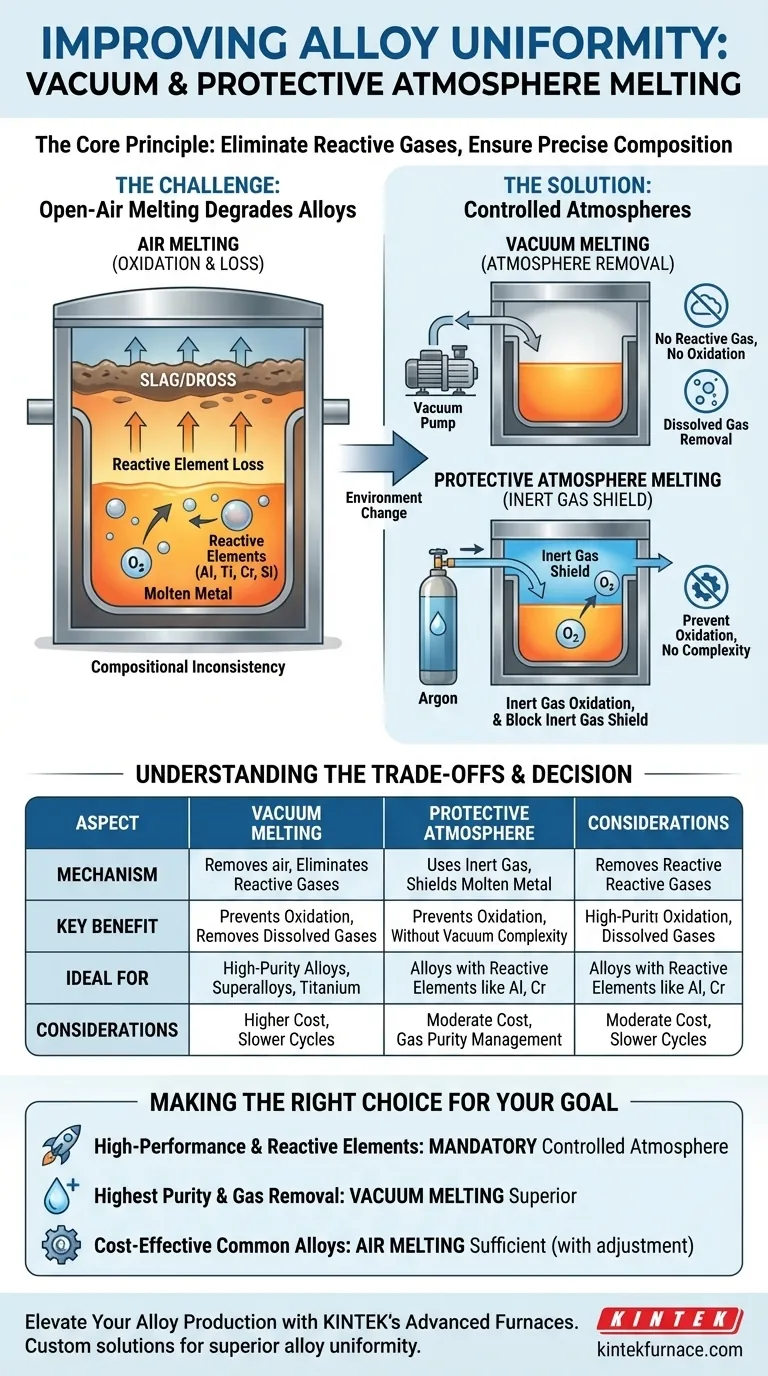
At its core, vacuum or protective atmosphere melting improves alloy uniformity by creating an environment free of reactive gases like oxygen. This prevents the loss of sensitive alloying elements that would otherwise react and be removed from the molten metal, ensuring the final composition precisely matches the intended formula.
By removing or replacing the atmosphere surrounding the molten metal, you are fundamentally eliminating the uncontrolled side reactions—primarily oxidation—that cause unpredictable variations in the alloy's final chemistry. This control is the key to achieving uniformity.
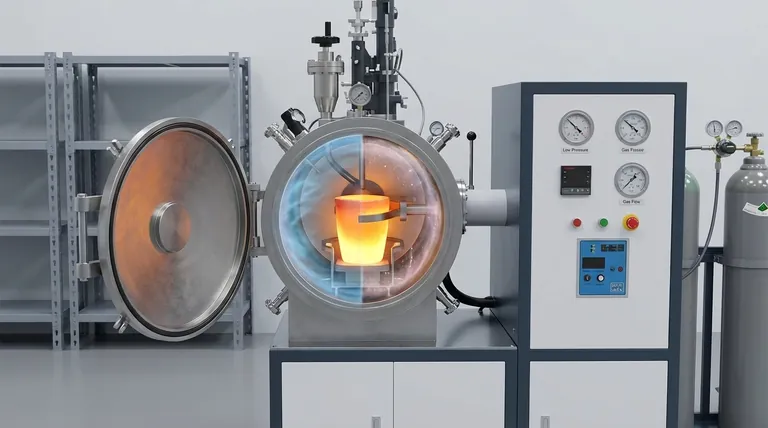

The Challenge: Why Open-Air Melting Degrades Alloys
When metals are melted in open air, they are exposed to a hostile environment at extreme temperatures. This exposure is the primary source of compositional inconsistency.
