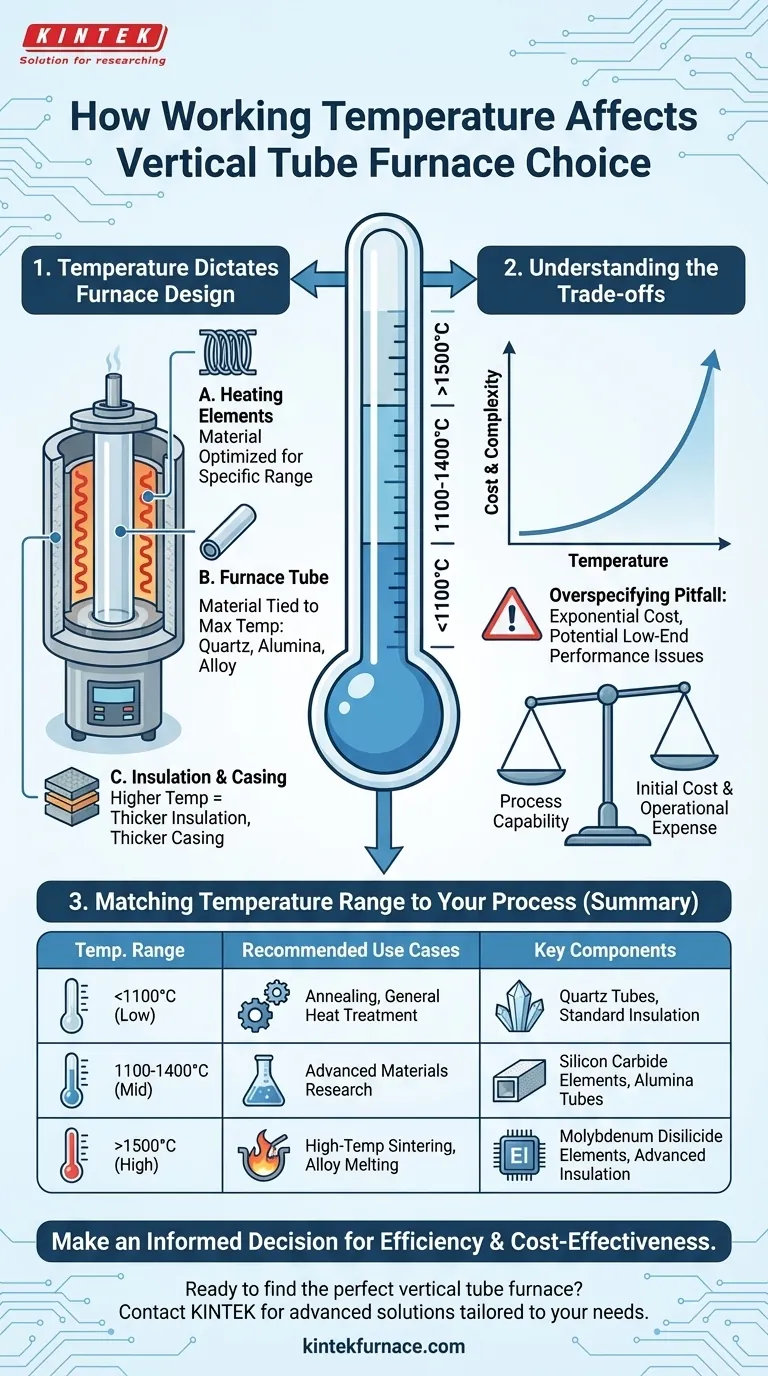
In short, the working temperature range is the single most important factor when choosing a vertical tube furnace. It directly dictates the furnace’s construction materials, its structural design, and its price. Selecting a furnace rated for a specific temperature range, such as 30-1100°C or 1400-1700°C, is not just about hitting a maximum number; it determines the entire system you are investing in.
Your required processing temperature dictates the fundamental engineering of the furnace. Choosing the right range is a critical balance between ensuring process capability and managing significant differences in initial cost and long-term operational expense.
