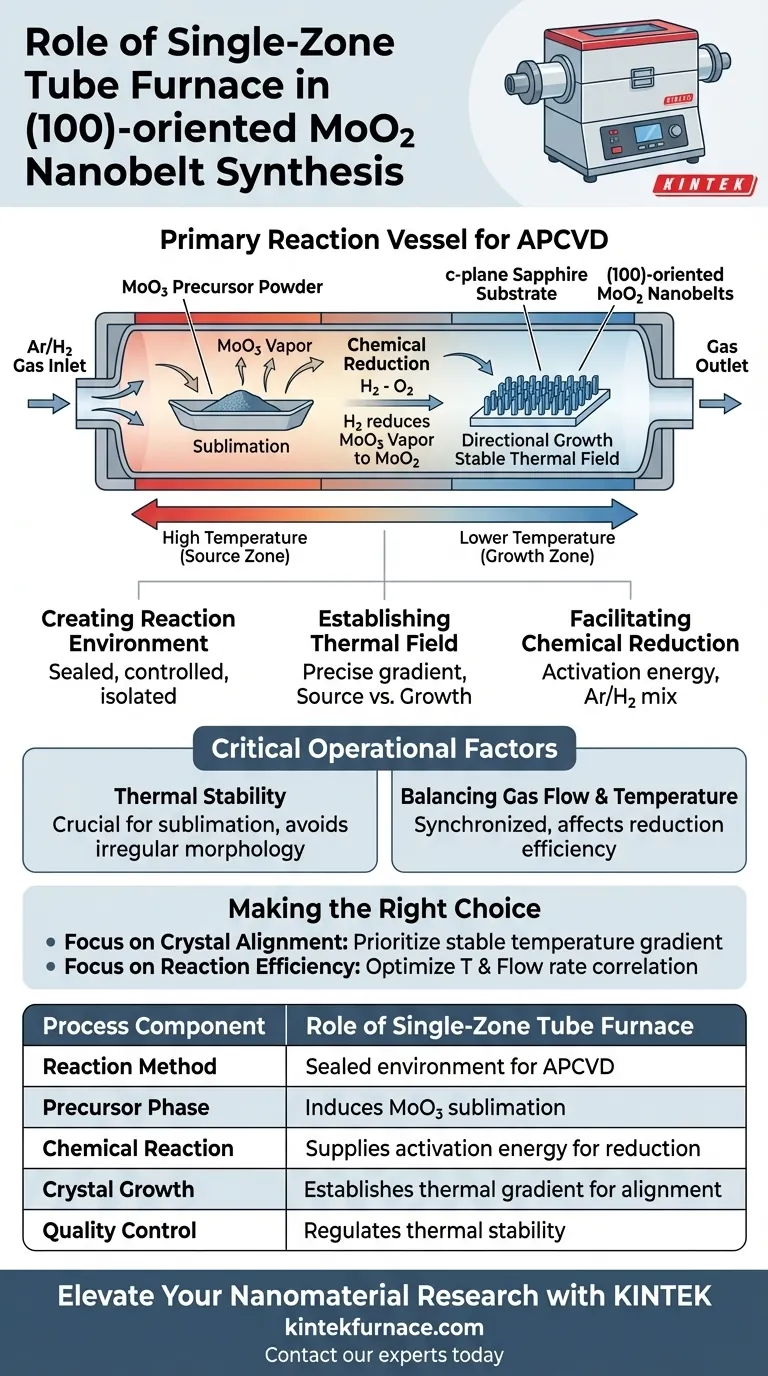
The single-zone tube furnace functions as the primary reaction vessel for the synthesis of (100)-oriented MoO2 nanobelts via Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Vapor Deposition (APCVD). It acts as the central control unit that initiates the sublimation of the Molybdenum Trioxide (MoO3) precursor and maintains the specific thermal environment required for the reduction and subsequent directional growth of the nanostructures.
By integrating precise temperature gradient control with regulated gas flow, the furnace creates the critical thermodynamic conditions necessary to transform raw precursor powder into highly aligned nanobelts on a substrate.
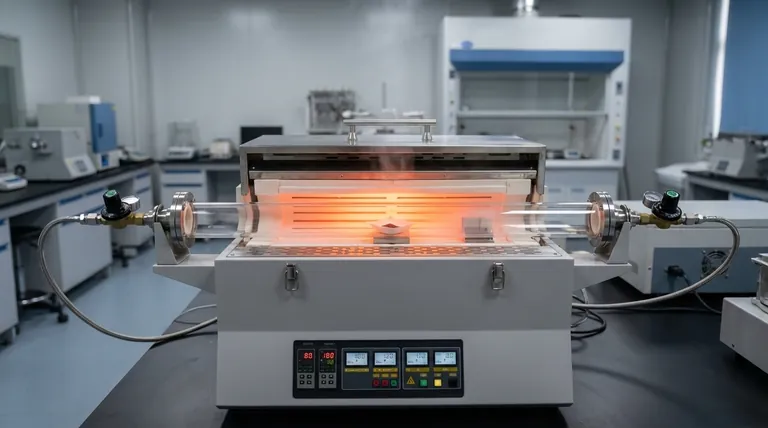

The Mechanism of APCVD Synthesis
Creating the Reaction Environment
The tube furnace provides a sealed, controlled environment essential for Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Vapor Deposition (APCVD).
