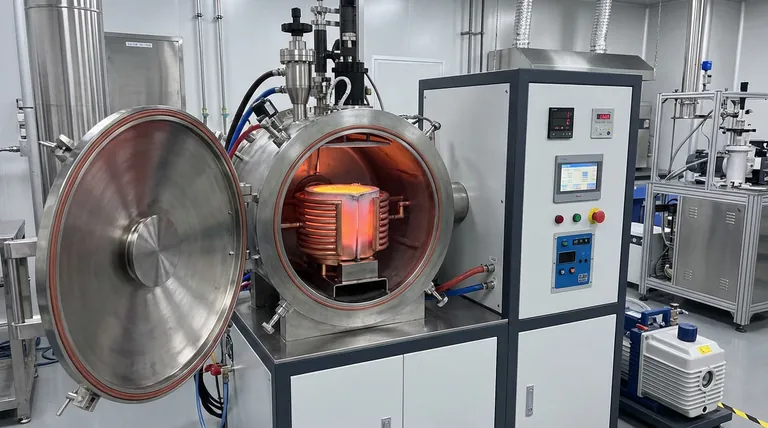
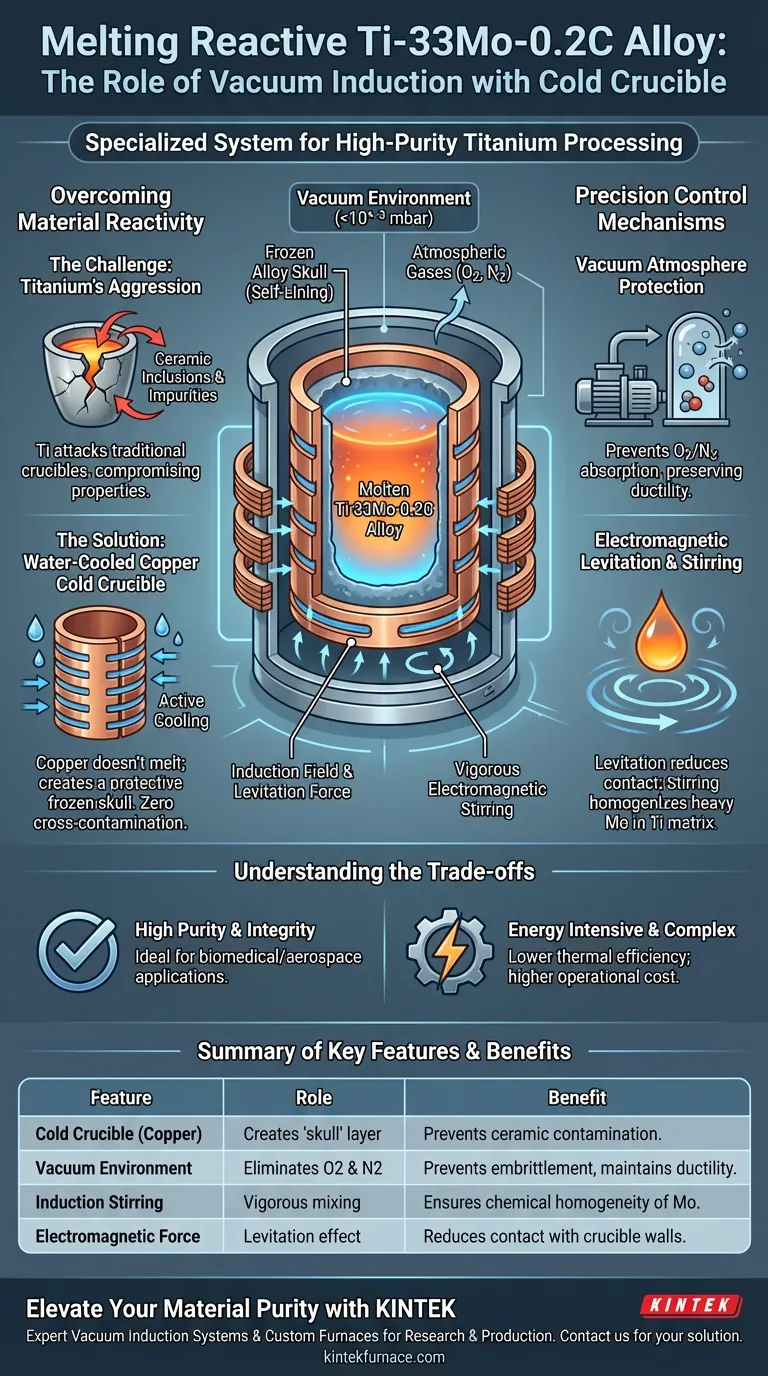
In the processing of Ti-33Mo-0.2C alloy, the vacuum induction furnace equipped with a water-cooled copper cold crucible serves as a specialized high-purity melting system designed to overcome the extreme chemical reactivity of molten titanium.
Its primary function is to eliminate contamination sources by combining a high-vacuum environment—which prevents the absorption of atmospheric gases like oxygen and nitrogen—with a cold crucible technique that prevents the molten alloy from ever touching a reactive ceramic liner.
