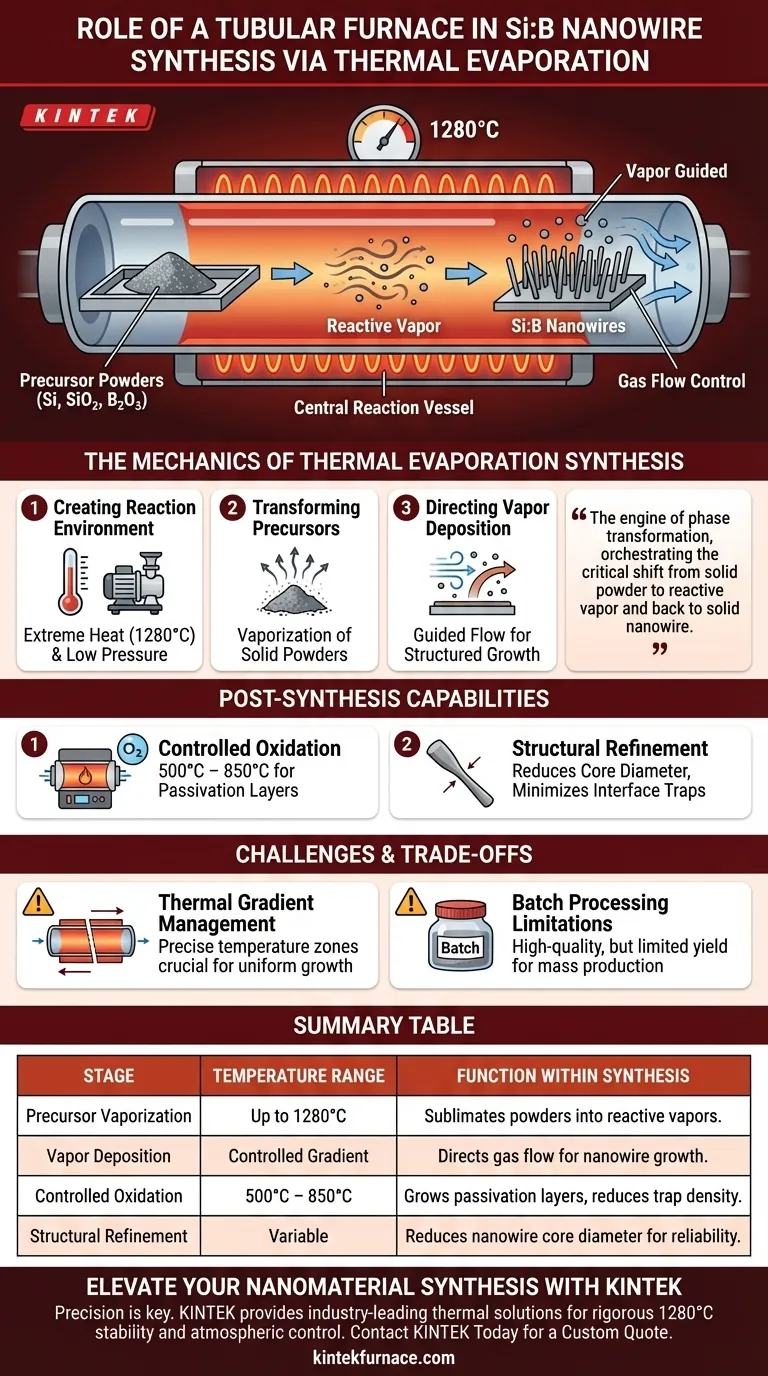
A tubular furnace serves as the central reaction vessel necessary for the synthesis of boron-doped silicon (Si:B) nanowires via thermal evaporation. It provides a precisely controlled high-temperature environment—typically reaching 1280°C—which allows solid precursors like silicon, silicon dioxide, and boron trioxide to vaporize and react under low-pressure conditions. Combined with gas flow control systems, the furnace directs the deposition of this vapor, effectively transforming raw powders into structured solid-state nanowires.
The tubular furnace acts as the engine of phase transformation, orchestrating the critical shift from solid powder to reactive vapor and back to solid nanowire. Its primary value lies in maintaining the rigorous thermal and atmospheric stability required to sustain chemical vapor reactions.

The Mechanics of Thermal Evaporation Synthesis
Creating the Reaction Environment
The synthesis of Si:B nanowires requires extreme thermal energy. The tubular furnace acts as a thermal chamber capable of sustaining temperatures around 1280°C.