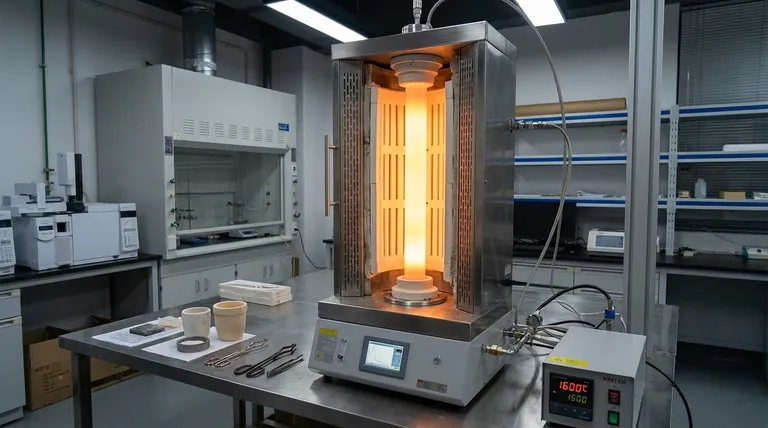

Why Temperature Dictates Furnace Design
A vertical tube furnace is a precision instrument where every component is chosen to survive and perform within a specific heat environment. The maximum rated temperature has a cascading effect on its entire design.
The Impact on Heating Elements
The core of the furnace, the heating elements, are made from different materials designed for specific temperature tiers. An element built for 1200°C will fail rapidly at 1600°C.
Conversely, elements designed for very high temperatures may not perform as efficiently or stably at much lower setpoints. This is why furnaces are optimized for distinct ranges.
The Demands on the Furnace Tube
The tube holding your sample must withstand the heat and any chemical reactions. The material choice is directly tied to the maximum operating temperature.
- Quartz tubes are common but are typically limited to about 1100°C. They offer excellent thermal shock resistance.
- High-purity alumina (ceramic) tubes are required for higher temperatures, often up to 1700°C or more.
- Metal alloy tubes are used for specialized applications, but their temperature limits vary widely based on the specific alloy.
The Requirements for Insulation and Casing
Higher temperatures generate more thermal energy that must be contained.
A 1700°C furnace requires significantly thicker, higher-grade ceramic fiber insulation than a 1200°C model to operate efficiently and keep the outer casing cool to the touch. This adds to the furnace's overall size, weight, and cost.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace isn't as simple as buying the one with the highest temperature rating. This approach often leads to unnecessary expense and potential performance issues.
The Pitfall of Overspecifying Temperature
The cost of a tube furnace does not increase linearly with temperature; it increases exponentially. A 1700°C furnace can be several times more expensive than a 1200°C model.
This is due to the exotic materials required for high-temperature heating elements (e.g., Molybdenum Disilicide), advanced insulation, and more sophisticated power control systems.
Furthermore, a furnace designed for very high heat may have poorer temperature uniformity and control at the low end of its range. You pay a premium for a capability you don't use, and may even sacrifice performance for your actual process.
Matching Temperature Range to Your Process
The correct approach is to identify the actual working temperature your materials require.
- Annealing or general heat treatment often occurs below 1100°C, making a lower-range furnace the most economical and efficient choice.
- Sintering advanced ceramics or melting certain alloys demands higher temperatures, necessitating an investment in a 1400°C to 1700°C furnace.
- Quenching tests benefit from the vertical furnace design, but the temperature must align with the material's specific heat treatment profile.
Safety and Longevity
Higher operating temperatures place greater stress on all components, from the thermocouple that measures heat to the safety circuits that prevent overheating.
Furnaces rated for higher temperatures must have more robust safety features, such as automatic power cut-offs for thermocouple failure or overheating. The cost and complexity of these systems are factored into the higher price.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the correct vertical tube furnace, align its maximum temperature with your most demanding planned process, but avoid significant over-specification.
- If your primary focus is on processes below 1100°C (e.g., annealing, standard heat treatments): A furnace with a maximum temperature of 1200°C provides the best combination of value, efficiency, and component longevity.
- If your primary focus is advanced materials research requiring up to 1400°C: Select a mid-range furnace built with Silicon Carbide (SiC) elements, as this tier meets many common research needs without the highest costs.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature sintering or processing above 1500°C: You must invest in a high-temperature model, accepting the associated costs for specialized components and robust safety systems.
An informed decision based on your specific temperature needs ensures you acquire a tool that is both capable and cost-effective for your work.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Recommended Use Cases | Key Components |
|---|---|---|
| Up to 1100°C | Annealing, general heat treatment | Quartz tubes, standard insulation |
| 1100°C - 1400°C | Advanced materials research | Silicon Carbide elements, alumina tubes |
| Above 1500°C | High-temperature sintering, alloy melting | Molybdenum Disilicide elements, advanced insulation |
Ready to find the perfect vertical tube furnace for your lab? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all with strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your research efficiency and cost-effectiveness!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing



















