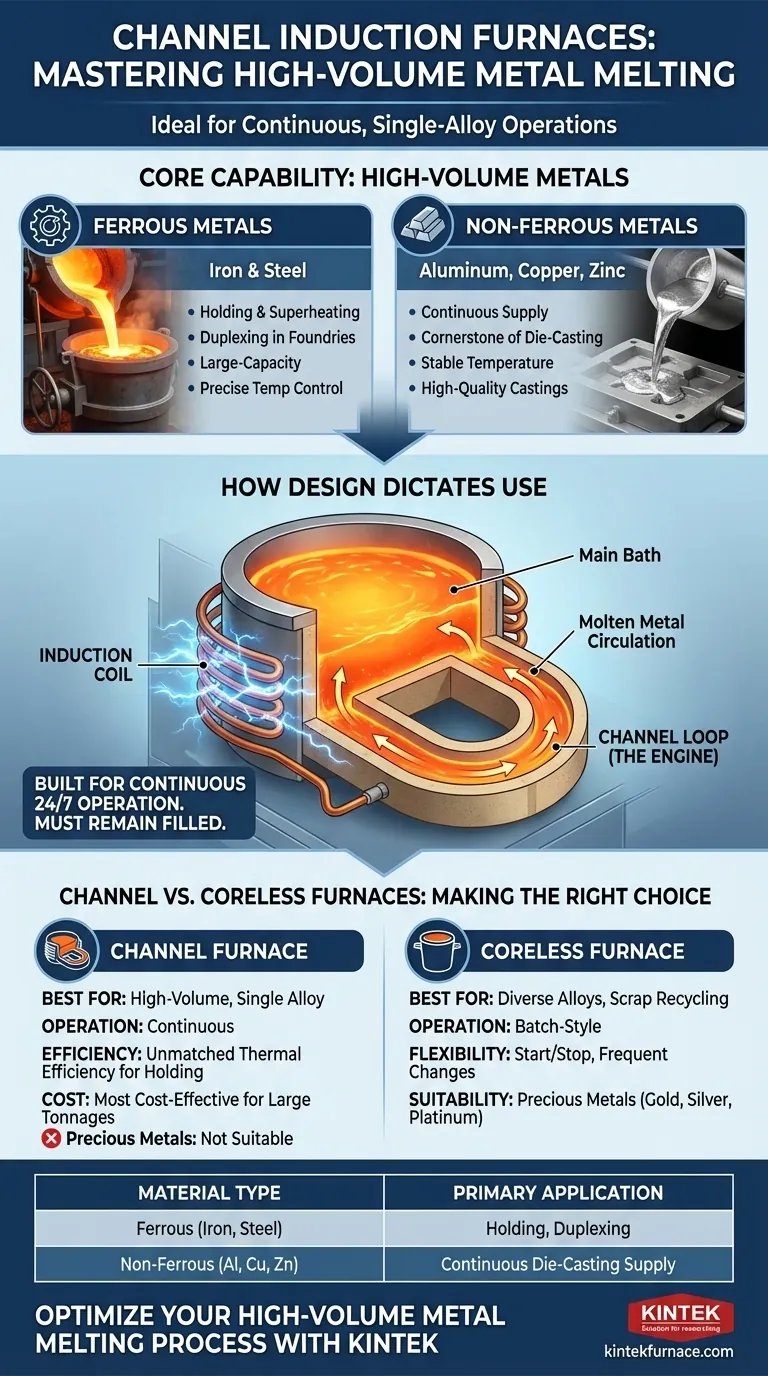
In short, channel induction furnaces are highly effective for melting a specific range of common industrial metals. They are workhorses for both ferrous metals like iron and steel, and non-ferrous metals such as aluminum, copper, and zinc alloys. Their design makes them particularly well-suited for large-volume, continuous operations where a single alloy is processed over a long period.
The critical insight is not just what materials a channel furnace can melt, but how its design dictates its use. It excels at efficiently holding and superheating massive quantities of a single metal, making it distinct from more flexible, all-purpose melting technologies.
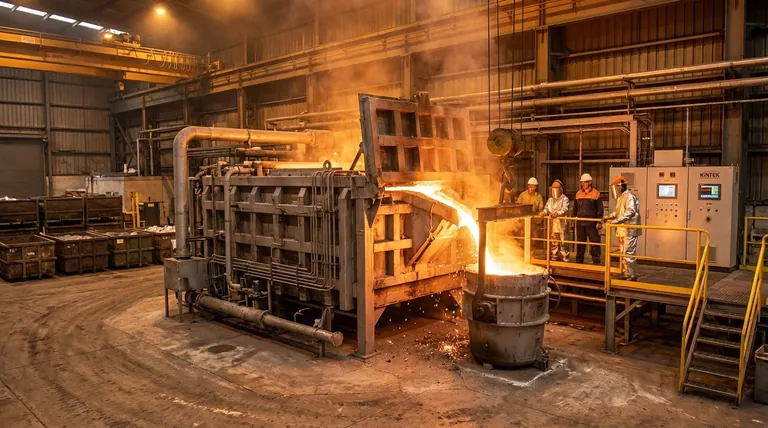

The Core Capability: High-Volume Metals
A channel furnace's primary function is to act as a highly efficient, continuous-duty vessel for molten metal. This operational model makes it ideal for specific, high-throughput industrial applications.
