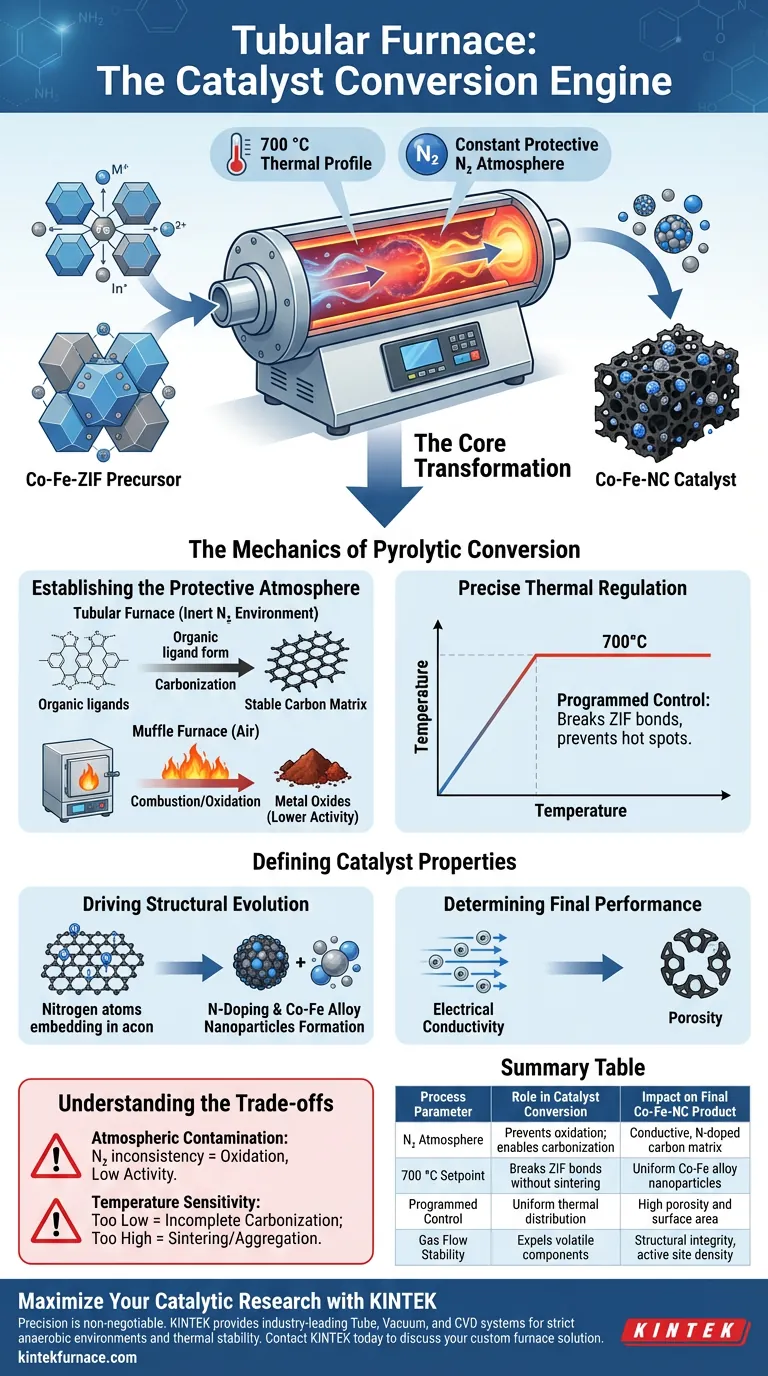
The tubular furnace serves as the precise reaction vessel required to convert Co-Fe-ZIF precursors into functional catalysts. It facilitates a single-stage pyrolysis process by maintaining a strict 700 °C thermal profile under a constant, protective nitrogen atmosphere. This controlled environment is the primary driver for transforming the metal-organic framework into a conductive, porous Co-Fe-NC catalyst containing uniform Co-Fe alloy nanoparticles.
The Core Transformation The tubular furnace does more than simply heat the material; it creates a strictly anaerobic environment that dictates the chemical evolution of the precursor. By preventing oxidation, the furnace forces the precursor to undergo carbonization and nitrogen doping simultaneously, determining the final catalyst's electrical conductivity and structural integrity.
The Mechanics of Pyrolytic Conversion
Establishing the Protective Atmosphere
The most critical function of the tubular furnace is the maintenance of a constant nitrogen atmosphere.
Unlike muffle furnaces which often operate in air, the tubular furnace creates an inert environment. This prevents the combustion of the organic ligands in the ZIF (Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework) precursor.
Instead of burning, the organic material undergoes carbonization, a process where volatile components are expelled, leaving behind a stable carbon matrix.
