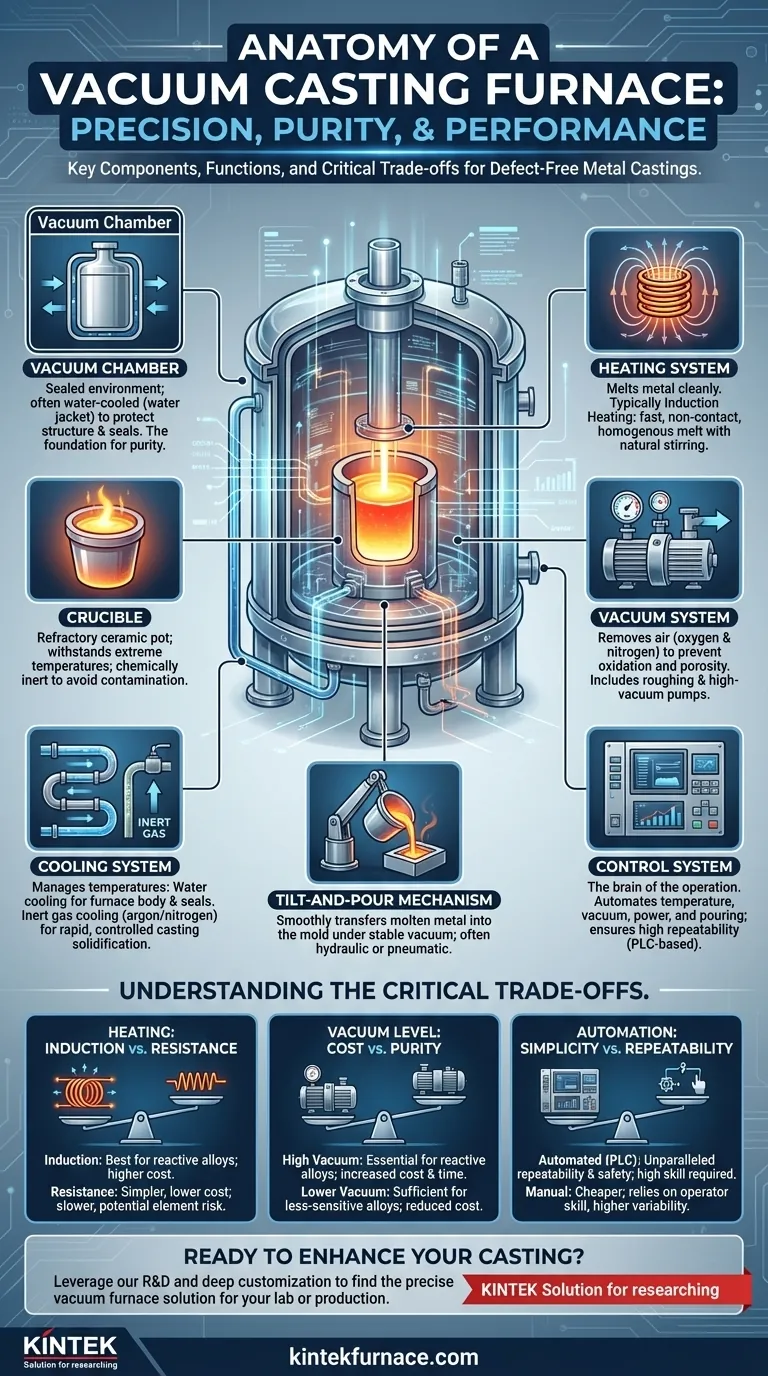
At its core, a vacuum casting furnace integrates seven primary components. These are the vacuum chamber that provides the sealed environment, a heating system (typically induction) to melt the metal within a crucible, a vacuum system to remove air and reactive gases, a tilt-and-pour mechanism to transfer the molten metal, a cooling system to manage temperatures, and a control system to automate the entire process.
A vacuum casting furnace is not merely a collection of parts, but a highly integrated system. Its purpose is to precisely control the atmosphere, temperature, and material flow to produce high-purity, defect-free metal castings that are impossible to achieve in a normal atmosphere.

The Anatomy of a Vacuum Casting Furnace
To understand how these furnaces achieve such high-quality results, we must look at how each component contributes to the tightly controlled process. The system is designed for one purpose: total environmental and thermal control.
The Containment Structure: The Vacuum Chamber
The vacuum chamber, also called the furnace body or vessel, is the sealed steel shell where the entire process takes place. It is the foundation of the system.
Most chambers are constructed from stainless steel with a double-wall, or "water jacket," design. This allows cooling water to circulate, protecting the chamber walls and critical seals from the intense internal heat.
The Heat Source: Melting the Alloy
The goal is to melt the metal alloy cleanly and efficiently. This is primarily handled by the heating system and the crucible that holds the material.