Core Takeaway Processing titanium alloys requires isolating the melt from both the air and the containment vessel itself. The cold crucible method uses electromagnetic forces to create a "skull" or levitation effect, ensuring the reactive alloy is melted solely within a container of its own frozen material, guaranteeing absolute compositional purity.
Overcoming Material Reactivity
The Challenge of Titanium Melting
Titanium is highly reactive in its liquid state. When melted in traditional ceramic or refractory crucibles, it aggressively attacks the vessel walls.
This reaction introduces ceramic inclusions and impurities into the melt, compromising the mechanical properties of the final Ti-33Mo-0.2C alloy.
The Water-Cooled Copper Solution
The "cold crucible" is constructed from segmented, water-cooled copper. Because copper is highly conductive and actively cooled, it does not melt.
Instead of the alloy touching the copper, the intense cooling causes a thin layer of the titanium alloy to freeze instantly against the wall.
The "Skull" Effect
This frozen layer is known as a skull. It acts as a protective lining, meaning the molten Ti-33Mo-0.2C is actually contained inside a shell of its own solid material.
This eliminates any interaction between the liquid metal and foreign refractory materials, ensuring zero cross-contamination.
Precision Control Mechanisms
Vacuum Atmosphere Protection
The vacuum induction furnace operates in an extremely pure vacuum environment.
This is critical because titanium absorbs oxygen and nitrogen rapidly at high temperatures. These interstitial elements can embrittle the alloy; the vacuum prevents this absorption, preserving the alloy's ductility.
Electromagnetic Levitation and Stirring
The induction field used to heat the metal also generates strong electromagnetic forces.
These forces can create a levitation effect, further reducing contact with the crucible walls. Additionally, induction provides vigorous electromagnetic stirring.
This stirring is vital for Ti-33Mo-0.2C because Molybdenum (Mo) has a higher density and melting point than Titanium. The stirring ensures the refractory Mo is fully dissolved and chemically homogenized within the Ti matrix.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Thermal Efficiency
While the cold crucible guarantees purity, it is thermally inefficient compared to traditional furnaces.
A significant amount of energy is lost through the water-cooled walls to maintain the "skull." This makes the process more energy-intensive and generally limits the maximum superheat (temperature above melting point) that can be achieved.
Complexity and Cost
The system requires complex power supplies and high-pressure water cooling systems.
It is generally reserved for high-value applications—such as biomedical or aerospace components—where material purity is more critical than production cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if this melting method aligns with your specific metallurgical objectives, consider the following:
- If your primary focus is absolute purity and biocompatibility: This is the definitive choice, as the cold crucible completely negates the risk of ceramic inclusions and refractory contamination.
- If your primary focus is precise composition control: The vacuum environment combined with electromagnetic stirring ensures that the specific ratio of Titanium, Molybdenum, and Carbon remains exact and homogeneous.
The cold crucible vacuum induction furnace is the industry standard for transforming reactive raw elements into high-integrity Ti-33Mo-0.2C alloy without structural compromise.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in Ti-33Mo-0.2C Melting | Benefit to Final Alloy |
|---|---|---|
| Cold Crucible (Copper) | Creates a "skull" (frozen alloy layer) | Prevents ceramic inclusion & contamination |
| Vacuum Environment | Eliminates atmospheric O2 and N2 | Prevents embrittlement & maintains ductility |
| Induction Stirring | Vigorous electromagnetic mixing | Ensures chemical homogeneity of Molybdenum |
| Electromagnetic Force | Provides a levitation effect | Reduces contact with crucible walls |
Elevate Your Material Purity with KINTEK
Precision melting of reactive alloys like Ti-33Mo-0.2C requires more than just heat—it requires a contamination-free environment. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Vacuum Induction Systems and custom lab high-temp furnaces (Muffle, Tube, Rotary, CVD) tailored to your specific research or production needs.
Ready to achieve absolute compositional integrity? Contact KINTEK experts today to discuss your custom furnace solution.
Visual Guide
References
- W. Szkliniarz, Agnieszka Szkliniarz. The Role of Titanium Carbides in Forming the Microstructure and Properties of Ti-33Mo-0.2C Alloy. DOI: 10.3390/coatings15050546
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What environmental benefits do channel induction furnaces provide? A Cleaner, Sustainable Melting Solution
- Why is a water-cooled copper crucible used for Sm-Co-Fe alloys? Ensuring Purity in Vacuum Arc Furnaces
- What are the key components of a vacuum casting furnace? Essential Parts for High-Purity Metal Casting
- How does vacuum or protective atmosphere melting improve alloy composition uniformity? Achieve Precise Alloy Chemistry Control
- What are the advantages of induction melting furnaces in metal processing? Boost Efficiency, Quality, and Safety
- What are the primary advantages of using a Vacuum Induction Cold Crucible Furnace (VCCF)? Achieve Extreme Steel Purity
- What makes induction vacuum melting possible? Unlock Ultra-Pure Metal Production
- What factors should be considered when selecting a crucible material for a vacuum casting furnace? Ensure Purity and Performance



















