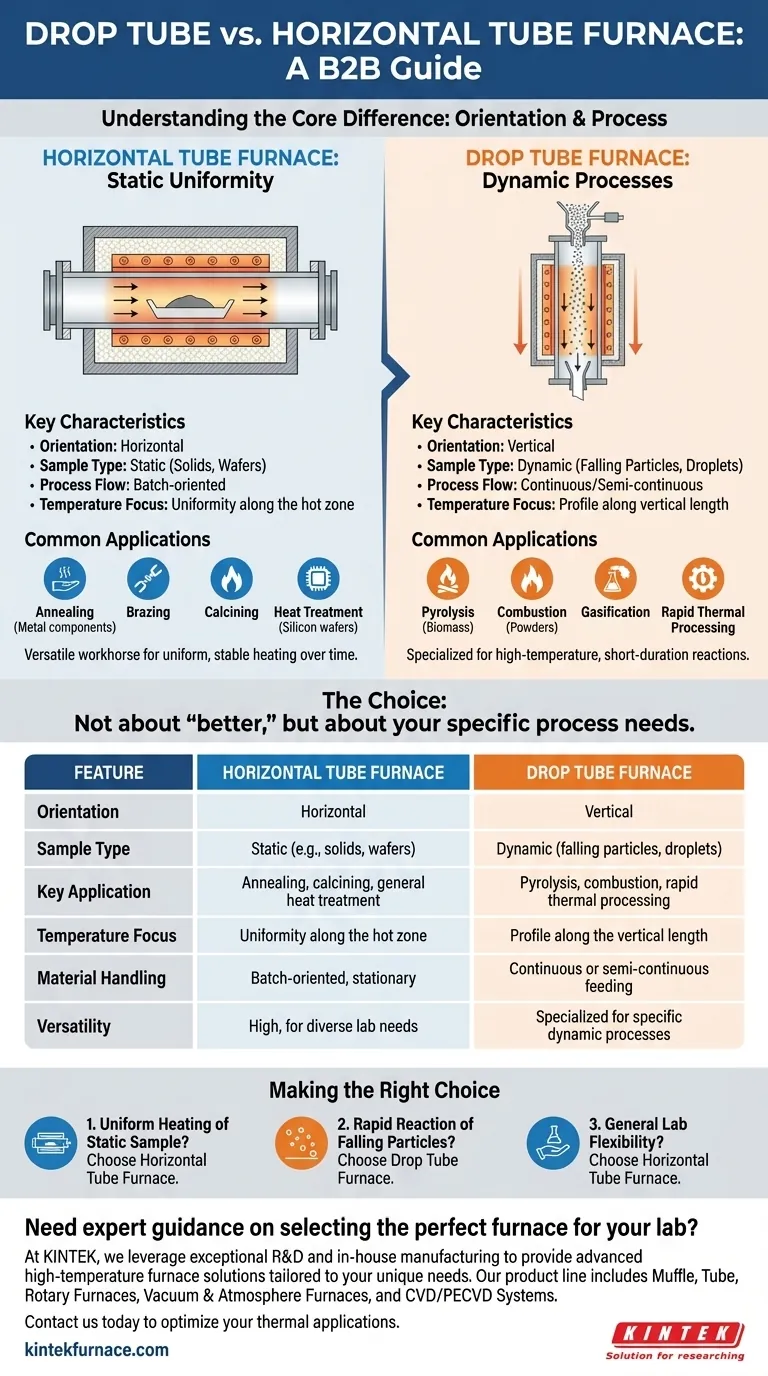
At its core, the difference between a drop tube furnace and a horizontal tube furnace is its physical orientation and the resulting impact on how materials are processed. A horizontal tube furnace is designed for static samples that require a stable, uniform temperature zone, while a drop tube furnace is vertically oriented specifically to use gravity to process falling particles or droplets through a controlled thermal environment.
The choice is not about which furnace is "better," but which is designed for your specific process. Horizontal furnaces provide stable, uniform heat for static samples, whereas vertical drop tube furnaces are specialized tools for studying dynamic processes involving falling materials.

The Defining Difference: Orientation and Process Flow
The primary distinction is how the furnace's orientation—horizontal versus vertical—enables entirely different types of material processing. This is the most critical factor in your decision.
