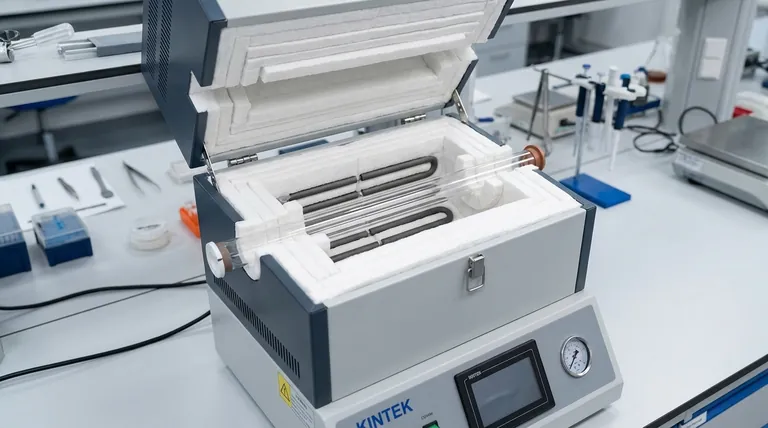
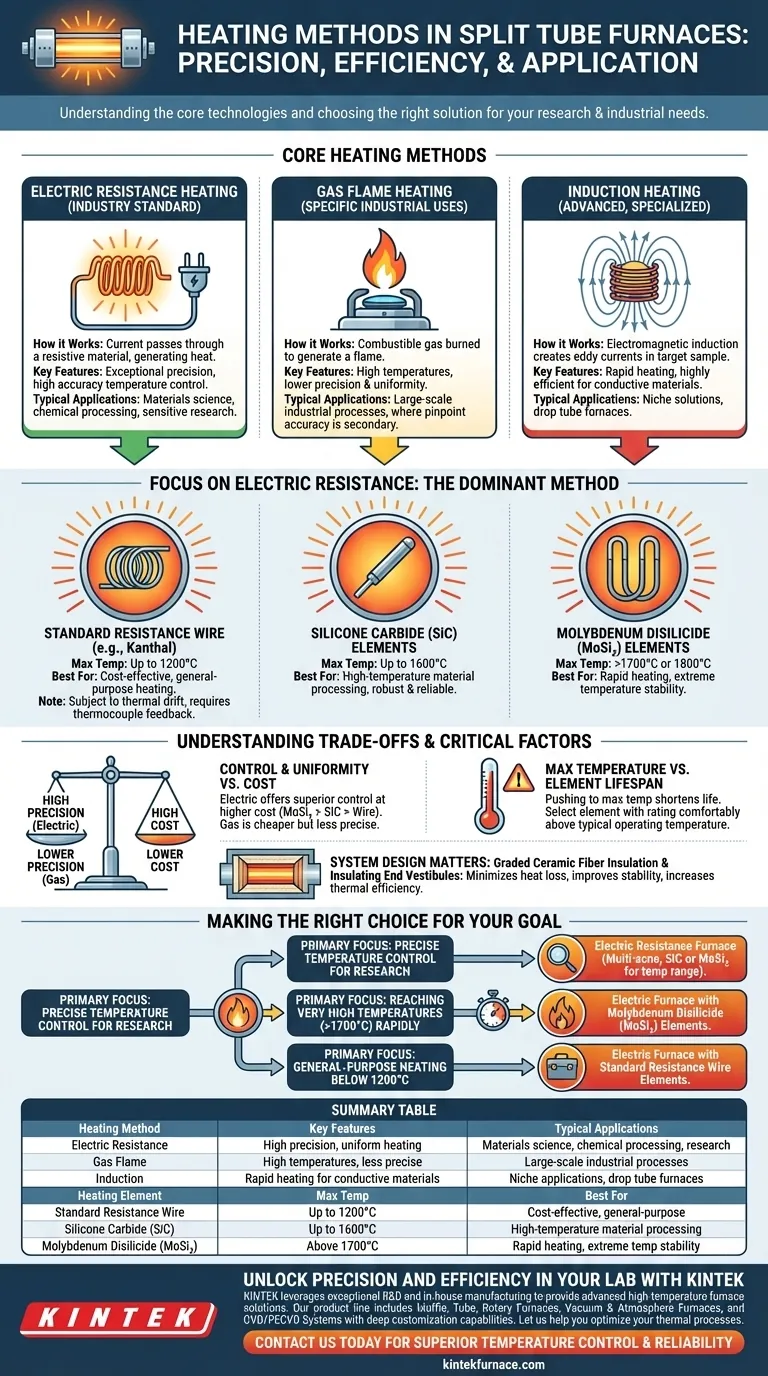
The primary heating methods for split tube furnaces are electric resistance and, in some cases, gas flame. Electric resistance is the most prevalent method, utilizing different heating element materials like standard resistance wire, Silicone Carbide (SiC), or Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) depending on the required operating temperature.
