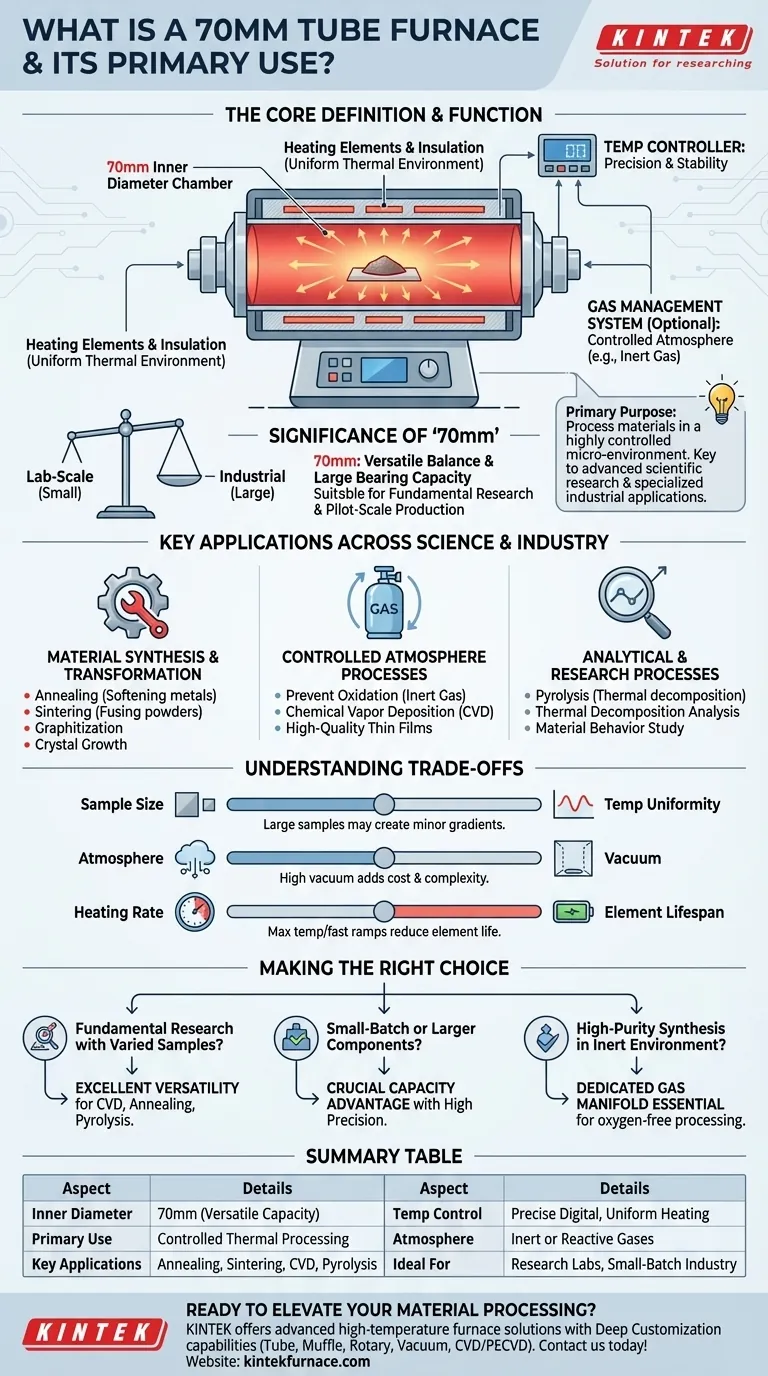
At its core, a 70mm tube furnace is a high-temperature electric heating device defined by its 70mm inner diameter cylindrical chamber. Its primary purpose is to process materials within a highly controlled and uniform thermal environment, making it an indispensable tool for advanced scientific research and specialized industrial applications.
The true value of a tube furnace is not just its ability to generate high heat, but its power to create a precisely managed micro-environment. This control over temperature, atmosphere, and uniformity is what enables the synthesis and transformation of advanced materials.

The Core Function: Precision in a Controlled Environment
A tube furnace's design is elegantly simple yet powerful. It provides an isolated chamber where heat and atmospheric conditions can be manipulated with a high degree of accuracy, which is essential for repeatable and reliable results.
