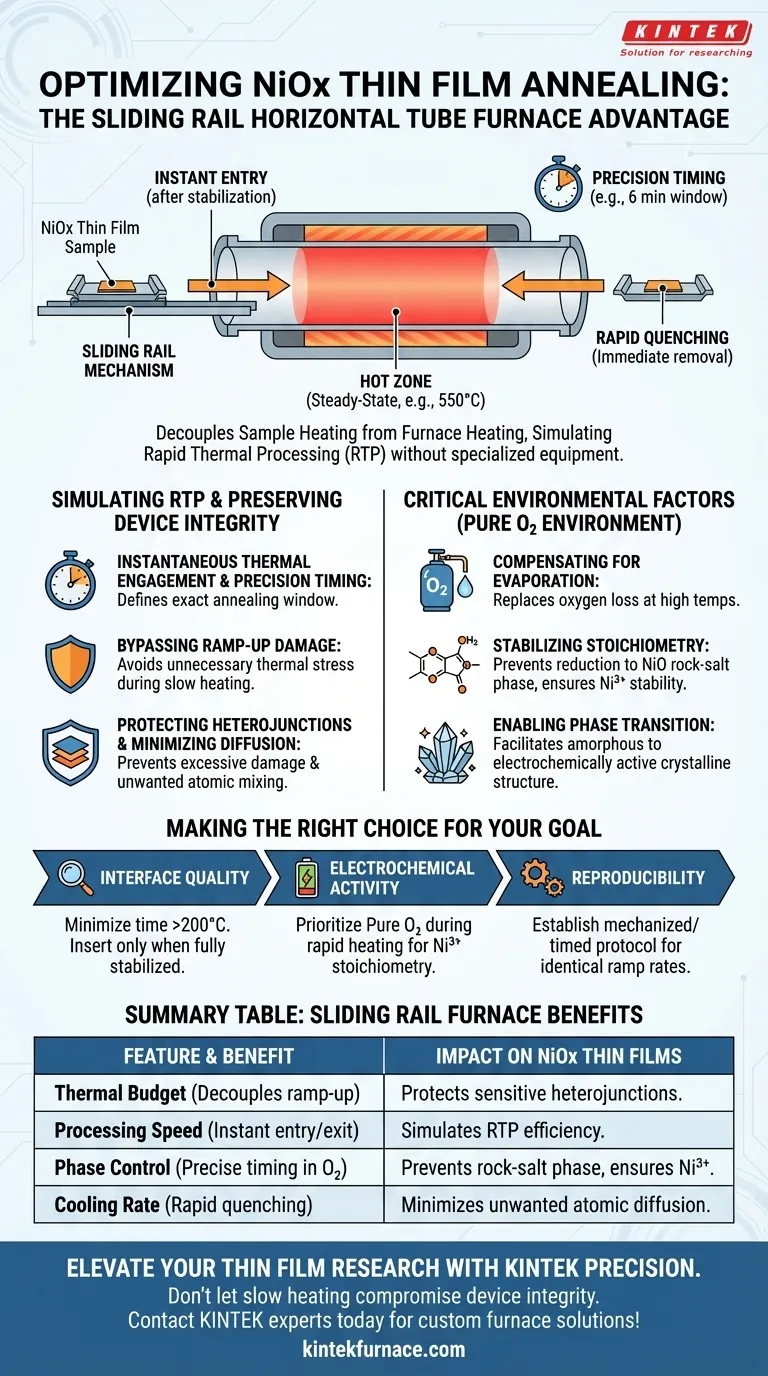
The technical significance of a horizontal tube furnace equipped with a sliding rail lies in its ability to decouple the heating of the sample from the heating of the furnace itself. By physically moving the sample into the hot zone only after the furnace maximizes temperature stability, and removing it immediately upon completion, this system effectively simulates a Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) environment without specialized RTP equipment.
By bypassing the slow ramp-up and cool-down phases of standard annealing, the sliding rail mechanism grants precise control over thermal budget, protecting sensitive heterojunction interfaces while ensuring the necessary crystalline transition.
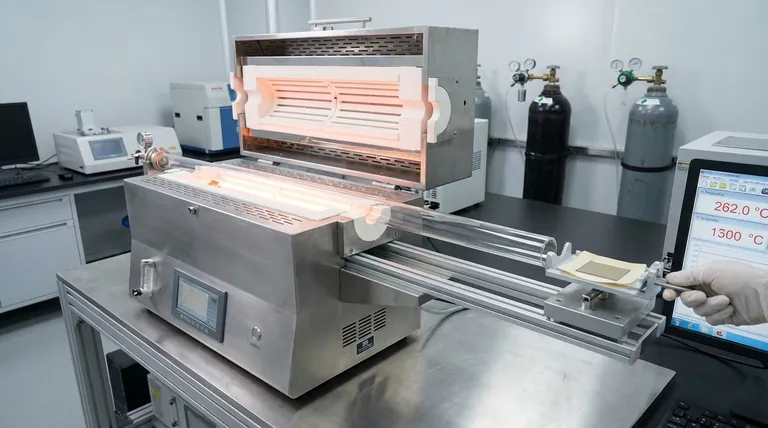

Simulating Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP)
Instantaneous Thermal Engagement
The sliding rail allows the user to introduce the NiOx thin films into the reaction zone only once the furnace has reached a steady-state temperature, such as 550 °C.