The Problem of Oxidation
At melting temperatures, most metallic elements have a strong affinity for oxygen. This causes them to react rapidly with the approximately 21% oxygen present in the air.
This reaction forms metallic oxides, which are non-metallic compounds. These oxides are often less dense than the molten metal and float to the surface, forming a layer of impurities known as slag or dross.
The Loss of Critical Alloying Elements
The real issue for alloy uniformity is that this oxidation process is not uniform. Certain elements—like aluminum, titanium, chromium, and silicon—are more reactive with oxygen than the base metal (e.g., iron or nickel).
These highly reactive elements are preferentially "scavenged" from the melt to form oxides. This means they are lost from the metallic solution, altering the carefully designed chemical balance of the alloy. The result is a final product that no longer has the intended composition.
How Controlled Atmospheres Preserve Composition
Vacuum and protective atmosphere melting directly counteract this destructive process by fundamentally changing the environment in which the metal is melted.
Mechanism 1: Vacuum Melting
The most direct approach is to remove the atmosphere entirely. A powerful vacuum system pumps the air out of the melting chamber before and during the process.
By reducing the pressure, you drastically reduce the number of oxygen, nitrogen, and other gas molecules available to react. With no reactant present, the oxidation and nitridation of sensitive alloying elements simply cannot occur.
Mechanism 2: Protective Atmosphere Melting
An alternative is to replace the reactive air with a gas that will not react with the molten metal. This is typically an inert gas, with argon being the most common choice.
The furnace chamber is purged of air and filled with high-purity argon. This inert gas blanket acts as a physical shield, preventing any residual or incoming oxygen from making contact with the surface of the molten metal.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While essential for quality, these advanced melting techniques introduce practical considerations that must be weighed against their benefits.
Increased Cost and Complexity
Vacuum induction melting (VIM) furnaces and the associated gas management systems are significantly more expensive to purchase, operate, and maintain than standard air-melt furnaces. This cost is ultimately passed on to the final product.
Slower Production Cycles
Achieving a high vacuum or thoroughly purging a chamber with inert gas takes time. These steps add to the overall "tap-to-tap" time, reducing the throughput compared to simpler melting methods.
When Is It Necessary?
For common alloys like basic carbon steels or certain cast irons, a predictable amount of element loss during air melting can often be compensated for by adjusting the initial charge. However, for high-performance superalloys, titanium alloys, or any material where trace elements have a powerful effect, controlled-atmosphere melting is not optional—it is a requirement.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use vacuum or protective atmosphere melting depends entirely on the chemical sensitivity of the alloy and the required precision of the final product.
- If your primary focus is producing high-performance alloys with reactive elements (e.g., titanium, aluminum, superalloys): Controlled atmosphere melting is mandatory to prevent the catastrophic loss of these critical elements and achieve the desired properties.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest purity and minimizing non-metallic inclusions: Vacuum melting is superior, as it not only prevents reactions but also helps remove dissolved gases like hydrogen and nitrogen from the melt.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective production of common, less-reactive alloys: Traditional air melting is often sufficient, as long as you can manage and compensate for a predictable degree of element loss.
Controlling the melting atmosphere is the definitive step in moving from simply making metal to precisely engineering a material.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Vacuum Melting | Protective Atmosphere Melting |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | Removes air to eliminate reactive gases | Uses inert gas (e.g., argon) to shield molten metal |
| Key Benefit | Prevents oxidation and removes dissolved gases | Prevents oxidation without vacuum complexity |
| Ideal For | High-purity alloys, superalloys, titanium alloys | Alloys with reactive elements like aluminum, chromium |
| Considerations | Higher cost, slower cycles | Moderate cost, requires gas purity management |
Elevate your alloy production with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored systems like Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, and Rotary Furnaces, as well as CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs, helping you achieve superior alloy uniformity and performance. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your high-performance alloy development!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does the Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) process work? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Control
- Why is a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace essential? Unlock Purity for Aerospace and Semiconductors
- How has vacuum smelting impacted the development of superalloys? Unlock Higher Strength and Purity
- What is vacuum induction melting technology and why is it important? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- What are the common applications of Vacuum Induction Melting? Essential for High-Performance Metals and Alloys



