Unlike open-air heating, this setup allows for the precise management of internal pressure and atmospheric composition.
It isolates the reactants from external contaminants, ensuring high-purity synthesis.
Sublimation of Precursor Material
The first critical role of the furnace is to induce a phase change in the source material.
By reaching specific high temperatures, the furnace causes the MoO3 precursor powder to sublime, turning it from a solid directly into a vapor.
This vapor generation is the starting point for the transport of molybdenum species to the growth zone.
Controlling Thermal and Chemical Dynamics
Establishing the Thermal Field
Success in this synthesis relies on more than just high heat; it requires a stable thermal field.
The single-zone furnace establishes a precise temperature gradient along the tube.
This gradient controls where the precursor vapor travels and where it eventually deposits, distinguishing the source zone from the growth zone.
Facilitating Chemical Reduction
The furnace maintains the necessary activation energy to drive the chemical reduction of the precursor.
A specific mixture of Argon (Ar) and Hydrogen (H2) gas flows through the heated tube.
The thermal energy provided by the furnace enables the hydrogen to reduce the vaporized MoO3, converting it chemically into MoO2.
Enabling Directional Growth
The final role of the thermal environment is to facilitate crystallization on the c-plane sapphire substrates.
The stable heat allows the MoO2 molecules to settle and align according to the substrate's lattice structure.
This controlled deposition is what yields the specific (100)-orientation of the nanobelts.
Critical Operational Factors
The Necessity of Thermal Stability
The stability of the thermal field is the most significant operational factor in this process.
Fluctuations in the furnace temperature can disrupt the sublimation rate of the MoO3.
Inconsistent temperatures may also alter the deposition kinetics, leading to poor alignment or irregular nanobelt morphology.
Balancing Gas Flow and Temperature
The furnace temperature must be perfectly synchronized with the Ar/H2 flow rate.
If the temperature is too low, the reduction reaction may not occur efficiently despite the presence of hydrogen.
Conversely, excessive heat combined with high flow rates could strip the precursor too quickly, preventing orderly growth.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the quality of your MoO2 nanobelts, you must tune the furnace parameters to your specific objectives.
- If your primary focus is Crystal Alignment: Prioritize the stability of the temperature gradient to ensure consistent deposition on the c-plane sapphire.
- If your primary focus is Reaction Efficiency: Optimize the correlation between the furnace temperature and the flow rate of the Ar/H2 mixture to maximize precursor conversion.
Precision in thermal control is the defining factor in transitioning from random deposition to structured, high-quality nanobelt growth.
Summary Table:
| Process Component | Role of Single-Zone Tube Furnace |
|---|---|
| Reaction Method | Provides a sealed environment for Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Vapor Deposition (APCVD). |
| Precursor Phase | Induces sublimation of MoO3 powder into vapor via high-temperature control. |
| Chemical Reaction | Supplies activation energy for H2 to reduce MoO3 vapor into MoO2. |
| Crystal Growth | Establishes the stable thermal gradient needed for (100) alignment on sapphire. |
| Quality Control | Regulates thermal stability to prevent irregular nanobelt morphology. |
Elevate Your Nanomaterial Research with KINTEK
Achieving the perfect (100)-oriented MoO2 nanobelt requires absolute precision in thermal gradients and gas dynamics. KINTEK provides the high-performance laboratory solutions necessary for sophisticated APCVD processes.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems. Our furnaces are fully customizable to meet the unique needs of your research, ensuring stable thermal fields and reliable chemical reduction for high-purity synthesis.
Ready to optimize your synthesis results? Contact our experts today to find the ideal furnace system for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
References
- Haojian Lin, Wenjing Zhang. Facet‐Engineered (100)‐Oriented MoO <sub>2</sub> Nanoribbons for Broadband Self‐Powered Photodetection. DOI: 10.1002/advs.202510753
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What critical role does a laboratory tube furnace play in pBN-CTF synthesis? Master Molecular Engineering
- What critical conditions does a tube furnace provide for Cu-Fe-NC-3 pyrolysis? Achieve Precision Catalyst Synthesis
- What are the common features of the heating chamber in a horizontal tube furnace? Achieve Precise Thermal Control for Your Lab
- What are the advantages of combining an online mass spectrometer with a fixed-bed reactor? Boost Kinetic Precision
- How does the working temperature range affect the choice of a vertical tube furnace? Optimize Your Lab's Performance and Budget
- How does a tubular furnace contribute to the conversion of Co-Fe-ZIF precursors into Co-Fe-NC catalysts?
- What are the technical functions of an industrial tube furnace for ZIF-8 carbonization? Master Precise Pyrolysis
- What are the key considerations for placing a multi zone tube furnace? Ensure Safety, Accuracy, and Longevity



