Precision Timing
This mechanism enables the definition of an exact annealing window (e.g., 6 minutes).
Rapid Quenching Capabilities
The sample can be retracted immediately after the process, eliminating the "thermal tail" associated with the slow natural cooling of a standard ceramic heater.
Preserving Device Integrity
Bypassing Ramp-Up Damage
Standard tube furnaces heat gradually; exposing the sample during this ramp-up subjects it to unnecessary thermal stress before the target processing temperature is even reached.
Protecting Heterojunctions
The primary advantage of the sliding rail is the prevention of excessive thermal damage to the heterojunction interface.
Minimizing Diffusion
Rapid insertion and removal limit the time available for unwanted atomic diffusion between layers, which often occurs during prolonged heating cycles.
Critical Environmental Factors
Compensating for Evaporation
While the rail controls the thermal profile, the furnace atmosphere plays a critical chemical role; a pure oxygen environment is required to compensate for oxygen loss caused by high-temperature evaporation.
Stabilizing Stoichiometry
The high-oxygen atmosphere prevents the reduction of Ni3+ ions into the undesirable NiO rock-salt phase.
Enabling Phase Transition
The combination of rapid thermal exposure and oxygen saturation facilitates the necessary transition of the thin film from an amorphous state to an electrochemically active crystalline structure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Mechanical Stability vs. Thermal Control
While the sliding rail offers superior thermal management, the physical movement of the sample introduces a risk of mechanical vibration.
Atmosphere Disturbances
Moving the sample along the rail can potentially disturb the gas flow dynamics within the tube.
Sample Shock
"Rapid" does not mean "instant"; the sample still undergoes significant thermal shock when moved from ambient to 550 °C.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of this setup for NiOx thin films, consider your specific processing priorities:
- If your primary focus is Interface Quality: Utilize the sliding rail to minimize the total time the sample spends above 200 °C, inserting it only when the furnace is fully stabilized at the target temperature.
- If your primary focus is Electrochemical Activity: Prioritize the maintenance of a pure oxygen environment during the rapid heating phase to ensure the correct Ni3+ stoichiometry and prevent rock-salt phase formation.
- If your primary focus is Reproducibility: Establish a mechanized or strictly timed manual protocol for the sliding action to ensure every sample experiences identical ramp rates.
The sliding rail transforms a standard furnace into a precision tool, allowing you to achieve the crystallinity of high-temperature annealing without sacrificing the integrity of the underlying layers.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Sliding Rail Furnace Benefit | Impact on NiOx Thin Films |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Budget | Decouples furnace ramp-up from sample exposure | Protects sensitive heterojunction interfaces from damage |
| Processing Speed | Instantaneous entry and exit from hot zone | Simulates Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) efficiency |
| Phase Control | Precise timing in O2-rich environments | Prevents NiO rock-salt phase; ensures Ni3+ stability |
| Cooling Rate | Rapid quenching by physical retraction | Minimizes unwanted atomic diffusion between layers |
Elevate Your Thin Film Research with KINTEK Precision
Don’t let slow heating cycles compromise your device integrity. KINTEK’s advanced horizontal tube furnaces with integrated sliding rail systems offer the precision needed to simulate RTP environments for sensitive NiOx annealing and heterojunction protection.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet your unique laboratory requirements.
Ready to optimize your thermal budget and achieve superior film stoichiometry?
Contact KINTEK experts today to discuss your custom furnace solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Roumen Nedev, N. Nedev. Effect of Deposition Temperature and Thermal Annealing on the Properties of Sputtered NiOx/Si Heterojunction Photodiodes. DOI: 10.3390/inorganics13010011
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Magnesium Extraction and Purification Condensing Tube Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a vacuum tube furnace play as a reactor during the coal gasification reaction stage?
- What is the function of a tube furnace in the synthesis of g-C3N4? Master Thermal Exfoliation for High-Surface Area
- What features contribute to the flexibility and diversity of a vertical tube furnace? Tailor Your Thermal Process
- How does a tube furnace differ from HPHT methods for Fe2B-HS? Compare Diffusion and Structural Integrity
- How does a horizontal tube furnace differ from a vertical tube furnace? Choose the Right Furnace for Your Lab
- How does a dual-temperature zone tube furnace contribute to the carbonization of biomass? Precise Material Engineering
- What accessories are typically included with a three-zone split tube furnace? Essential Tools for Safe Operation
- What role does a tube furnace play in the high-temperature heat treatment of vermiculite? Precision Control Expert



















