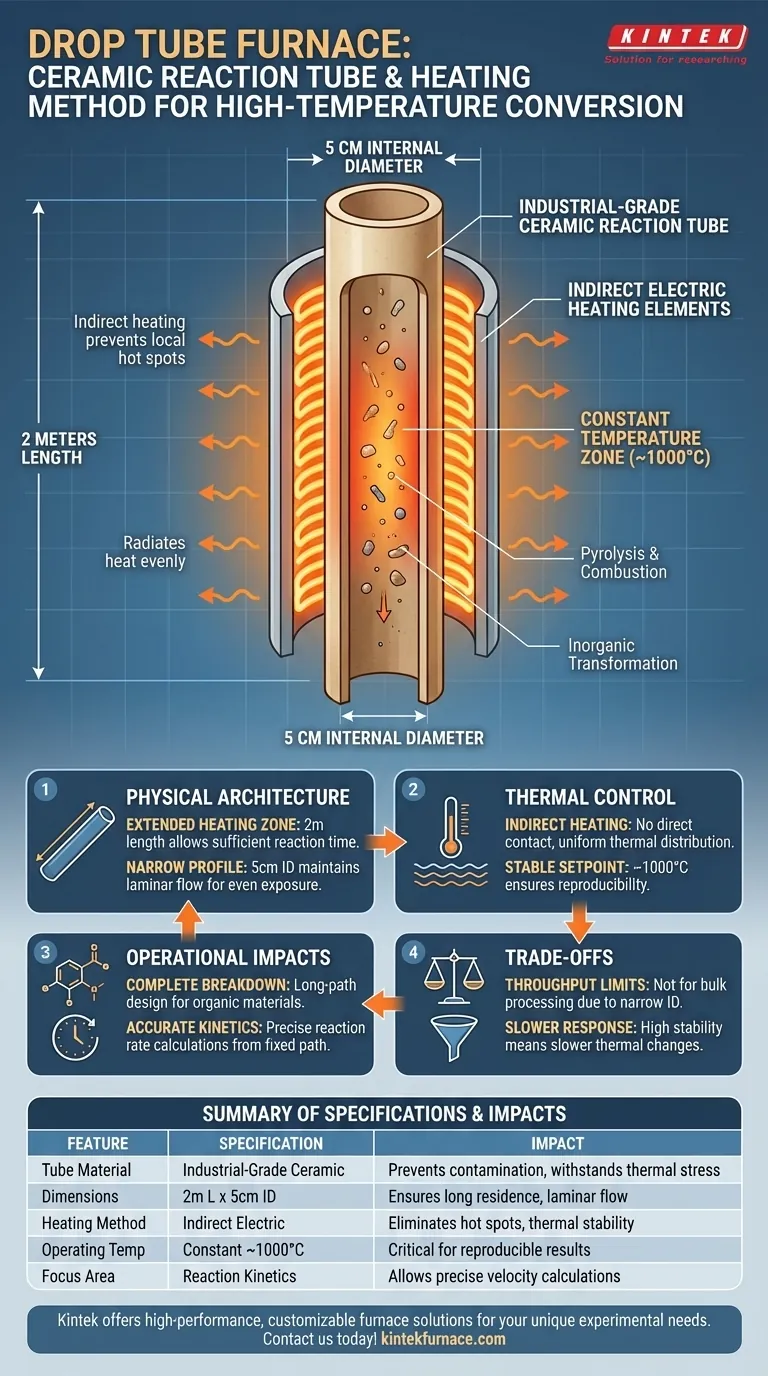
The technical architecture of a Drop Tube Furnace for high-temperature conversion relies on an industrial-grade ceramic reaction tube typically measuring 2 meters in length with a 5-centimeter internal diameter. This system utilizes indirect electric heating to maintain a constant temperature of approximately 1000°C, creating a stable, long-path environment essential for precise pyrolysis and combustion experiments.
The specific combination of a high-aspect-ratio ceramic tube and indirect heating provides a thermally uniform zone. This design is critical for ensuring sufficient residence time and stability, allowing for accurate observation of reaction kinetics and inorganic transformations.

Physical Architecture of the Reaction Zone
Tube Dimensions and Geometry
The core of the furnace is a 2-meter long ceramic tube. This significant length creates an extended "heating zone," which allows materials sufficient time to react as they travel through the system.
