The tube furnace acts as the definitive reaction vessel where liquid precursor films are transformed into solid, functional materials. In the context of Polymer-Assisted Deposition (PAD), acts as a precision instrument that provides a specific temperature ramp and controlled gas environment to sequentially decompose organic components and drive the epitaxial growth of inorganic oxides.
The tube furnace performs a critical dual function: it first eliminates the organic polymer matrix at lower temperatures and subsequently provides the high thermal energy required to fuse remaining metal ions into a dense, crystalline structure aligned with the substrate.
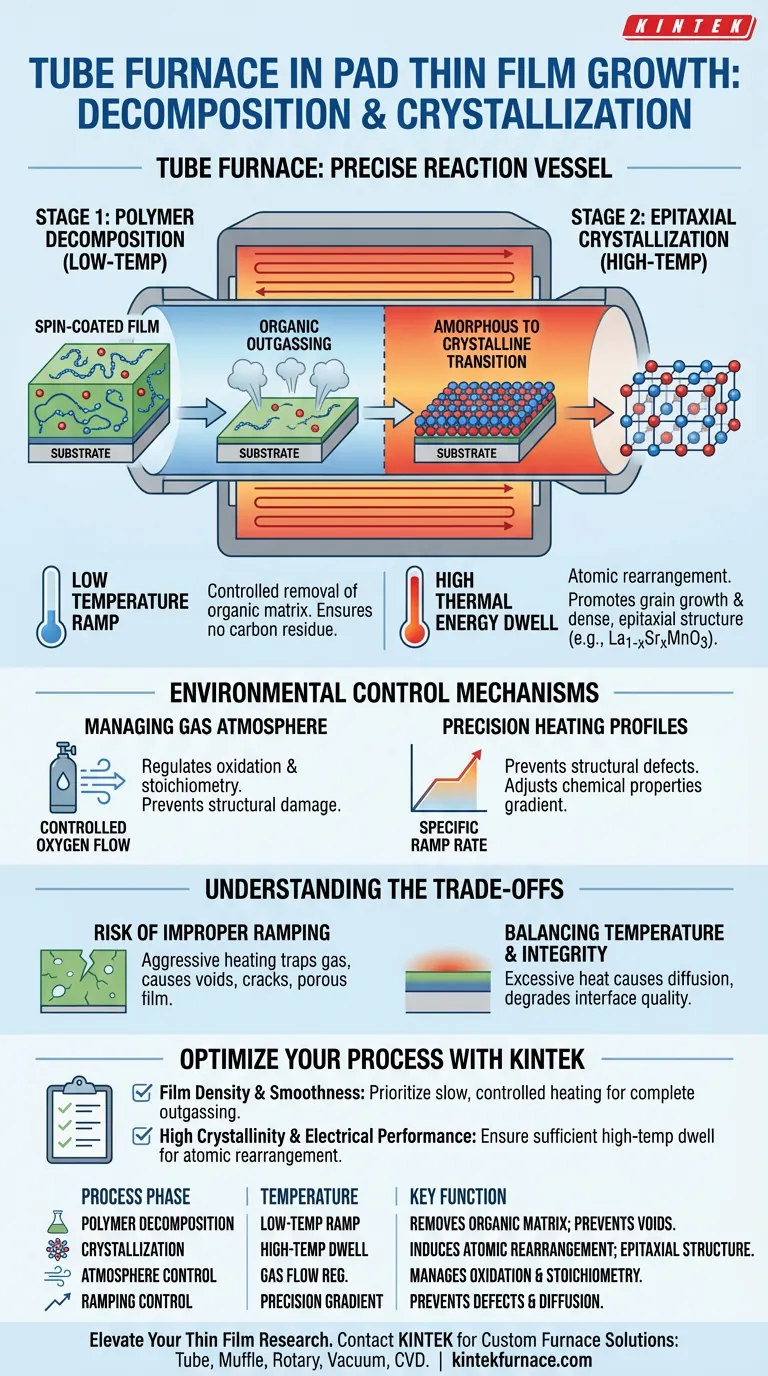
The Dual-Stage Thermal Process
Stage 1: Polymer Decomposition
The initial role of the tube furnace is the controlled removal of the organic "vehicle."
The spin-coated film contains a polymer matrix that binds metal ions. The furnace executes a specific temperature ramp to decompose and eliminate these organic components at lower temperatures.