Ferrous Metals: Iron and Steel
Channel furnaces are frequently used in iron foundries and steel mills. They often serve as large-capacity holding furnaces, receiving molten metal from a primary melting unit like a cupola or an electric arc furnace.
Their role is to maintain the metal at a precise temperature and homogenize its chemistry before it is transferred to the casting line. This process is often called duplexing.
Non-Ferrous Metals: Aluminum, Copper, and Zinc
This is where channel furnaces truly excel, especially in casting operations. They are a cornerstone of the aluminum industry, particularly for supplying die-casting machines.
The furnace provides a constant, ready supply of molten aluminum at a stable temperature. The gentle, natural stirring action within the channel is sufficient to maintain alloy consistency without introducing excessive gas or inclusions, which is critical for high-quality castings.
How Design Dictates Material Choice
The name "channel furnace" refers directly to its construction. Understanding this design is key to understanding its capabilities and limitations.
The "Channel" Loop is the Engine
Unlike other furnaces, a channel furnace has a distinct, loop-shaped channel of refractory material that contains a portion of the molten metal. This loop passes through an induction coil.
When power is applied, the metal within this loop acts as a secondary coil, generating intense heat. This hot metal then circulates into the main bath, transferring heat through natural convection.
Built for Continuous Operation
This design requires the channel to remain filled with molten metal at all times to function. It cannot be started easily from cold and is not designed to be completely emptied between uses.
As a result, channel furnaces are ideal for 24/7 operations where they hold and superheat a single alloy for weeks or months at a time. This continuous duty makes their high electrical efficiency a major economic advantage.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Channel vs. Coreless Furnaces
The term "induction furnace" is broad and often causes confusion. The primary alternative to a channel furnace is a coreless induction furnace, and they serve very different purposes.
When to Choose a Channel Furnace
A channel furnace is the superior choice for high-volume, single-alloy production. Its unmatched thermal efficiency makes it the most cost-effective option for holding large tonnages of metal like iron or aluminum for continuous casting.
When a Coreless Furnace is a Better Fit
A coreless induction furnace functions like a crucible or pot surrounded by an induction coil. It is a batch-style melter that can be started from cold and emptied completely after each melt.
This makes coreless furnaces ideal for foundries that need to melt a wide variety of alloys, process scrap metal of varying types, or require the flexibility to shut down and change materials frequently.
The Question of Precious Metals
While references often mention induction melting for gold, silver, and platinum, this work is almost exclusively done in coreless induction furnaces.
The small batch sizes, the absolute need for complete metal recovery between melts, and the variety of alloys involved make the channel furnace's continuous design entirely unsuitable for precious metal applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct furnace technology depends entirely on your operational goals.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, continuous production of one alloy (e.g., aluminum for die casting): The channel induction furnace is the most energy-efficient and effective choice.
- If your primary focus is melting diverse materials, frequent alloy changes, or recycling scrap: A coreless induction furnace provides the necessary operational flexibility.
- If your primary focus is refining precious metals or producing high-purity specialty alloys: The batch control and complete emptying of a coreless induction furnace are non-negotiable.
Ultimately, understanding the fundamental difference between continuous (channel) and batch (coreless) operation is the key to selecting the right tool for your job.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Common Examples | Primary Application |
|---|---|---|
| Ferrous Metals | Iron, Steel | Holding, superheating, and duplexing in foundries |
| Non-Ferrous Metals | Aluminum, Copper, Zinc alloys | Continuous supply for die-casting and casting operations |
| Not Suitable For | Precious metals, frequent alloy changes, small batches | Requires batch-style coreless furnaces |
Optimize Your High-Volume Metal Melting Process with KINTEK
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements.
If you are engaged in high-volume, continuous production of a single alloy—such as aluminum for die casting or iron for foundry operations—our channel induction furnace expertise can deliver unmatched energy efficiency and operational stability for your business.
Contact our experts today to discuss how a custom KINTEK furnace solution can enhance your melting process and drive productivity.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How has vacuum smelting impacted the development of superalloys? Unlock Higher Strength and Purity
- How does vacuum melting technology contribute to sustainability? Boost Durability and Recycling Efficiency
- What is the purpose of vacuum melting, casting and re-melting equipment? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- What is vacuum induction melting technology and why is it important? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in Fe-5%Mn-C alloys? Ensure Chemical Integrity and High Purity



















