At first glance, the difference between a horizontal and vertical tube furnace is simply the orientation of the heating chamber. A horizontal furnace positions samples along a horizontal axis, while a vertical furnace stacks them vertically. However, the true distinction lies in how this orientation fundamentally impacts process quality, uniformity, and suitability for specific high-precision applications.
The choice is not merely about floor space. For applications demanding the highest purity and uniformity, such as semiconductor manufacturing, the vertical furnace design offers inherent advantages in controlling temperature gradients and preventing particle contamination.

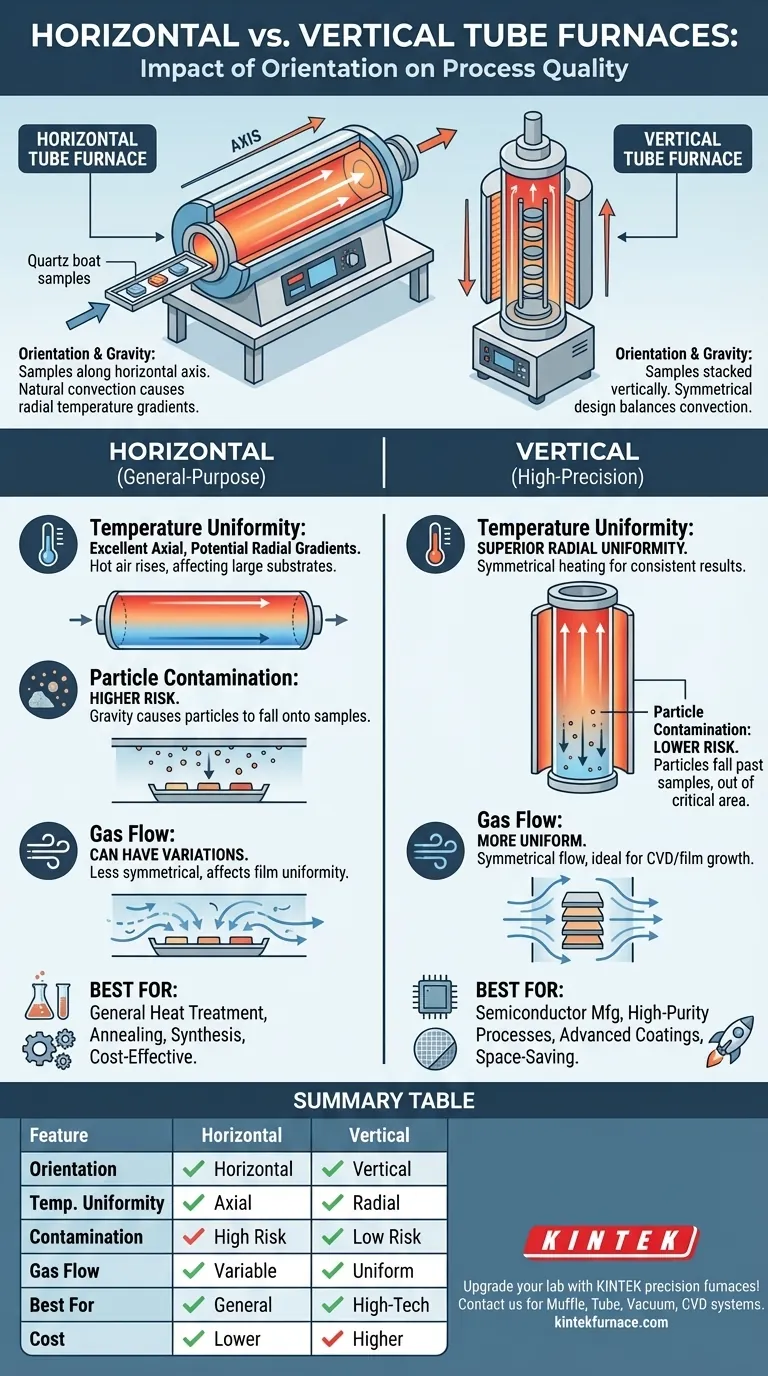
The Core Design Principle: Orientation and Gravity
The orientation of the furnace tube dictates how samples interact with heat, gas flow, and gravity. This single design choice has significant downstream effects on the final product.
