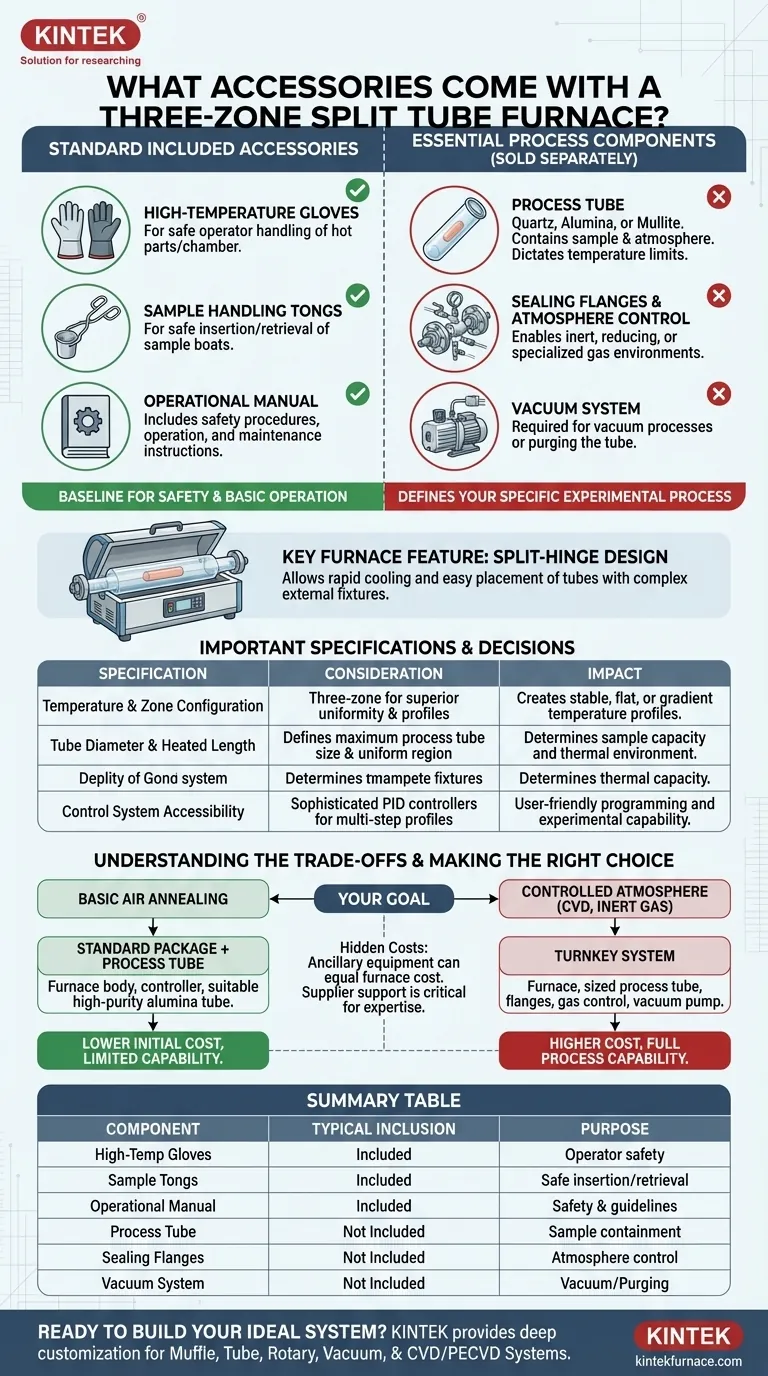
When you acquire a three-zone split tube furnace, the accessories included in the standard package are typically minimal. You can expect to receive a pair of high-temperature gloves for operator safety, a set of tongs for handling hot sample boats or crucibles, and a detailed operational manual.
The standard included accessories are for basic furnace operation and safety, not for conducting a specific thermal process. The critical components that define your experiment—such as the process tube, vacuum flanges, and gas control systems—are almost always specified and purchased separately.

Deconstructing the "Standard" Accessory Kit
The accessories that come in the box with the furnace itself are designed to provide a baseline for safe interaction with the equipment.
High-Temperature Gloves
These are an essential piece of personal protective equipment (PPE). They allow the operator to safely open the furnace chamber or handle fixtures that have been exposed to high temperatures.
