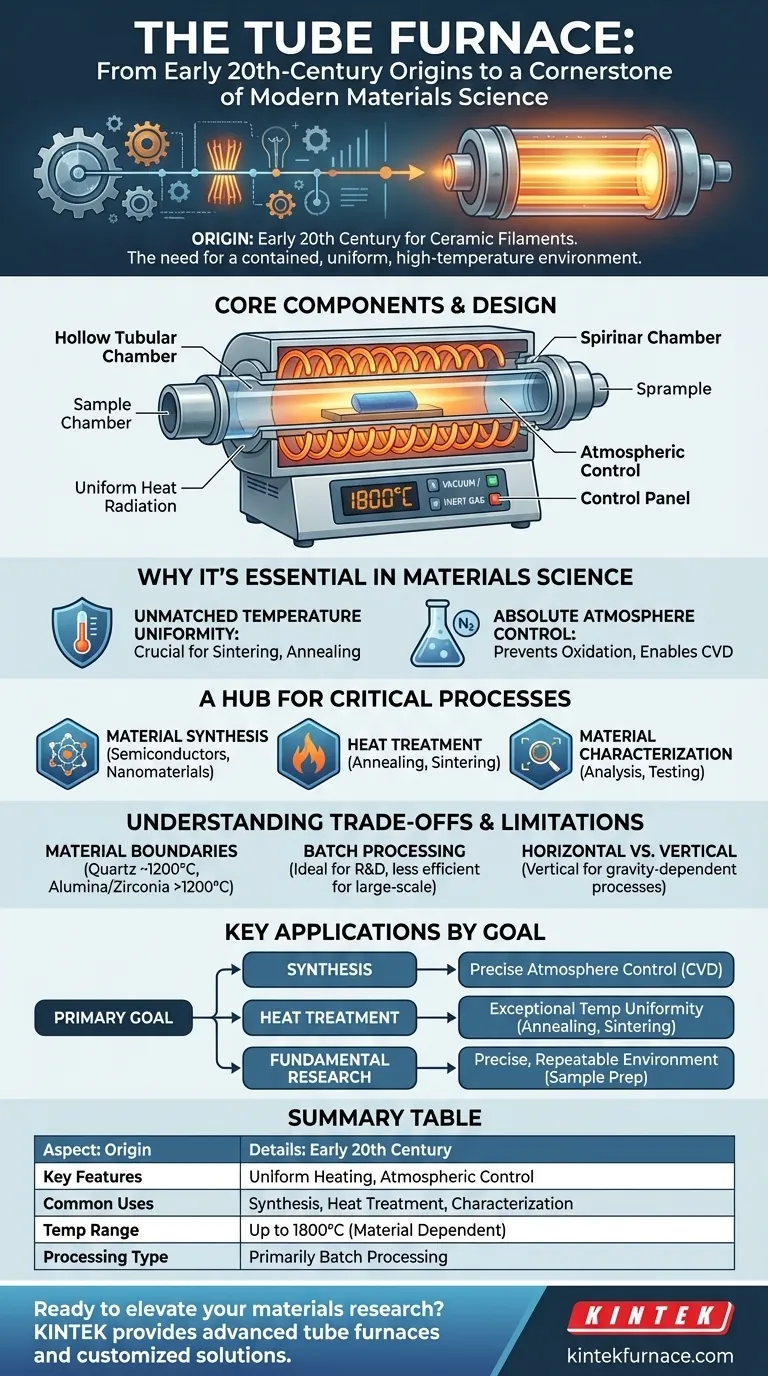
To understand the bedrock of modern materials science, one must understand its essential tools. The tube furnace originated in the early 20th century from research into fine ceramic filaments, which required a new type of cylindrical heating chamber. Today, this fundamental design is a cornerstone of high-temperature work, found everywhere from university research labs to industrial factory floors.
The true value of a tube furnace is not just its ability to get hot, but its power to create a perfectly controlled and isolated environment. This combination of uniform heat and atmospheric control is what enables the synthesis and refinement of the world's most advanced materials.

