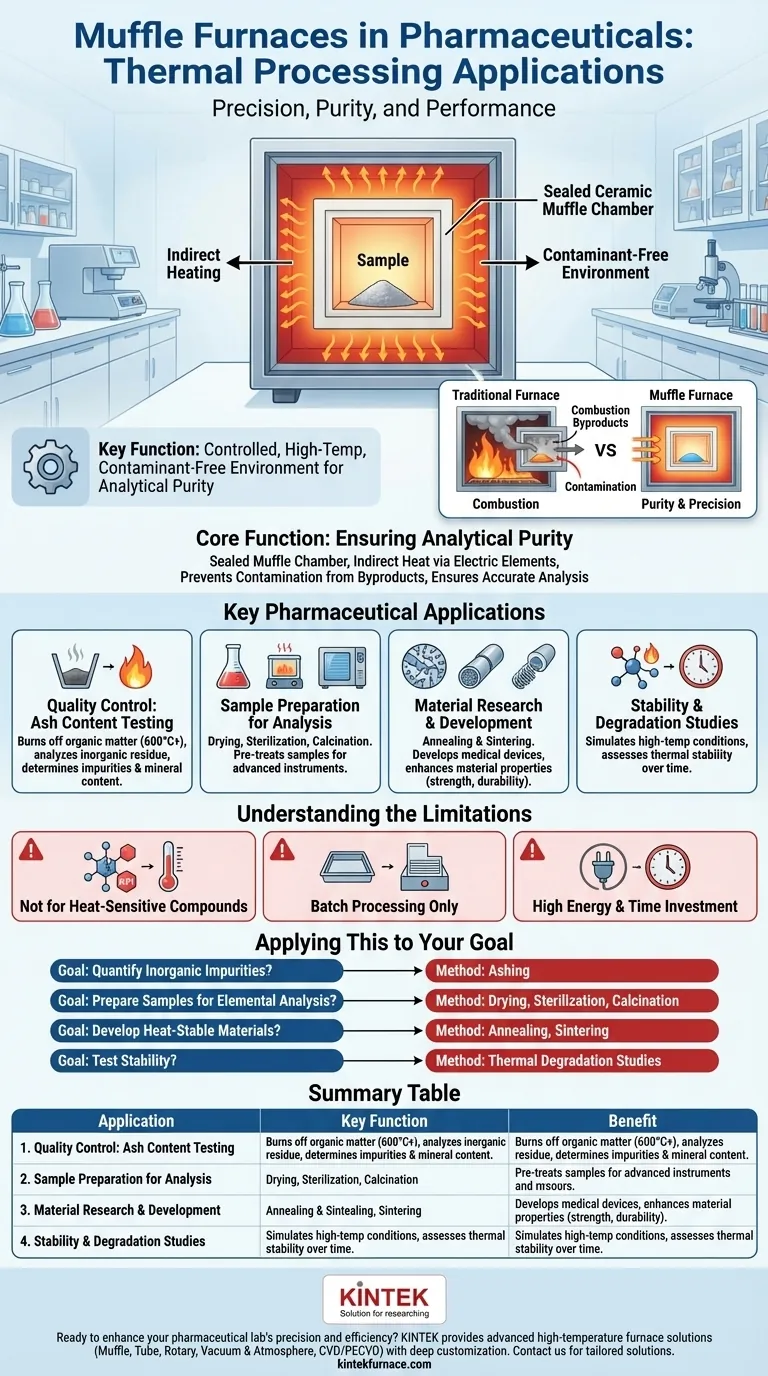
In the pharmaceutical industry, muffle furnaces are primarily used for quality control testing and the preparation of medical samples for analysis. Their key function is to provide a highly controlled, high-temperature environment that is free from contaminants, which is essential for processes like ashing, material heat treatment, and thermal degradation studies.
A muffle furnace's value in pharmaceuticals is not just its high heat, but its ability to heat a sample indirectly. This isolates the material from combustion byproducts, ensuring that analytical results for purity and composition are precise and uncompromised.