Horizontal Tube Furnaces: The Standard for Static Uniformity
A horizontal tube furnace is the versatile workhorse for many thermal processes. Its design prioritizes creating a long, consistent, and stable hot zone along the length of the process tube.
Samples are typically placed in a ceramic or quartz boat and remain stationary during the heating cycle. This makes them ideal for processes where uniform temperature exposure over time is the main objective.
Common applications include annealing, brazing, calcining, and the heat treatment of components like silicon wafers.
Drop Tube Furnaces: Engineered for Dynamic Processes
A drop tube furnace is a specialized instrument where the vertical orientation is the key feature. It is not designed for static samples.
Instead, materials such as fine powders, biomass, or liquid droplets are introduced at the top and fall through the heated column. This setup allows for the study of processes that occur in very short timeframes, like combustion, pyrolysis, or gasification.
The goal is to achieve rapid thermal processing and observe the material's reaction as it moves through a controlled temperature profile via gravity.
Key Operational Considerations
Beyond orientation, the two furnace types differ in how they manage temperature, handle materials, and fit into a lab environment.
Temperature Profile vs. Temperature Uniformity
Horizontal furnaces are engineered for exceptional temperature uniformity along their central heating zone. This ensures a sample is heated evenly across its entire length.
Drop tube furnaces, by contrast, are focused on creating a precise temperature profile along their vertical length. The particle experiences a controlled rate of heating and cooling as it falls, which is the entire point of the experiment.
Material Handling and Sample Type
Horizontal furnaces handle solid samples, wafers, or powders held in static containers (boats). The process is typically batch-oriented.
Drop tube furnaces are designed for the continuous or semi-continuous feeding of fine particles or droplets. The material is in motion throughout the entire process.
Atmosphere Control
Both furnace types can be designed to operate under controlled atmospheres. They can be sealed to maintain a vacuum or to allow for the flow of specific inert or reactive gases.
Therefore, atmosphere control is a general feature of tube furnaces and not a primary differentiator between the horizontal and vertical designs.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between these furnaces involves recognizing their inherent limitations and specialized strengths.
The Versatility of Horizontal Furnaces
The horizontal tube furnace is a more general-purpose tool. Its ability to perform a wide range of heat treatment processes on static samples makes it a staple in many materials science and engineering labs. If you need a flexible furnace for multiple types of experiments, this is often the default choice.
The Specificity of Drop Tube Furnaces
Drop tube furnaces are highly specialized. They are the superior—and often only—choice for studying the high-temperature, short-duration reactions of falling particles. However, they are not suitable for general-purpose heat treatments like annealing a solid part.
Physical Footprint and Installation
The physical layout is a practical consideration. A horizontal furnace requires significant bench or floor space, while a drop tube furnace requires vertical clearance, often extending across more than one level of a building or requiring a dedicated high-bay area.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision must be guided by the material you are processing and the thermal treatment you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is uniform heating of a static sample: A horizontal tube furnace is the correct and most versatile choice for applications like annealing, calcining, and general heat treatment.
- If your primary focus is studying the rapid reaction of falling particles: A drop tube furnace is the only suitable option, specifically designed for processes like pyrolysis or combustion analysis.
- If your primary focus is general laboratory flexibility: A horizontal tube furnace offers the widest range of applications and is the more adaptable instrument for diverse research needs.
Ultimately, select the furnace that is purpose-built for the physics of your process.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Horizontal Tube Furnace | Drop Tube Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Orientation | Horizontal | Vertical |
| Sample Type | Static (e.g., solids, wafers) | Dynamic (falling particles, droplets) |
| Key Application | Annealing, calcining, general heat treatment | Pyrolysis, combustion, rapid thermal processing |
| Temperature Focus | Uniformity along the hot zone | Profile along the vertical length |
| Material Handling | Batch-oriented, stationary | Continuous or semi-continuous feeding |
| Versatility | High, for diverse lab needs | Specialized for specific dynamic processes |
Need expert guidance on selecting the perfect furnace for your lab? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, with strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your experimental requirements. Whether you're working with static samples or dynamic particle processes, we can help optimize your thermal applications. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your research efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety



