Sample Handling Tongs
Often referred to as hot tongs or boat tongs, these are used to insert and retrieve sample carriers (like ceramic "boats" or crucibles) from the hot zone of the furnace tube without reaching into the chamber.
The Operational Manual
This is a critical document that outlines safety procedures, operational instructions for the temperature controller, maintenance schedules, and technical specifications.
Beyond the Box: The Components That Define Your Process
A functional experimental setup requires much more than the base furnace and its handling tools. The most important components are selected based on your specific application and are rarely included as "standard."
The Process Tube
This is the heart of your setup. The tube, typically made of quartz, alumina, or mullite, contains your sample and atmosphere. Its material dictates your maximum operating temperature and chemical compatibility. It is almost always sold separately.
Sealing Flanges and Atmosphere Control
To run a process in anything other than ambient air, you need a way to seal the process tube. Sealing flanges are complex assemblies that provide ports for gas inlet/outlet, vacuum connections, and instrumentation. These are essential for creating an inert, reducing, or specialized gas environment.
The Vacuum System
If your process requires a vacuum or you need to purge the tube before introducing a process gas, a vacuum system is mandatory. This includes a vacuum pump (roughing or turbomolecular) and the associated gauges and fittings, all of which are separate purchases.
The Split-Hinge Design
The key feature of a split tube furnace is its hinged body, which can be opened lengthwise. This design allows for rapid cooling and easy placement of process tubes that have complex external fixtures or flanges already attached.
Key Furnace Specifications to Consider
When specifying the furnace itself, you are making decisions that directly impact your experimental capability.
Temperature and Zone Configuration
A three-zone furnace provides superior temperature uniformity over a central area compared to a single-zone furnace. Each zone is controlled independently, allowing you to create a stable, flat temperature profile or a specific gradient along the tube's length.
Tube Diameter and Heated Length
The furnace's inner diameter determines the maximum outer diameter of the process tube you can use. The total heated length, and the length of each individual zone, will define the size of the uniform temperature region for your samples.
Control System Accessibility
Modern furnaces use sophisticated PID controllers that allow you to program multi-step thermal profiles. Ensure the controller is user-friendly and has the programming capability your experiments demand.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Procuring a furnace involves balancing cost, capability, and completeness. Misunderstanding this can lead to significant delays and budget overruns.
Standard Package vs. Turnkey System
A supplier's "list price" is often for the furnace body and controller only. A "turnkey system" includes the furnace, a properly sized process tube, a full vacuum flange and plumbing package, and a vacuum pump. The cost difference is substantial.
The Hidden Costs of Ancillary Equipment
Be aware that the cost of the necessary ancillary equipment—the pump, flanges, gas flow controllers, and process tubes—can easily equal or exceed the cost of the furnace itself.
The Importance of Supplier Support
When purchasing, you are not just buying hardware; you are investing in expertise. A good supplier will act as a consultant, helping you specify every component required to achieve your specific process goals. After-sales support is critical for troubleshooting and service.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure you get a fully functional system, you must communicate your end goal clearly to your supplier.
- If your primary focus is basic air annealing: You can likely begin with just the furnace and a suitable high-purity alumina process tube.
- If your primary focus is controlled atmosphere processing (e.g., CVD or inert gas): You must specify and budget for a complete system including sealing flanges, a vacuum pump, and mass flow controllers.
- If your primary focus is maximizing temperature uniformity: Pay close attention to the length of the heated zones and select a process tube with a diameter that leaves minimal air gaps inside the furnace chamber.
Ultimately, understanding the distinction between standard accessories and essential process components is the key to building a successful high-temperature processing system.
Summary Table:
| Component Type | Typical Inclusion | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| High-Temperature Gloves | Included | Operator safety for handling hot parts |
| Sample Handling Tongs | Included | Safe insertion and retrieval of samples |
| Operational Manual | Included | Safety, operation, and maintenance guidelines |
| Process Tube | Not Included | Contains sample and atmosphere; material-specific |
| Sealing Flanges | Not Included | Enables vacuum and gas control for specialized environments |
| Vacuum System | Not Included | Creates vacuum or purges tube for controlled atmospheres |
Ready to build your ideal high-temperature processing system? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, whether for basic annealing or complex controlled atmosphere processes. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's efficiency and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
People Also Ask
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating



















