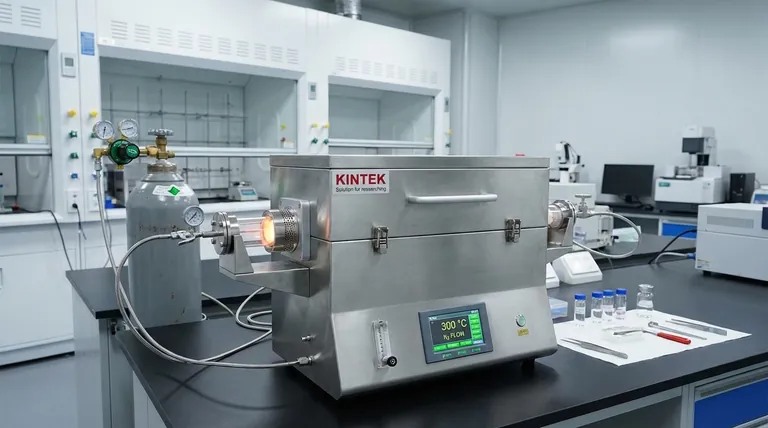
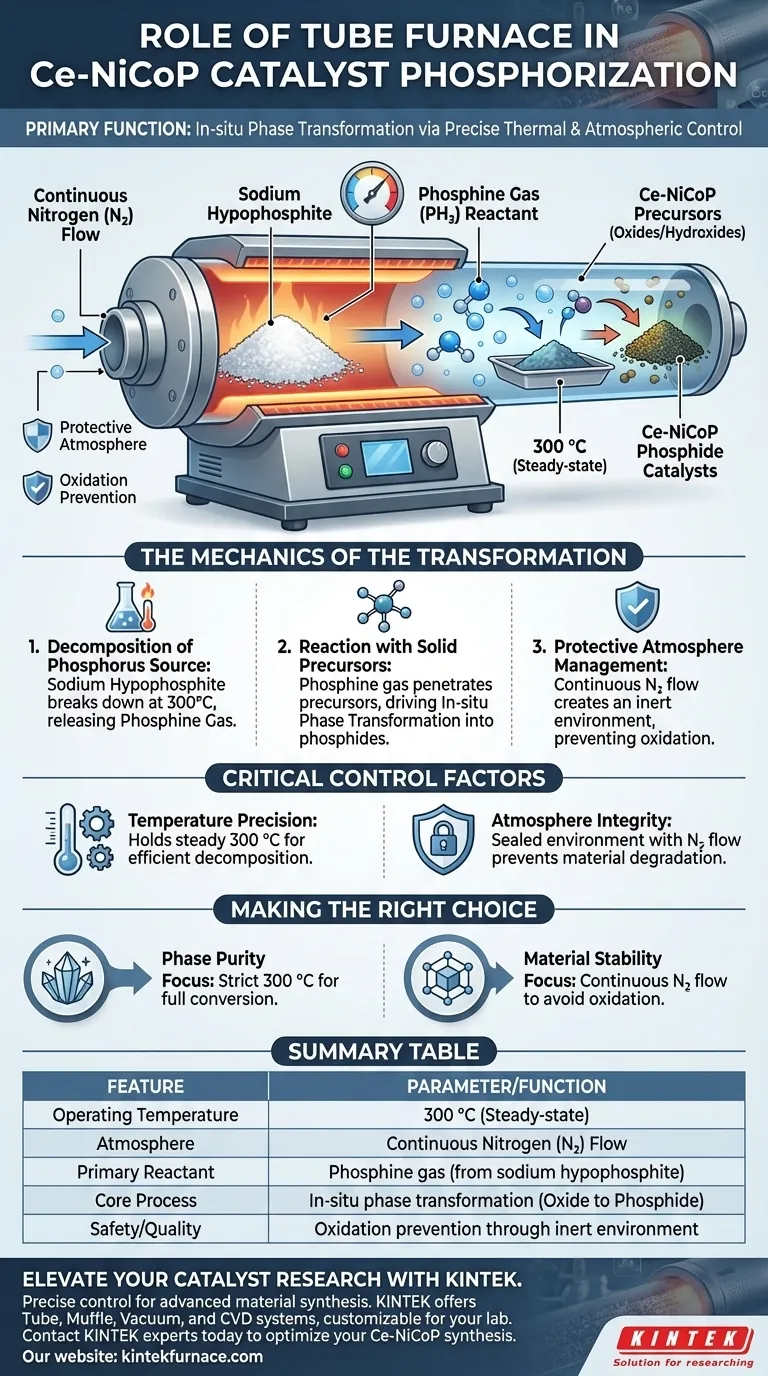
The primary function of a tube furnace in the phosphorization of Ce-NiCoP catalysts is to facilitate an in-situ phase transformation through precise thermal and atmospheric control. Specifically, it maintains a temperature of 300 °C under a nitrogen gas flow to decompose sodium hypophosphite into reactive phosphine gas, which then converts solid precursors into the desired phosphides.