The Genesis of Precision Heating
The tube furnace wasn't invented by accident. It was born from a specific need for a contained, uniform, high-temperature environment that other heating methods of the time could not provide.
From Ceramic Filaments to a Universal Tool
Early 20th-century innovators needed a way to process fine ceramic filaments at extreme temperatures without contamination or uneven heating. The solution was a cylindrical heating chamber, the direct ancestor of the modern tube furnace. This design has proven so effective that it has remained a staple for over a century.
The Core Components
A tube furnace consists of three primary parts. A hollow tubular chamber, typically made of quartz or a durable ceramic like alumina, holds the sample. Heating elements surround this tube, and a temperature control system provides precise thermal regulation, often exceeding 1800°C.
Why the Tube Furnace is a Cornerstone of Materials Science
The tube furnace's simple design is its greatest strength. It excels at delivering two critical conditions required for advanced material processing: exceptional temperature uniformity and precise atmospheric control.
Unmatched Temperature Uniformity
The cylindrical shape ensures that heat radiates evenly from all sides toward the center. This uniform heating is crucial for processes like sintering and annealing, where even slight temperature variations can ruin a sample's structural integrity.
Absolute Atmosphere Control
Many advanced materials react aggressively with oxygen or other gases at high temperatures. A tube furnace can be sealed and operated under a vacuum or filled with an inert gas (like argon or nitrogen). This prevents unwanted chemical reactions, such as oxidation, and is essential for processes like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), where new materials are grown layer by layer from precursor gases.
A Hub for Critical Processes
This controlled environment makes the tube furnace indispensable for a wide range of applications:
- Material Synthesis: Creating novel materials, including semiconductors and nanomaterials.
- Heat Treatment: Improving the properties of metals and ceramics through processes like annealing (softening and relieving stress) and sintering (fusing powders together).
- Material Characterization: Preparing samples for analysis or testing the thermal stability of new compounds.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, the tube furnace is a specialized tool with inherent limitations that are important to recognize. Understanding these trade-offs ensures you are using the right tool for the job.
Material and Temperature Boundaries
The maximum achievable temperature is dictated by the material of the process tube. Quartz tubes are common and cost-effective but are typically limited to around 1200°C. For higher temperatures, more expensive ceramic tubes (like alumina or zirconia) are required.
Batch Processing by Design
Most tube furnaces are designed for batch processing, where one sample or a small group of samples is processed at a time. This makes them ideal for research and development but less efficient for continuous, large-scale industrial manufacturing.
Horizontal vs. Vertical Orientations
While the standard is a horizontal tube, vertical furnaces serve specific needs. They are ideal for processes where a sample needs to be dropped into the heat zone or to prevent materials from sagging or deforming at very high temperatures.
Key Applications by Goal
Your specific objective will determine which feature of the tube furnace is most critical for your success.
- If your primary focus is creating new materials (Synthesis): You will rely on precise atmosphere control for processes like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) and crystal growth.
- If your primary focus is improving existing materials (Heat Treatment): You will depend on the exceptional temperature uniformity for consistent results in annealing, sintering, and tempering.
- If your primary focus is fundamental research (Analysis): You will leverage the furnace's precise, repeatable environment for sample preparation, catalyst testing, and thermal decomposition studies.
Ultimately, the tube furnace empowers you to master the high-temperature, controlled environment necessary to innovate.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Origin | Early 20th century for ceramic filaments |
| Key Features | Uniform heating, atmospheric control (vacuum/inert gas) |
| Common Uses | Material synthesis, heat treatment, characterization |
| Temperature Range | Up to 1800°C, depending on tube material |
| Processing Type | Primarily batch processing |
Ready to elevate your materials research with precision high-temperature solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced tube furnaces, muffle furnaces, rotary furnaces, vacuum & atmosphere furnaces, and CVD/PECVD systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored furnace solutions can drive your innovations forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide



