This step is vital for ensuring that no carbon residue remains to interfere with the final film quality.
Stage 2: Epitaxial Crystallization
Once the organics are removed, the furnace transitions to its high-temperature role.
At elevated temperatures, the furnace induces the crystallization of the remaining inorganic material. The thermal energy facilitates atomic rearrangement, transitioning the material from a disordered or amorphous state into a structured phase.
This high-heat environment promotes grain growth and ensures the formation of a dense, epitaxial structure (such as La1-xSrxMnO3) on the substrate.
Environmental Control Mechanisms
Managing the Gas Atmosphere
The tube furnace allows for the precise regulation of the reaction environment.
For oxide films, a controlled oxygen flow is maintained to facilitate proper oxidation and stoichiometry.
This controlled atmosphere ensures that chemically active sites are managed correctly without damaging the material structure.
Precision Heating Profiles
Success in PAD relies on a specific "ramp" or heating rate, not just a static temperature.
The furnace controls how quickly the temperature rises, which is essential to prevent structural defects.
A controlled ramp allows for the gradient adjustment of chemical properties, preventing shock to the film or substrate.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Risk of Improper Ramping
If the heating rate is too aggressive during the polymer decomposition phase, gas may become trapped.
This often leads to voids, cracks, or a porous film rather than the desired dense structure.
Balancing Temperature and Substrate Integrity
While high temperatures are necessary for crystallization, excessive heat can be detrimental.
Overheating may cause chemical diffusion between the film and the substrate, degrading the interface quality.
It creates a delicate balance where the temperature must be high enough to induce the phase transition but low enough to preserve the substrate's integrity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To optimize your Polymer-Assisted Deposition process using a tube furnace, consider these specific adjustments:
- If your primary focus is film density and smoothness: Prioritize a slow, controlled heating ramp during the low-temperature phase to ensure gentle, complete outgassing of the polymer.
- If your primary focus is high crystallinity and electrical performance: Ensure the high-temperature dwell time is sufficient to allow complete atomic rearrangement and phase transition into the desired lattice structure.
The tube furnace is not merely a heater; it is the environment that dictates the structural purity and epitaxial quality of your final thin film.
Summary Table:
| Process Phase | Temperature Role | Key Function |
|---|---|---|
| Polymer Decomposition | Low-Temperature Ramp | Removes organic matrix; prevents carbon residue and voids. |
| Crystallization | High-Temperature Dwell | Induces atomic rearrangement for dense, epitaxial structure. |
| Atmosphere Control | Gas Flow Regulation | Manages oxidation and stoichiometry for pure oxide films. |
| Ramping Control | Precision Gradient | Prevents structural defects and avoids film/substrate diffusion. |
Elevate Your Thin Film Research with KINTEK
Precision in thermal processing is the difference between a porous film and a perfect epitaxial structure. At KINTEK, we understand the critical nature of temperature ramping and atmospheric control in Polymer-Assisted Deposition (PAD).
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, along with other lab high-temp furnaces—all fully customizable to meet your unique research needs. Our systems provide the stability and control required to ensure complete polymer outgassing and superior crystalline alignment.
Ready to optimize your material synthesis? Contact us today to discuss your custom furnace requirements with our technical team!
Visual Guide
References
- Meritxell Toda‐Casaban, B. Martı́nez. Tuning of Antiferromagnetic Phase in La<sub>1–<i>x</i></sub>Sr<sub><i>x</i></sub>MnO<sub>3</sub> Epitaxial Thin Films by Polymer-Assisted Deposition Synthesis. DOI: 10.1021/acs.cgd.4c00229
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Reliable High-Temp Processing
- Why is maintenance important for split tube furnaces? Ensure Precision, Safety, and Efficiency
- What is a high temperature tube furnace? Achieve Precise Heat and Atmosphere Control
- What temperature range and applications is this tube furnace suitable for? Ideal for 500°C to 1800°C thermal processes
- How are tubular furnaces utilized in semiconductor manufacturing? Precision Thermal Processing for High-Yield ICs
- What factors should be considered when choosing tube furnace cracking? Optimize Your Thermal Decomposition Process
- Why is a tube high-temperature furnace required for Au@MoSe2/graphene composites? Precision Reaction Control
- What role does a high-temperature tube furnace play in converting polymer precursors? Precision Synthesis Guide



















