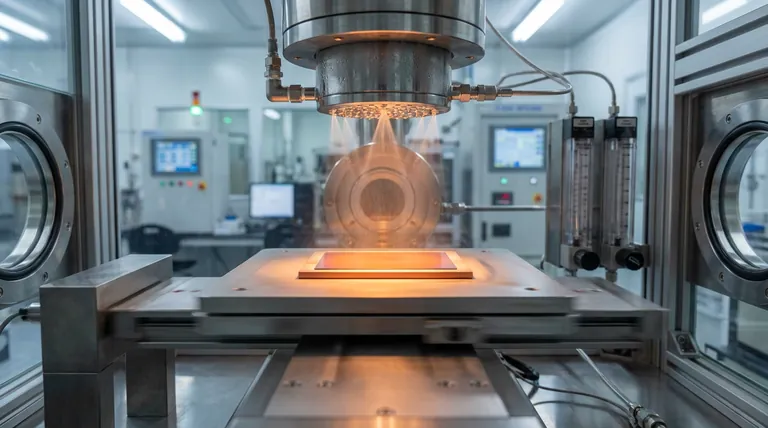
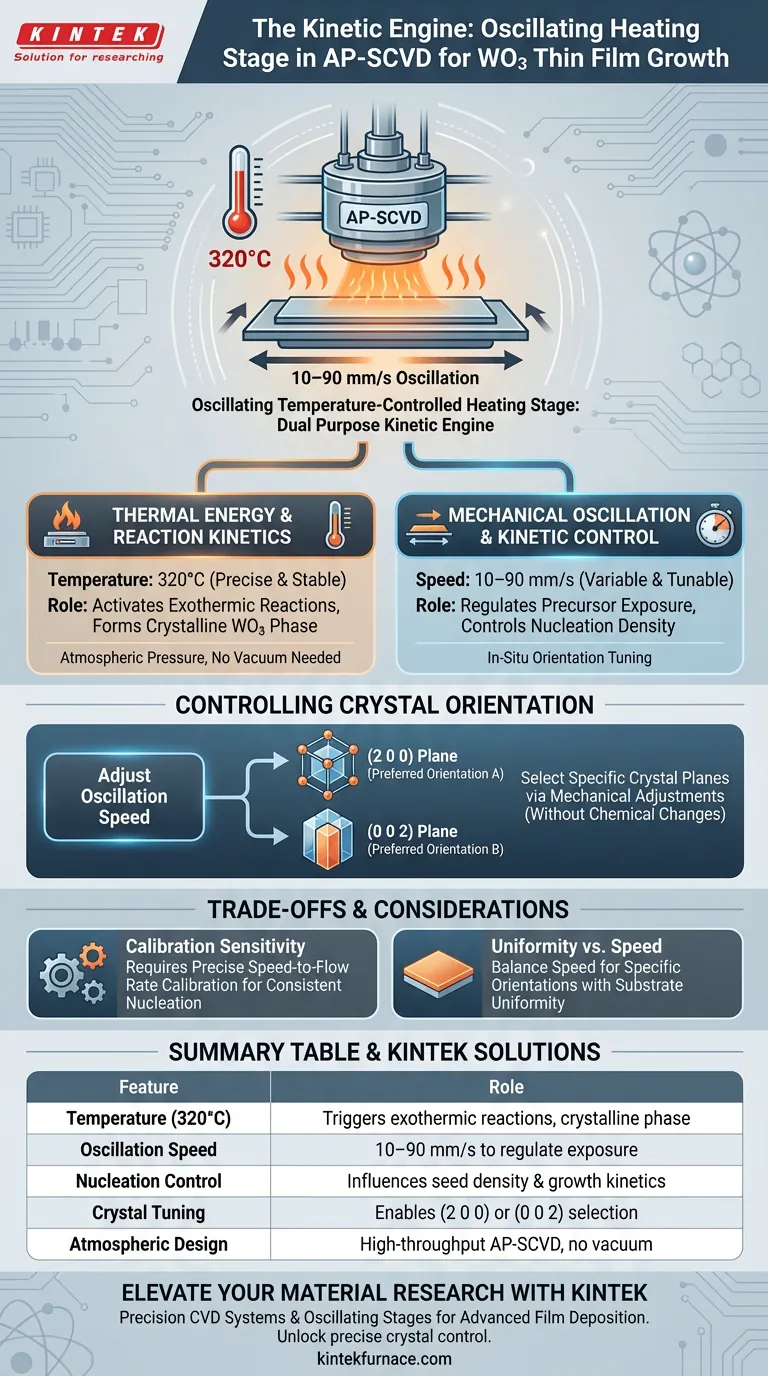
The oscillating temperature-controlled heating stage acts as the kinetic engine for the entire deposition process. It serves a dual purpose: providing the precise thermal energy required to trigger chemical reactions and utilizing mechanical movement to dictate how the film nucleates and grows. By strictly maintaining the substrate at 320°C while oscillating at specific speeds (10–90 mm/s), this component allows you to control the crystal orientation of tungsten trioxide (WO3) thin films without altering the chemical precursors.