How a Tube Furnace Operates
The furnace works by converting electrical energy into heat through specialized heating elements that surround the central ceramic or quartz tube.
These elements radiate thermal energy, which is absorbed uniformly by the tube and the sample material placed inside. High-quality insulation minimizes heat loss, ensuring temperature stability and energy efficiency.
Key Components and Their Roles
A standard tube furnace consists of several critical parts:
- Heated Chamber: The central tube (often alumina, mullite, or quartz) that holds the sample.
- Insulation: A refractory ceramic layer that contains the heat and protects the outer casing.
- Temperature Controller: The digital "brain" that monitors the temperature via a thermocouple and adjusts power to the heating elements to follow a precise heating profile.
- Gas Management System: An optional but common feature that allows for the introduction of inert or reactive gases, creating a specific, non-oxidizing, or reactive atmosphere.
The Significance of the '70mm' Diameter
The 70mm diameter represents a versatile balance. It is large enough to accommodate bigger samples or small-batch processing compared to smaller lab-scale furnaces.
This "large bearing capacity" makes it suitable for both fundamental research and pilot-scale production, offering more flexibility than narrower tubes without the footprint of a large industrial furnace.
Key Applications Across Science and Industry
The ability to precisely control heat and atmosphere makes the 70mm tube furnace a workhorse in materials science, chemistry, and engineering.
Material Synthesis and Transformation
This is the most common use category. Processes like annealing (softening metals), sintering (fusing powders into a solid mass), and graphitization all rely on the uniform heat of a tube furnace.
It is also used for the synthesis and purification of inorganic compounds and for growing specialized crystals.
Controlled Atmosphere Processes
Many advanced materials are sensitive to oxygen at high temperatures. A tube furnace allows for processing in a controlled atmosphere.
By flowing an inert gas like argon or nitrogen, researchers can prevent oxidation. It is also the foundational equipment for Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), a process used to grow high-quality thin films.
Analytical and Research Processes
Tube furnaces are essential for studying how materials behave under heat.
Processes like pyrolysis (thermal decomposition in an inert atmosphere) and thermal decomposition analysis help scientists understand a material's stability and composition.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly useful, it's important to understand the operational trade-offs to use a tube furnace effectively.
Sample Size vs. Temperature Uniformity
A key strength of any tube furnace is its temperature uniformity. While a 70mm furnace provides excellent consistency, it's a physical reality that extremely large samples can create minor temperature gradients within the tube. For most applications, this is negligible.
Atmosphere vs. Vacuum
Standard tube furnaces are optimized for processing at atmospheric pressure or with a positive flow of gas. Achieving a high vacuum requires specialized flanges, seals, and a compatible quartz tube, which can add significant cost and complexity to the setup.
Heating Rate vs. Element Lifespan
Most furnaces are capable of rapid heating. However, consistently running the furnace at its absolute maximum temperature and fastest ramp rates will reduce the operational lifespan of the heating elements, which are consumable components.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right furnace depends entirely on your end goal.
- If your primary focus is fundamental research with varied samples: A 70mm furnace provides excellent versatility for processes like CVD, annealing, or pyrolysis, with enough space for different sample sizes.
- If your primary focus is small-batch processing or treating larger components: The 70mm diameter offers a crucial capacity advantage over smaller research furnaces while maintaining high precision.
- If your primary focus is high-purity synthesis in an inert environment: A system with a dedicated gas management manifold is essential to ensure a clean, oxygen-free processing atmosphere.
Ultimately, a 70mm tube furnace empowers you to precisely dictate the conditions for creating and refining materials at the microscopic level.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Inner Diameter | 70mm, offering versatile sample capacity |
| Primary Use | Controlled thermal processing for material synthesis and transformation |
| Key Applications | Annealing, sintering, CVD, pyrolysis, and thermal analysis |
| Temperature Control | Precise digital controllers for uniform heating |
| Atmosphere Options | Inert or reactive gases for oxidation-free environments |
| Ideal For | Research labs and small-batch industrial processing |
Ready to elevate your material processing with precision and reliability? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all supported by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in research or industrial applications, let us help you achieve superior results. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can benefit your lab!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab



