This high heat is essential to initiate the chemical vapor reactions of the source materials. Additionally, the furnace operates under low-pressure conditions to facilitate the evaporation process.
Transforming Precursor Materials
The process begins with solid precursors in powder form. Specifically, silicon, silicon dioxide, and boron trioxide powders are placed within the furnace.
As the furnace heats these powders, they undergo vaporization. This controlled sublimation creates the reactant gases needed for nanowire growth.
Directing Vapor Deposition
Simply creating vapor is not enough; it must be transported effectively. The tubular furnace works in tandem with gas flow control systems.
These systems guide the vaporized material through the tube. This directed flow ensures the vapor deposits correctly, enabling the growth of the nanowires on the desired substrate.
Post-Synthesis Capabilities
Controlled Oxidation
While the primary reference focuses on high-temperature synthesis, the tubular furnace is also versatile enough for lower-temperature post-processing.
Operating between 500°C and 850°C, the furnace can act as an oxidation chamber. By regulating the oxygen atmosphere, it facilitates the growth of a sacrificial oxide or passivation layer on the nanowires.
Structural Refinement
This secondary heat treatment is critical for refining the physical properties of the nanowire. It allows researchers to reduce the physical diameter of the nanowire core.
Furthermore, this process minimizes interface trap density. This improvement is essential for enhancing the reliability of devices built using these nanowires.
Understanding the Challenges and Trade-offs
Thermal Gradient Management
A common pitfall in using tubular furnaces is the management of thermal zones.
If the temperature gradient along the tube is not precise, the vaporization and deposition zones may become misaligned. This can lead to uneven nanowire growth or incomplete reactions.
Batch Processing Limitations
Tubular furnaces are generally designed for batch processing rather than continuous flow manufacturing.
While they offer excellent control for research and high-quality synthesis, the yield is limited by the physical size of the tube. This makes scaling up for mass production a significant logistical challenge.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the utility of a tubular furnace for Si:B nanowire projects, align your equipment settings with your specific phase of development:
- If your primary focus is Synthesis: Prioritize a furnace capable of reaching and maintaining 1280°C with high vacuum integrity to ensure efficient precursor vaporization.
- If your primary focus is Device Reliability: Utilize the furnace's low-temperature range (500–850°C) to grow high-quality passivation layers that reduce interface trap density.
Success relies on using the furnace not just as a heat source, but as a precise instrument for atmospheric and thermal flow control.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Temperature Range | Function within Synthesis |
|---|---|---|
| Precursor Vaporization | Up to 1280°C | Sublimates Si, SiO2, and B2O3 powders into reactive vapors. |
| Vapor Deposition | Controlled Gradient | Directs gas flow for structured nanowire growth on substrates. |
| Controlled Oxidation | 500°C – 850°C | Grows passivation layers to reduce interface trap density. |
| Structural Refinement | Variable | Reduces nanowire core diameter for enhanced device reliability. |
Elevate Your Nanomaterial Synthesis with KINTEK
Precision is the difference between success and failure in Si:B nanowire growth. KINTEK provides industry-leading thermal solutions, including Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, specifically engineered to maintain the rigorous 1280°C stability and atmospheric control your research demands.
Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, our high-temp furnaces are fully customizable to meet your unique synthesis and post-processing requirements. Partner with us to achieve unmatched material purity and structural integrity.
Contact KINTEK Today for a Custom Quote
Visual Guide
References
- Feng Yang, Shihua Zhao. Preparation and photoelectric properties of Si:B nanowires with thermal evaporation method. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0316576
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How is heat transferred to the material inside a tube furnace? Master the 3-Stage Process for Precise Thermal Control
- What is the primary function of a tube furnace during Ce-NiCoP phosphorization? Achieve Precise Catalyst Synthesis
- How does a drop tube furnace compare to a horizontal tube furnace? Choose the Right Furnace for Your Process
- What role do furnace chamber working conditions play in selecting a vertical tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Process Success
- What role does a three-zone tube furnace play in converting 6FDA-TFDB-x precursors? Precision CMS Membrane Carbonization
- What are the technical specifications of a Drop Tube Furnace? Optimize Your High-Temperature Conversion Experiments
- Why is a Quartz Tube Furnace with Gas Flow Control Required for Iodine Doping? Precision Single-Atom Catalyst Synthesis
- What role does a high-temperature tube furnace play in the preparation of cellulose-based carbon nanofibers?



















