be insufficient for the reduction reaction, leaving unreacted hematite (Fe2O3) and resulting in poor magnetic properties.
If the temperature is too high: You risk over-sintering or unwanted secondary phase reactions that could degrade the specific surface area or porosity of the carbon composite.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of the muffle furnace in your synthesis, align your process parameters with your specific objectives:
- If your primary focus is Phase Purity: Ensure the furnace is calibrated to maintain exactly 800°C to maximize the conversion of Fe2O3 to Fe3O4 without inducing secondary impurities.
- If your primary focus is Material Homogeneity: Prioritize the duration of the hold time within the furnace to ensure the carbon reduction reaction propagates through the entire bulk of the material.
The muffle furnace is not just a heat source; it is the kinetic driver that determines whether your red mud becomes waste or a functional magnetic composite.
Summary Table:
| Process Parameter | Role in Fe3O4/C Synthesis | Impact on Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature (800°C) | Activates carbon reduction & phase transformation | Ensures Fe2O3 converts to magnetic Fe3O4 |
| Thermal Stability | Maintains uniform high-temperature field | Guarantees consistent material quality and phase purity |
| Reaction Kinetics | Overcomes activation energy barriers | Determines the rate and completeness of conversion |
| Duration/Hold Time | Facilitates material dehydration & sintering | Achieves bulk homogeneity and material activation |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK
Precision is the difference between waste and a functional composite. KINTEK provides high-performance thermal solutions including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all engineered to deliver the exact kinetic conditions your research demands.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, our systems are fully customizable to meet your unique synthesis needs—ensuring stable thermal fields and reliable phase reconstruction for your lab.
Ready to optimize your high-temperature processes?
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom furnace solution
Visual Guide
References
- Jiaxing Cai, Michael Hitch. Preparation of Fe3O4/C Composite Material from Red Mud for the Degradation of Acid Orange 7. DOI: 10.3390/ma18010151
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the primary attribute of a Muffle Furnace? Unlock Contaminant-Free Heating for Your Lab
- Why is high-temperature thermal treatment in a muffle furnace required for cobalt oxide nanoparticles? Guide to Co3O4
- How does a high-temperature box furnace contribute to the sintering of doped zirconate ceramics? Achieve 94% Density
- How does a muffle furnace differ from a pusher furnace? Choose the Right Furnace for Your Lab
- How does a muffle furnace with precision temperature control contribute to the debinding of alumina ceramic green bodies?
- What are the typical specifications for lab box furnaces? Find Your Perfect Fit for Materials Processing
- What are the typical applications for this muffle furnace? Achieve Precise Heat Treatment and Analysis
- What thermal processing applications do muffle furnaces have in pharmaceuticals? Essential for Purity and Quality Control



















