A tube furnace functions as a precision reactor that provides the essential high-temperature environment and controlled atmosphere required for synthesizing graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) nanosheets. By circulating a carrier gas like nitrogen and maintaining specific thermal stages, it drives the polymerization of precursors and the subsequent exfoliation of bulk material into high-performance porous nanostructures.
Core Insight: The tube furnace enables the dual processes of thermal polycondensation and thermal exfoliation under a strictly controlled atmosphere. This precise environmental management allows for the conversion of precursors into bulk material and the subsequent breaking of interlayer forces to create ultra-thin, high-surface-area nanosheets.
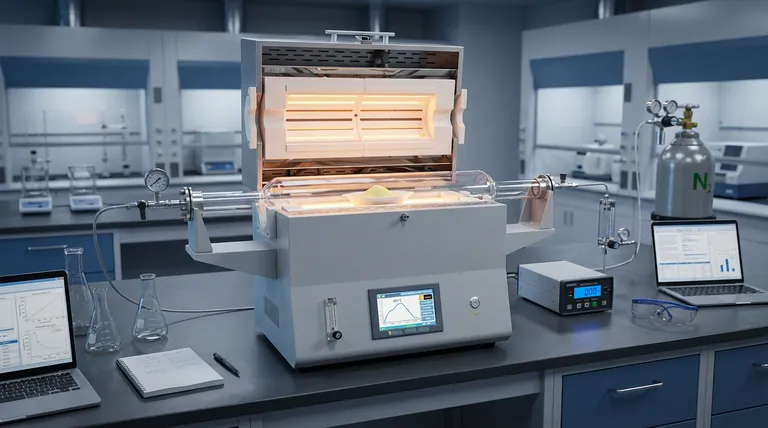

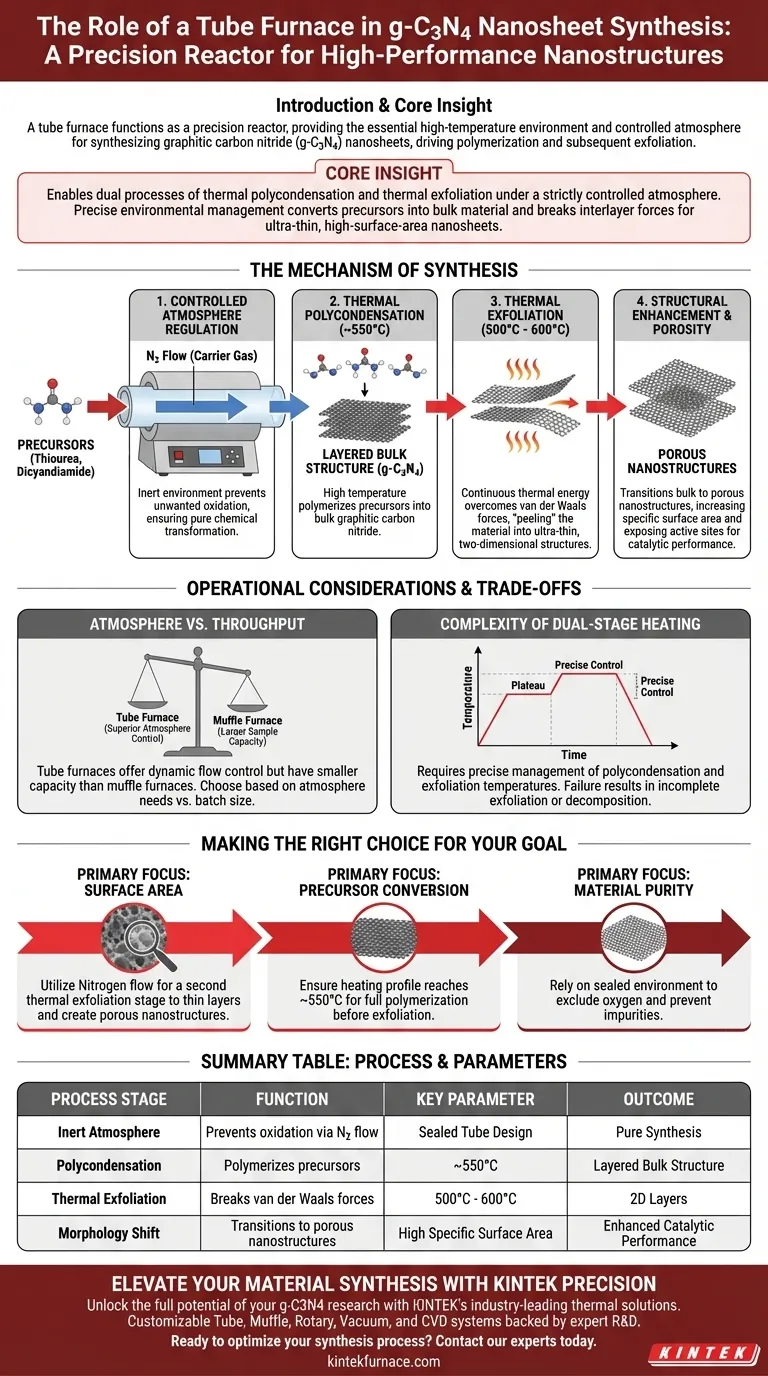
The Mechanism of Synthesis
Controlled Atmosphere Regulation
Unlike standard heating ovens, a tube furnace allows for the introduction of a specific carrier gas, typically nitrogen.