The tube features a relatively narrow 5-centimeter internal diameter. This slender profile helps maintain laminar flow and ensures that the material is evenly exposed to the heat source from all sides.
Material Composition
The reaction tube is constructed from industrial-grade ceramic. This material is selected for its ability to withstand extreme thermal stress without deforming or chemically interacting with the sample.
Ceramics also offer excellent thermal insulation properties, helping to contain the heat within the reaction zone and improve energy efficiency.
Thermal Control and Heating Methodology
Indirect Electric Heating
The furnace employs indirect electric heating rather than direct flame or contact heating. This means the heating elements surround the ceramic tube, radiating heat inward.
This method prevents local hot spots on the sample. It ensures the thermal energy is distributed evenly across the entire 5-centimeter cross-section of the tube.
Maintaining Constant Temperature
The system is designed to hold a stable setpoint, typically around 1000°C.
Maintaining this constant temperature is vital for reproducibility. It eliminates thermal fluctuations that could otherwise skew data regarding reaction rates or material composition changes.
Operational Impacts on Material Conversion
Facilitating Pyrolysis and Combustion
The stable 1000°C environment is optimized for pyrolysis and combustion. The long-path design ensures that even complex organic materials have time to break down completely before exiting the heating zone.
Enabling Inorganic Transformation
The high temperature and controlled residence time allow for complete inorganic transformation.
Researchers rely on this consistency to study how mineral components change phases or structure during the heating process.
Accurate Reaction Kinetics
Because the temperature is constant and the path length is fixed, researchers can precisely calculate reaction rates.
This allows for the isolation of specific variables, ensuring that observed changes are due to material properties and not equipment instability.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Throughput Limitations
The 5-centimeter internal diameter restricts the physical size of the sample.
While excellent for uniform heating, this geometry is not suitable for processing bulk materials or large batches simultaneously.
Thermal Response Time
Indirect heating through a thick ceramic tube provides high stability, but it often results in a slower thermal response.
Rapidly changing the temperature setpoint during an active experiment may be difficult due to the thermal mass of the ceramic assembly.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the utility of this Drop Tube Furnace configuration, align your experimental design with its physical constraints:
- If your primary focus is Reaction Kinetics: Calculate your drop velocity carefully against the 2-meter length to ensure the sample remains in the 1000°C zone for the exact required duration.
- If your primary focus is Material Purity: Rely on the ceramic construction and indirect heating to prevent contamination from combustion gases or heating element contact.
Success in high-temperature conversion relies on balancing the need for thermal stability with the physical constraints of the reaction path.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Specification | Impact on Experiment |
|---|---|---|
| Tube Material | Industrial-Grade Ceramic | Prevents contamination and withstands extreme thermal stress |
| Dimensions | 2m L x 5cm ID | Ensures long residence time and laminar flow for uniform heating |
| Heating Method | Indirect Electric | Eliminates hot spots; provides radiation-based thermal stability |
| Operating Temp | Constant ~1000°C | Critical for reproducible pyrolysis and inorganic transformations |
| Focus Area | Reaction Kinetics | Allows precise velocity calculations for fixed path lengths |
Precision is paramount in high-temperature research. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all customizable for your unique experimental needs. Whether you are studying reaction kinetics or material transformations, our lab furnaces provide the thermal stability you require. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom furnace solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Tor Sewring, Fredrik Weiland. The Influence of Oxyfuel Combustion Conditions on the Behavior of Inorganic Cooking Chemicals during Black Liquor Conversion. DOI: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.5c02613
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
People Also Ask
- What role does a single-zone tube furnace play in the synthesis of (100)-oriented MoO2 nanobelts? Precision APCVD Control
- How does a tube furnace work? Master Precise Heat and Atmosphere Control
- At what pressures can gases be introduced into the 3-Zone tube furnace? Optimize Your Thermal Process Control
- How does a tube furnace contribute to the synthesis of electrocatalysts from hydrochar? Precision Thermal Engineering
- What role does a high-vacuum tube furnace play in helium bubble studies? Master Thermal Activation & Material Purity
- What is a 70mm tube furnace and what is its primary use? Unlock Precision in Material Processing
- What are the key features of a split tube furnace? Unlock Superior Access and Control for Complex Samples
- What are the pros and cons of vertical tube furnaces? Precision vs. Capacity for Your Lab



