While several heating technologies exist, electric resistance heating is the dominant standard for split tube furnaces due to its unparalleled temperature precision and control. The critical decision is not just the method, but the specific heating element and furnace insulation, as this combination ultimately dictates performance, efficiency, and suitability for your application.

Understanding the Core Heating Methods
A split tube furnace's effectiveness is defined by how it generates and contains heat. The choice of heating method is the foundational decision that impacts every aspect of its operation.
Electric Resistance Heating: The Industry Standard
Electric resistance heating works by passing an electrical current through a material that resists the flow of electricity, generating heat. This is the most common method used in modern split tube furnaces.
Its popularity stems from its exceptional precision. Temperature can be controlled with remarkable accuracy by modulating the electrical power, which is essential for materials science, chemical processing, and other sensitive research applications.
Gas Flame Heating: For Specific Industrial Uses
In this method, a combustible gas is burned to generate a flame that directly or indirectly heats the furnace tube. This approach is less common for split tube furnaces, especially in laboratory settings.
While capable of producing high temperatures, gas flame heating offers far less temperature precision and uniformity compared to electric resistance. It is sometimes considered for specific, large-scale industrial processes where pinpoint accuracy is not the primary concern.
Induction Heating: An Advanced, Specialized Alternative
Induction heating uses electromagnetic induction to create eddy currents within the material inside the furnace, generating heat directly in the target sample. This method is typically found in specialized furnaces, such as certain drop tube designs.
It is highly efficient for heating conductive materials very rapidly. However, its complexity and material-specific nature make it a niche solution rather than a general-purpose method for standard split tube furnaces.
Choosing the Right Electric Heating Element
For the vast majority of users, the key decision lies in selecting the correct electric heating element for their temperature needs.
Standard Resistance Wire (e.g., Kanthal)
These elements are used for lower to moderate temperature applications, typically up to around 1200°C. They are cost-effective and reliable for many general-purpose heating tasks.
However, they can be subject to thermal drift, where their resistance changes over time, affecting temperature accuracy. This is effectively managed by using a thermocouple feedback loop to ensure the controller delivers the correct power for the target temperature.
Silicone Carbide (SiC) Elements
When application temperatures exceed the limits of wire elements, SiC becomes the standard. These robust elements are built for high-temperature work, often operating reliably for extended periods up to 1600°C. They are a workhorse in many high-temperature material processing applications.
Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) Elements
For the highest temperature requirements, often exceeding 1700°C or even 1800°C, MoSi₂ elements are the superior choice. They are known for their ability to heat up very rapidly and maintain stability at extreme temperatures.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a heating system involves balancing performance, cost, and operational complexity. Objectively weighing these factors is crucial for making a sound investment.
Control and Uniformity vs. Cost
Electric resistance furnaces offer superior temperature control and uniformity, especially in multi-zone configurations. This precision comes at a higher initial cost compared to simpler gas systems. Within electric furnaces, high-performance MoSi₂ elements are significantly more expensive than SiC or wire elements.
Maximum Temperature vs. Element Lifespan
Pushing any heating element to its absolute maximum rated temperature will drastically shorten its operational life. For longevity and reliability, it is best practice to select an element whose maximum rating is comfortably above your typical operating temperature.
System Design Is as Important as the Element
The heating element is only one part of the equation. High-quality furnace design, which incorporates graded layers of ceramic fiber insulation and insulating end vestibules, is critical. This design minimizes heat loss, improves temperature stability, and increases overall thermal efficiency, directly impacting operational costs and performance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific objective should guide your selection of a heating system.
- If your primary focus is precise temperature control for research: Choose an electric resistance furnace, specifying multi-zone control for uniformity and the right element (SiC or MoSi₂) for your temperature range.
- If your primary focus is reaching very high temperatures (>1700°C) rapidly: An electric furnace equipped with Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) elements is the definitive choice.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heating below 1200°C: An electric furnace with standard resistance wire elements offers the best balance of performance and cost.
Understanding these heating principles ensures you select a furnace that is not just a tool, but a precise solution to your specific thermal processing challenge.
Summary Table:
| Heating Method | Key Features | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Electric Resistance | High precision, uniform heating, temperature control | Materials science, chemical processing, research labs |
| Gas Flame | High temperatures, less precise, lower cost | Large-scale industrial processes |
| Induction | Rapid heating for conductive materials, specialized | Niche applications, drop tube furnaces |
| Heating Element | Max Temperature | Best For |
| Standard Resistance Wire | Up to 1200°C | Cost-effective, general-purpose heating |
| Silicone Carbide (SiC) | Up to 1600°C | High-temperature material processing |
| Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) | Above 1700°C | Rapid heating, extreme temperature stability |
Unlock Precision and Efficiency in Your Lab with KINTEK
Struggling to choose the right heating method for your split tube furnace? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental requirements.
Whether you're in materials science, chemical processing, or industrial applications, we help you achieve superior temperature control, efficiency, and reliability. Don't let heating challenges hold you back—contact us today to discuss how our solutions can optimize your thermal processes and drive your research forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis



