This creates an inert environment that prevents unwanted oxidation during the heating process. It ensures that the chemical transformation of precursors remains pure and consistent throughout the synthesis.
Thermal Polycondensation
The furnace facilitates the first critical stage: converting precursors such as thiourea and dicyandiamide into bulk graphitic carbon nitride.
This occurs at high temperatures, typically around 550°C. The furnace provides the sustained thermal energy required to polymerize these organic compounds into a layered bulk structure.
Thermal Exfoliation
Following the formation of bulk material, the tube furnace performs a secondary thermal treatment, often around 500°C to 600°C.
This stage is designed to overcome the van der Waals forces holding the bulk layers together. By applying continuous thermal energy, the thick layered material is "peeled" or exfoliated into ultra-thin, two-dimensional structures.
Structural Enhancement and Porosity
The ultimate function of this dual-stage heating is to dramatically alter the morphology of the material.
The process transitions the material from a bulk state to porous nanostructures. This significantly increases the specific surface area, exposing more active sites which is critical for catalytic performance.
Operational Considerations and Trade-offs
Atmosphere vs. Throughput
While tube furnaces offer superior control over the reaction atmosphere (e.g., nitrogen flow), they typically have a smaller sample capacity compared to muffle furnaces.
If your process requires massive batch sizes of bulk material, a muffle furnace might be more efficient, though it lacks the dynamic flow control of a tube furnace.
Complexity of Dual-Stage Heating
Achieving high-quality nanosheets requires precise management of two distinct temperature plateaus (polycondensation and exfoliation).
Failure to strictly control the heating rates or dwell times at 550°C and 500°C can result in incomplete exfoliation or thermal decomposition of the material, negating the benefits of the tube furnace.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the quality of your g-C3N4 nanosheets, align your equipment settings with your specific chemical precursors.
- If your primary focus is surface area: Utilize the tube furnace’s nitrogen flow to facilitate a second thermal exfoliation stage, which thins the layers and creates porous nanostructures.
- If your primary focus is precursor conversion: Ensure your heating profile reaches at least 550°C to fully polymerize thiourea or dicyandiamide into the graphitic phase before attempting exfoliation.
- If your primary focus is material purity: Rely on the tube furnace's sealed environment to exclude oxygen, preventing impurities that can occur in open-air calcination methods.
The tube furnace is not just a heater; it is the tool that physically unlocks the active surface area of your material through precise atmospheric and thermal control.
Summary Table:
| Process Stage | Function | Key Parameter |
|---|---|---|
| Inert Atmosphere | Prevents oxidation via N2 flow | Sealed Tube Design |
| Polycondensation | Polymerizes precursors (Thiourea/Dicyandiamide) | ~550°C |
| Thermal Exfoliation | Breaks van der Waals forces into 2D layers | 500°C - 600°C |
| Morphology Shift | Transitions bulk to porous nanostructures | High Specific Surface Area |
Elevate Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK Precision
Unlock the full potential of your g-C3N4 research with KINTEK’s industry-leading thermal solutions. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet your unique laboratory requirements.
Whether you need precise atmospheric control for exfoliation or high-throughput systems for precursor conversion, our furnaces deliver the uniformity and reliability your data demands.
Ready to optimize your synthesis process? Contact our technical experts today to find the perfect high-temperature furnace for your lab.
Visual Guide
References
- Jianhua Hou, Xiaozhi Wang. Grinding preparation of 2D/2D g-C3N4/BiOCl with oxygen vacancy heterostructure for improved visible-light-driven photocatalysis. DOI: 10.1007/s44246-023-00089-7
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
People Also Ask
- How does a tube resistance furnace contribute to the microstructural control of Ti–Cu alloys? Precision Heat Treatment
- How did the tube furnace originate and where is it commonly used today? Discover Its Evolution and Modern Applications
- What is the specific purpose of using a laboratory tube furnace with a wet argon environment? Optimize Siloxane Curing
- What is the purpose of using a tube furnace for a second calcination at 750°C? Mastering Biochar Activation
- What role does a high-temperature tube furnace play in flash annealing Mg/SiOx? Precision for Advanced Anode Synthesis
- Why is a silicate glass fixed-bed reactor used instead of stainless steel? Ensure Pure Methanol Decomposition Data
- Why is an inert atmosphere tube furnace required for P3-type layered oxide synthesis? Ensure Pure Crystal Structures
- How does a laboratory tube sintering furnace facilitate the synthesis of BiCuSeO? Master Precise Thermal Diffusion



