By coupling constant thermal energy with variable mechanical speed, this system allows for in-situ tuning of material properties. It shifts the control mechanism from chemical composition to physical kinetics, enabling the selection of specific crystal planes simply by adjusting the motion of the stage.

Thermal Energy and Reaction Kinetics
The first role of the heating stage is fundamental thermodynamics. Without precise temperature control, the chemical vapor deposition process cannot initiate effectively.
Activation of Exothermic Reactions
The stage creates the necessary environment for film formation by maintaining the substrate at 320°C.
This specific temperature is critical. It provides the thermal energy required to induce the exothermic reactions that form the crystalline phase of WO3.
Eliminating Vacuum Dependencies
Because this occurs in an Atmospheric Pressure Spatial Chemical Vapor Deposition (AP-SCVD) system, the heating stage operates in an open environment.
This design supports the continuous supply of precursors without the need for complex vacuum pumps or sealed reaction chambers.
The Role of Mechanical Oscillation
The "oscillating" aspect of the stage is where the system differentiates itself from static deposition methods. It turns the physical movement of the sample into a variable for controlling growth.
Regulating Precursor Exposure
The stage moves the substrate back and forth beneath the reactor head using a reciprocating motion.
This oscillation dictates the exact duration the substrate is exposed to the precursor gases.
Impact on Nucleation Density
By adjusting the oscillation speed between 10 and 90 mm/s, you directly influence the growth kinetics.
Higher or lower speeds change the exposure time. This variation modifies the nucleation density, determining how many crystal seeds form on the surface.
Controlling Crystal Orientation
The ultimate value of this heating stage lies in its ability to determine the structural alignment of the thin film.
In-Situ Orientation Tuning
You can select specific crystal orientations purely through mechanical adjustments.
By manipulating the oscillation speed, the system promotes growth along preferred planes.
Specific Plane Selection
The primary reference highlights that this mechanism enables control over specific orientations, such as the (2 0 0) or (0 0 2) planes.
This allows for the customization of the film's properties to suit specific applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the oscillating stage offers high throughput and flexibility, it introduces specific operational considerations.
Calibration Sensitivity
The link between oscillation speed and film quality is direct and sensitive.
If the speed is not precisely calibrated to the precursor flow rate, you risk inconsistent nucleation density.
Uniformity vs. Speed
While the system is designed for large-area uniformity, extreme oscillation speeds could theoretically disrupt the laminar flow of gases in the open atmosphere.
Operators must balance the need for specific crystal orientations with the requirement for uniform film thickness across the entire substrate.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of the oscillating heating stage, align your settings with your specific material requirements.
- If your primary focus is Reaction Initiation: Ensure the stage is calibrated to maintain a stable 320°C to reliably trigger the necessary exothermic reactions.
- If your primary focus is Crystal Orientation: Vary the oscillation speed between 10 and 90 mm/s to selectively favor the (2 0 0) or (0 0 2) planes.
- If your primary focus is Throughput: Leverage the reciprocating oscillation to process large-area substrates continuously without breaking a vacuum seal.
Mastering the velocity of your heating stage is just as critical as selecting the right chemical precursors for high-quality WO3 films.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in WO3 Thin Film Growth |
|---|---|
| Temperature (320°C) | Triggers exothermic reactions for crystalline phase formation |
| Oscillation Speed | Varies between 10–90 mm/s to regulate precursor exposure time |
| Nucleation Control | Influences seed density and film growth kinetics via motion |
| Crystal Tuning | Enables selection of (2 0 0) or (0 0 2) planes without chemical changes |
| Atmospheric Design | Eliminates vacuum dependency for high-throughput AP-SCVD |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK
Precision is the backbone of high-quality thin film deposition. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, including specialized solutions for lab high-temp processes. Whether you need an oscillating stage for AP-SCVD or a fully customizable furnace for unique material requirements, our engineering team is ready to assist you.
Unlock precise control over your crystal orientations today.
Visual Guide
References
- Zhuotong Sun, Judith L. MacManus‐Driscoll. Low-temperature open-atmosphere growth of WO<sub>3</sub> thin films with tunable and high-performance photoresponse. DOI: 10.1039/d3tc02257a
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station CVD Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using a microwave reaction system? Rapid & Uniform Synthesis of Doped Hydroxyapatite
- What is the significance of pre-equilibrating samples in silicate studies? Maximize Experimental Efficiency
- Why is a vacuum sealing process necessary for the synthesis of TaAs2 single crystals? Ensuring Purity in CVT Method
- What is the purpose of using a laboratory electric thermostatic blast drying oven in the pretreatment of sludge? Efficiency & Accuracy
- How are heat treatment furnaces utilized in the automotive industry? Enhance Component Durability and Performance
- What is the purpose of performing a 1200°C solution treatment for high-entropy alloys? Achieve Total Homogenization
- What function does a fluidized bed reactor perform in oil sludge pyrolysis? Enhance Thermal Efficiency
- What are the complexities and maintenance requirements of continuous furnaces? Optimize High-Volume Production with Expert Insights



















