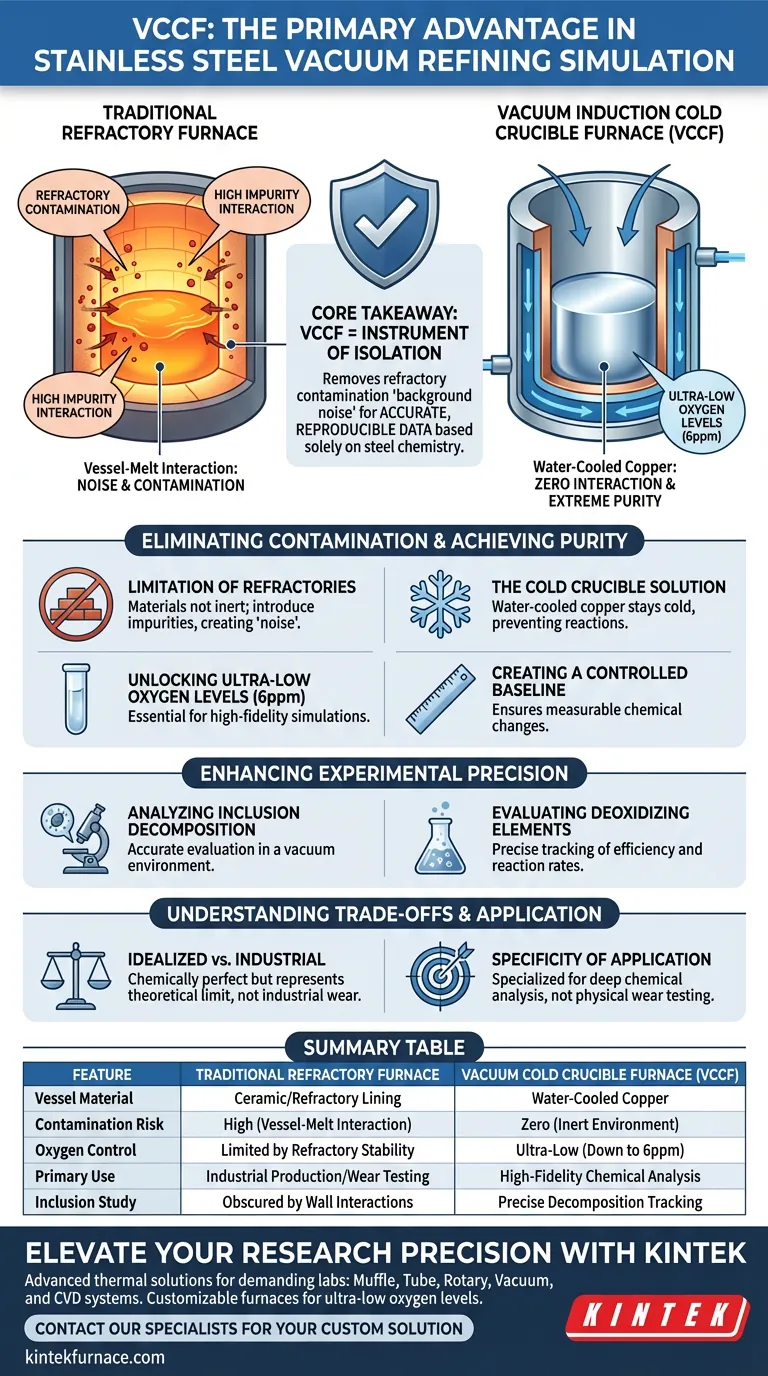
The primary advantage of the Vacuum Induction Cold Crucible Furnace (VCCF) is its ability to completely eliminate external contamination during stainless steel refining simulations. By replacing traditional refractory linings with a water-cooled copper crucible, the VCCF prevents chemical interactions between the vessel and the molten metal. This allows researchers to achieve extreme purity levels—such as reducing oxygen content to 6ppm—providing a pristine environment for analyzing specific chemical behaviors.
Core Takeaway: The VCCF is an instrument of isolation. Its value lies in removing the "background noise" of refractory contamination, ensuring that observed data regarding inclusion decomposition and deoxidizer behavior is accurate, reproducible, and solely a result of the steel chemistry itself.

Eliminating Contamination Sources
The Limitation of Refractories
Traditional furnaces rely on refractory linings to contain molten metal. These materials are not inert; they inevitably interact with the steel at high temperatures.
This interaction introduces impurities into the melt. In sensitive simulations, this "noise" makes it difficult to distinguish between internal chemical reactions and external contamination from the vessel walls.