Induction Heating System
For casting, induction heating is the most common method. An electromagnetic coil generates a powerful magnetic field that heats the conductive metal inside the crucible directly, quickly, and cleanly, without contact. This process also creates a natural stirring effect, ensuring a homogenous melt.
The Crucible
The crucible is the refractory ceramic pot that contains the metal charge during melting. It must withstand extreme temperatures and be chemically inert to avoid contaminating the molten alloy.
The Environmental Control: Vacuum and Cooling
Controlling the atmosphere is the defining feature of a vacuum furnace. This involves both removing unwanted gases and managing heat.
The Vacuum System
This is a multi-part system designed to remove air—specifically oxygen and nitrogen—from the chamber. Removing these reactive gases prevents oxidation and porosity, which are common defects in conventional casting.
A typical system includes mechanical pumps for initial air removal (roughing) and high-vacuum pumps (like molecular or diffusion pumps) to achieve the final low pressure. Valves and gauges control and monitor the vacuum level throughout the process.
The Cooling System
Cooling happens in two key areas. First, a water cooling system continuously circulates water through the furnace body and door to protect the structure and seals.
Second, after the metal is poured, an inert gas cooling system often backfills the chamber with a gas like argon or nitrogen to help cool the finished casting rapidly and in a controlled manner.
The Action Center: Control and Handling
These systems manage the physical operation and ensure the process is repeatable and safe.
The Control System
Modern furnaces are governed by a Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) or a similar automated system. This central brain monitors and controls temperature, vacuum pressure, heating power, and the timing of the pouring sequence, ensuring high consistency from one batch to the next.
The Tilt-and-Pour Mechanism
Once the metal reaches the correct temperature and the vacuum is stable, a hydraulic or pneumatic system physically tilts the crucible and induction coil assembly. This action smoothly pours the molten metal into the mold, which is also located inside the vacuum chamber.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
Selecting or operating a vacuum furnace involves balancing competing priorities. Understanding these trade-offs is key to making an informed decision.
Heating Method: Induction vs. Resistance
Induction heating is fast, clean, and provides excellent melt stirring, making it ideal for reactive and complex alloys. However, the equipment is more expensive and complex.
Resistance heating, using elements like graphite or molybdenum, is simpler and less costly. However, it can be slower and carries a slight risk of element material contaminating the melt.
Vacuum Level: Cost vs. Purity
Achieving a high vacuum requires sophisticated and expensive multi-stage pumps. This is essential for extremely reactive alloys like titanium but increases cycle time and maintenance costs.
A lower vacuum using only mechanical pumps is sufficient for many less-sensitive alloys. This significantly reduces the furnace's cost and complexity.
Automation: Simplicity vs. Repeatability
A fully automated PLC system offers unparalleled repeatability, process logging, and safety interlocks. This is critical for certified production but comes at a high initial cost and requires specialized skills to program and maintain.
Manual or semi-manual controls are far cheaper and simpler. However, they rely heavily on operator skill and introduce a higher risk of process variability and human error.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific manufacturing goal dictates which components and features are most critical for your success.
- If your primary focus is casting highly reactive alloys (like titanium or superalloys): Prioritize a furnace with a high-vacuum system and clean, non-contact induction heating.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput production: A robust, automated tilt-pour mechanism and an efficient inert gas cooling system are critical for minimizing cycle times.
- If your primary focus is operational safety and reliability: Invest in a furnace with a well-designed water cooling system, comprehensive safety interlocks, and a modern PLC-based control system.
Understanding how these components function as an interconnected system empowers you to specify, operate, and maintain a furnace that precisely meets your manufacturing requirements.
Summary Table:
| Component | Key Function |
|---|---|
| Vacuum Chamber | Provides a sealed environment for the casting process |
| Heating System | Melts metal using induction or resistance methods |
| Crucible | Holds and contains the molten metal charge |
| Vacuum System | Removes air and gases to prevent oxidation |
| Tilt-and-Pour Mechanism | Transfers molten metal into the mold |
| Cooling System | Manages temperatures and cools the casting |
| Control System | Automates and monitors the entire process for consistency |
Ready to enhance your metal casting with precision and purity? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for laboratories and production facilities. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental and production needs. Whether you're working with reactive alloys or aiming for high throughput, our expertise ensures reliable, defect-free results. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your goals with a customized vacuum casting furnace solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- What are the common applications of Vacuum Induction Melting? Essential for High-Performance Metals and Alloys
- What is the purpose of vacuum melting, casting and re-melting equipment? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- How does vacuum melting technology contribute to sustainability? Boost Durability and Recycling Efficiency
- Why is a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace essential? Unlock Purity for Aerospace and Semiconductors
- What is vacuum induction melting technology and why is it important? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications



