The tube furnace acts as a specialized chemical reactor, creating the precise conditions required to convert inert oxides or hydroxides into active phosphide catalysts while preventing destructive oxidation.

The Mechanics of the Transformation
Decomposition of the Phosphorus Source
The furnace provides the thermal energy necessary to decompose sodium hypophosphite. By maintaining a consistent temperature of 300 °C, the device triggers the breakdown of this solid compound. This thermal decomposition releases phosphine gas, which acts as the active reactant in the process.
Reaction with Solid Precursors
Once generated, the phosphine gas interacts directly with the solid Ce-NiCoP precursors. These precursors typically start as oxides or hydroxides. The tube furnace environment allows the gas to penetrate the material, driving an in-situ phase transformation that converts them into the final phosphide structure.
Protective Atmosphere Management
Crucially, this process occurs within a continuous flow of nitrogen gas. The tube furnace creates an enclosed, inert environment that prevents external oxygen from interfering. This ensures the material undergoes phosphorization rather than oxidation or degradation during the heating cycle.
Critical Control Factors
Temperature Precision
The effectiveness of the phosphorization relies heavily on the furnace's ability to hold a steady 300 °C. Significant deviations in temperature can prevent the sodium hypophosphite from decomposing efficiently. Without this decomposition, the necessary phosphine gas will not be available to react with the precursors.
Atmosphere Integrity
The isolation provided by the tube is essential for chemical stability. If the nitrogen atmosphere is compromised, the high reactive surface area of the precursors could degrade. A sealed, controlled environment is non-negotiable for achieving the correct chemical phase.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure the successful synthesis of Ce-NiCoP catalysts, focus on the following operational parameters:
- If your primary focus is phase purity: Ensure the furnace maintains a strict 300 °C profile to guarantee the complete decomposition of the phosphorus source and full conversion of precursors.
- If your primary focus is material stability: Verify that the nitrogen flow is continuous and the tube seal is intact to prevent oxidation during the high-temperature phase.
By mastering the thermal and atmospheric environment of the tube furnace, you ensure the reproducible creation of high-performance catalytic materials.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Parameter/Function |
|---|---|
| Operating Temperature | 300 °C (Steady-state) |
| Atmosphere | Continuous Nitrogen (N₂) Flow |
| Primary Reactant | Phosphine gas (from sodium hypophosphite) |
| Core Process | In-situ phase transformation (Oxide to Phosphide) |
| Safety/Quality | Oxidation prevention through inert environment |
Elevate Your Catalyst Research with KINTEK
Precise phosphorization demands absolute control over thermal and atmospheric variables. KINTEK provides industry-leading Tube, Muffle, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed for the rigorous requirements of advanced material synthesis. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, our lab high-temp furnaces are fully customizable to meet your specific research needs—ensuring phase purity and material stability every time.
Ready to optimize your Ce-NiCoP synthesis? Contact KINTEK experts today to find the perfect thermal solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
References
- Mingfang Zhang, Tianyi Ma. Electronic Modulation of Nickel Cobalt Phosphide Nanosheets by Ce Doping for Efficient Overall Water Splitting. DOI: 10.1002/smll.202504837
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What types of heating methods are used in split tube furnaces? Optimize Your High-Temp Processes
- What are the functions of a quartz tube fixed-bed reactor? Ensure Precision in Catalyst Evaluation
- Why is a high-temperature tube furnace required for the annealing process during graphene growth? Optimize Substrates
- What is the necessity of using high-purity argon (Ar) gas in a tube furnace for Sb sulfurization?
- What are the key benefits of using split tube furnaces? Unlock Superior Access and Control for Your Lab
- How does a tube furnace contribute to the chemical activation stage of producing activated carbon? Expert Insights
- What is the three-step heating process in graphite furnace atomization? Master Precise Trace Metal Analysis
- How does a laboratory high-temperature tube resistance furnace contribute to the aging treatment of Ni-W-Co-Ta alloys?



