The Horizontal Tube Furnace
A horizontal furnace is a classic and versatile design where the process tube lies flat. Samples are placed inside, often on a quartz "boat," and pushed into the heated center zone.
This configuration is straightforward and works well for a wide range of general-purpose applications like annealing, calcination, and basic material synthesis.
The Vertical Tube Furnace
In a vertical furnace, the process tube stands upright. Samples are loaded from the bottom or top and positioned in a vertical stack within the heated chamber.
This design was engineered to overcome the limitations of horizontal systems, especially for processes requiring exceptional control.
How Orientation Impacts Process Quality
The seemingly minor change in orientation creates major differences in performance, particularly in temperature uniformity and particle control.
Temperature Uniformity
Horizontal furnaces, especially three-zone models, can achieve excellent temperature uniformity along the length of the tube. This is known as axial uniformity.
However, natural convection can create a temperature gradient across the diameter of the tube. Hot air rises, making the top of the tube slightly hotter than the bottom, which can affect processes on large, flat substrates like silicon wafers.
Vertical furnaces provide superior radial uniformity. Because the heating elements and gas flow are symmetrical around the vertically stacked samples, convection effects are more balanced, leading to a more consistent temperature across the entire sample surface.
Particle Contamination
This is a critical differentiator. In a horizontal furnace, any particles generated during the process or flaking from the tube walls can fall directly onto the surface of the samples due to gravity.
In a vertical furnace, particles tend to fall straight down, past the samples, and out of the critical process area. This drastically reduces the risk of defects, a non-negotiable requirement in fields like microelectronics.
Gas Flow and Film Growth
The symmetrical nature of a vertical furnace also promotes more uniform gas flow. This results in more consistent film thickness during processes like chemical vapor deposition (CVD), avoiding the variations often seen in horizontal systems.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither design is universally superior; the choice depends entirely on your process requirements and budget.
When to Choose a Horizontal Furnace
A horizontal furnace is often the most practical and cost-effective choice for many applications. Its versatility makes it a workhorse in research and general materials processing.
Common uses include basic heat treatment, drying, and synthesizing materials where microscopic uniformity and ultra-low particle counts are not the primary constraints.
Why Vertical Furnaces Dominate High-Tech
Vertical furnaces are the mainstream choice in industries like semiconductor fabrication for a clear reason: they solve the inherent physics problems of the horizontal design.
They minimize gravity-induced particle defects and provide the exceptional thermal and film uniformity needed to produce reliable, high-yield integrated circuits and other advanced electronic components.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your application's sensitivity to uniformity and contamination is the deciding factor.
- If your primary focus is maximum process uniformity and minimal contamination (e.g., semiconductor fabrication or advanced coatings): A vertical furnace is the standard and necessary choice.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heat treatment or material synthesis (e.g., annealing metals or creating powders): A horizontal furnace offers excellent performance and versatility at a lower cost.
- If your primary focus is optimizing laboratory floor space: The smaller footprint of a vertical furnace can be a significant advantage.
Understanding how furnace orientation interacts with the laws of physics is the key to selecting the right tool for your work.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Horizontal Tube Furnace | Vertical Tube Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Orientation | Horizontal axis | Vertical axis |
| Temperature Uniformity | Excellent axial uniformity, potential radial gradients | Superior radial uniformity, balanced convection |
| Particle Contamination | Higher risk due to gravity | Lower risk, particles fall away from samples |
| Gas Flow | Can have variations | More uniform, ideal for CVD |
| Best For | General-purpose heat treatment, annealing, synthesis | High-purity processes, semiconductor manufacturing |
| Cost | Generally more cost-effective | Higher cost, specialized for precision |
Upgrade your laboratory with precision furnace solutions from KINTEK! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide advanced high-temperature furnaces tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, with strong deep customization capabilities to meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in semiconductor fabrication or general materials processing, KINTEK ensures superior performance and reliability. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your process quality and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety



