The Core Function: Ensuring Analytical Purity
A traditional furnace burns fuel to generate heat, and the byproducts of this combustion can interact with the sample being heated. In pharmaceuticals, where even trace contaminants can invalidate results, this is unacceptable.
How a Muffle Furnace Works
A muffle furnace solves this problem by using a "muffle"—a sealed inner chamber, typically made of high-temperature ceramic.
Electric heating elements heat the outside of this chamber. The heat then radiates through the chamber walls to the sample inside, ensuring it is never exposed to anything but a clean, heated atmosphere.
Why Contaminant-Free Heating is Critical
The core of pharmaceutical quality control is ensuring a product contains exactly what it is supposed to, and nothing more.
Processes performed in a muffle furnace are often destructive tests designed to reveal the fundamental composition of a sample. Any contamination from the heating process itself would introduce variables that make it impossible to guarantee the safety and efficacy of the final drug product.
Key Pharmaceutical Applications
The precise, clean heat of a muffle furnace makes it an indispensable tool for several key analytical and research tasks.
Quality Control: Ash Content Testing
Ashing is the most common pharmaceutical application. The process involves heating a sample to a very high temperature (e.g., 600 °C or higher) to completely burn off all organic matter.
What remains is the ash, which is the sample's inorganic content. Analyzing this residue helps determine the presence and quantity of inorganic impurities or verify the concentration of essential mineral components in a formulation.
Sample Preparation for Further Analysis
Many advanced analytical instruments require samples to be in a specific state before testing.
A muffle furnace is used for pre-treatment steps like drying to remove all moisture, sterilization of heat-stable equipment, or calcination (heating to high temperatures without fusion) to induce a phase transition or remove volatile fractions from a compound.
Material Research and Development
Muffle furnaces are used to test and develop materials for medical devices or advanced drug delivery systems.
Processes like annealing (heating and slow cooling) and sintering (heating to fuse particles together) alter a material's physical properties. These treatments can enhance the strength, durability, and performance of ceramics or metals used in implants and other medical applications.
Stability and Degradation Studies
To understand how a drug product or material behaves over time or under stress, it is subjected to forced degradation. A muffle furnace can create a precise high-temperature environment to simulate these conditions, helping researchers assess the thermal stability of a substance.
Understanding the Limitations
While powerful, a muffle furnace is a specific tool with clear limitations that define its proper use.
Not for Heat-Sensitive Compounds
The extremely high temperatures will destroy most active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and other organic molecules. Its primary role is therefore not in processing final drug formulations, but in analyzing their raw components or inorganic characteristics.
Designed for Batch Processing
A muffle furnace processes samples in discrete batches. This makes it ideal for laboratory-scale quality control and research but unsuitable for integration into a continuous, high-volume manufacturing line.
High Energy and Time Investment
These furnaces consume significant energy and require considerable time to heat up to temperature and cool down safely. This operational cycle must be factored into lab workflow and scheduling.
Applying This to Your Goal
Your choice of thermal process depends entirely on what you need to learn about your material.
- If your primary focus is quantifying inorganic impurities: Ashing is the definitive method for preparing your sample for analysis.
- If your primary focus is preparing samples for elemental analysis: A muffle furnace is the correct tool for drying, sterilizing, or ashing samples to ensure accurate results.
- If your primary focus is developing new heat-stable materials for devices: Use annealing or sintering to test and modify the physical properties of your materials.
- If your primary focus is testing the stability of a substance at extreme temperatures: A muffle furnace provides the controlled environment needed for thermal degradation studies.
Ultimately, the muffle furnace serves as a gatekeeper for quality, enabling the rigorous analysis required to ensure pharmaceutical safety and efficacy.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Function | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Ash Content Testing | Burns off organic matter to analyze inorganic impurities | Ensures purity and composition accuracy |
| Sample Preparation | Drying, sterilization, or calcination for analysis | Prepares samples for advanced instruments |
| Material R&D | Annealing and sintering for medical devices | Enhances material properties like strength |
| Stability Studies | Simulates high-temperature degradation | Assesses thermal stability of substances |
Ready to enhance your pharmaceutical lab's precision and efficiency? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can support your quality control, sample preparation, and material research needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production



