The Cold Crucible Solution
The VCCF solves this by utilizing a water-cooled copper crucible. The cooling mechanism keeps the copper significantly below the melting point of the steel.
Because the crucible remains cold, it does not react with the molten stainless steel. This design effectively seals off the simulation from environmental interference.
Achieving Extreme Purity
Unlocking Ultra-Low Oxygen Levels
The elimination of refractory materials allows for exceptional control over the atmosphere within the furnace.
According to technical benchmarks, VCCF systems can reduce oxygen content to as low as 6ppm. This level of purity is essential for high-fidelity simulations of vacuum refining processes.
Creating a Controlled Baseline
Starting with such high purity is critical for experimental accuracy. It establishes a reliable baseline, ensuring that any subsequent changes in the metal's chemistry are deliberate and measurable.
Enhancing Experimental Precision
Analyzing Inclusion Decomposition
One of the most difficult aspects of steel research is tracking how non-metallic inclusions break down.
In a VCCF, researchers can accurately evaluate inclusion decomposition. Without interference from crucible materials, the data reflects the true behavior of the inclusions in a vacuum environment.
Evaluating Deoxidizing Elements
The VCCF is particularly valuable for studying deoxidizers.
It enables the precise tracking of how deoxidizing elements behave. Researchers can observe efficiency and reaction rates without the confounding variable of oxygen re-introduction from a ceramic lining.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Idealized vs. Industrial Conditions
While the VCCF provides a chemically perfect environment, it is important to note that it creates an idealized simulation.
Industrial steelmaking almost always involves refractory contact. Therefore, data derived from VCCF simulations represents the theoretical limit of the metal's chemistry, rather than the exact conditions found in a commercial ladle where refractory wear is a constant factor.
Specificity of Application
The VCCF is a specialized tool. It is designed for deep chemical analysis rather than physical wear testing.
If your goal is to study slag-line erosion or refractory life, a VCCF is not the correct tool, as the very component you wish to study (the refractory) has been removed.
How to Apply This to Your Project
To determine if a VCCF is the right tool for your simulation, assess your primary research objectives:
- If your primary focus is Chemical Purity: Choose the VCCF to eliminate variables and achieve oxygen levels as low as 6ppm.
- If your primary focus is Inclusion Mechanics: Use the VCCF to observe decomposition and deoxidation behaviors without the interference of crucible interactions.
By removing the vessel from the chemical equation, the VCCF empowers you to see the steel as it truly is.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Traditional Refractory Furnace | Vacuum Cold Crucible Furnace (VCCF) |
|---|---|---|
| Vessel Material | Ceramic/Refractory Lining | Water-Cooled Copper |
| Contamination Risk | High (Vessel-Melt Interaction) | Zero (Inert Environment) |
| Oxygen Control | Limited by Refractory Stability | Ultra-Low (Down to 6ppm) |
| Primary Use | Industrial Production/Wear Testing | High-Fidelity Chemical Analysis |
| Inclusion Study | Obscured by Wall Interactions | Precise Decomposition Tracking |
Elevate Your Research Precision with KINTEK
Don't let refractory contamination compromise your experimental data. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced thermal solutions designed for the most demanding laboratory environments. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, including high-performance induction technologies.
Our furnaces are fully customizable to meet your unique simulation needs, ensuring you achieve the ultra-low oxygen levels and chemical purity your projects require. Ready to eliminate the 'background noise' in your metallurgical simulations?
Contact our specialists today to find your custom furnace solution.
Visual Guide
References
- Shunsuke Narita, Yoshinori Sumi. Effect of deoxidizing elements on inclusions in vacuum refining of stainless steel. DOI: 10.1088/1757-899x/1329/1/012005
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering and Brazing Furnace
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- What types of materials can channel induction furnaces melt? The Ideal High-Volume Metal Melting Solution
- How does electrical conductivity affect induction coil life? Maximize Furnace Durability with Superior Conductivity
- How does the Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) process work? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Control
- What industries commonly use vacuum or protective atmosphere induction furnaces? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and More
- What additional features might advanced induction heater circuits incorporate? Enhance Precision, Efficiency, and Safety
- Why are hollow copper tubes used for induction furnace coils? Essential Cooling for High-Power Melting
- What is the purpose of performing multiple argon gas flushing cycles? Ensuring Purity in Sm-Co-Fe Alloy Melting
- What determines the depth of heating in induction processes? Master Frequency & Material Control



