Precise Thermal Regulation
The conversion process relies on programmed temperature control to reach and maintain a steady state of 700 °C.
This specific thermal energy is required to break down the chemical bonds of the ZIF precursor without destroying the desired micro-structure.
The stability of this temperature ensures the reaction proceeds uniformly throughout the batch, preventing hot spots that could lead to inconsistent catalytic properties.
Defining Catalyst Properties
Driving Structural Evolution
Inside the furnace, the heat treatment drives the physical transformation of the material.
The process promotes nitrogen doping, effectively embedding nitrogen atoms into the newly formed carbon support. This is essential for the catalyst's chemical activity.
Simultaneously, the furnace environment facilitates the reduction and crystallization of metal ions, resulting in the uniform formation of Co-Fe alloy nanoparticles.
Determining Final Performance
The parameters set within the tubular furnace are decisive in establishing the physical characteristics of the final product.
Specifically, the treatment determines the electrical conductivity of the carbon support, which is vital for electron transfer during catalytic reactions.
It also governs the porosity of the material. Proper heating rates and gas flow ensure the pore structure remains open, maximizing the surface area available for chemical reactions.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Risk of Atmospheric Contamination
The efficacy of the tubular furnace relies entirely on the integrity of the inert atmosphere.
If the nitrogen flow is inconsistent or if oxygen leaks into the tube, the precursor will oxidize rather than carbonize. This destroys the desired Co-Fe-NC structure and results in metal oxides with significantly lower catalytic activity.
Temperature Sensitivity
While 700 °C is the target for this specific process, deviations can drastically alter the outcome.
Temperatures that are too low may result in incomplete carbonization and poor conductivity. Conversely, excessive temperatures can cause the Co-Fe nanoparticles to aggregate (sinter), reducing the active surface area and overall performance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the quality of your Co-Fe-NC catalyst, focus on the specific parameters of your furnace operation:
- If your primary focus is Electrical Conductivity: Prioritize the precision of the programmed temperature control to ensure the graphitization degree of the carbon support is fully realized at 700 °C.
- If your primary focus is Active Site Uniformity: Ensure the nitrogen gas flow is constant and stable to facilitate the even dispersion of Co-Fe alloy nanoparticles and prevent local oxidation.
The tubular furnace is not just a heat source; it is the instrument that orchestrates the simultaneous carbonization and metal alloying required for high-performance catalysis.
Summary Table:
| Process Parameter | Role in Catalyst Conversion | Impact on Final Co-Fe-NC Product |
|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen Atmosphere | Prevents oxidation; enables carbonization | Creates conductive, nitrogen-doped carbon matrix |
| 700 °C Setpoint | Breaks ZIF bonds without sintering | Ensures uniform Co-Fe alloy nanoparticle formation |
| Programmed Control | Uniform thermal distribution | Maintains high porosity and surface area |
| Gas Flow Stability | Expels volatile organic components | Determines structural integrity and active site density |
Maximize Your Catalytic Research with KINTEK
Precision is non-negotiable when converting complex precursors into high-performance catalysts. KINTEK provides industry-leading Tube, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to maintain the strict anaerobic environments and thermal stability your synthesis requires.
Whether you need customized gas flow controls for nitrogen doping or high-accuracy heating for nanoparticle crystallization, our expert R&D and manufacturing teams are ready to build a furnace tailored to your unique lab requirements.
Ready to elevate your material science? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom furnace solution.
Visual Guide
References
- Dhayanantha Prabu Jaihindh, Chun-Yi Chen. Bimetallic and Magnetic CoFe-/Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Nanocomposites as Catalysts for the Degradation of Rhodamine B. DOI: 10.1021/acsanm.5c02849
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does an industrial-grade high-temperature tube furnace play in the two-step pyrolysis of Fe–Mn–N–C? Optimize Synthesis
- What is the technical significance of a horizontal tube furnace with a sliding rail for NiOx annealing? Enhance Control
- Why might someone choose a tube furnace over a chamber furnace? Unlock Precision and Purity for Small Samples
- What specific process conditions does a laboratory tube furnace provide? Optimize Biomass Carbonization Success
- What is the function of a tubular furnace in the sulfurization of Cu2SnS3? Master Semiconductor Phase Transformation
- What precautions should be taken when using a 70mm tube furnace? Ensure Safety and Precision in High-Temp Experiments
- How does a laboratory horizontal tube furnace establish a controlled environment? Precision Corrosion Testing Guide
- What types of containers are used in vacuum tube furnaces? Choose Quartz or Corundum for Optimal Performance



















