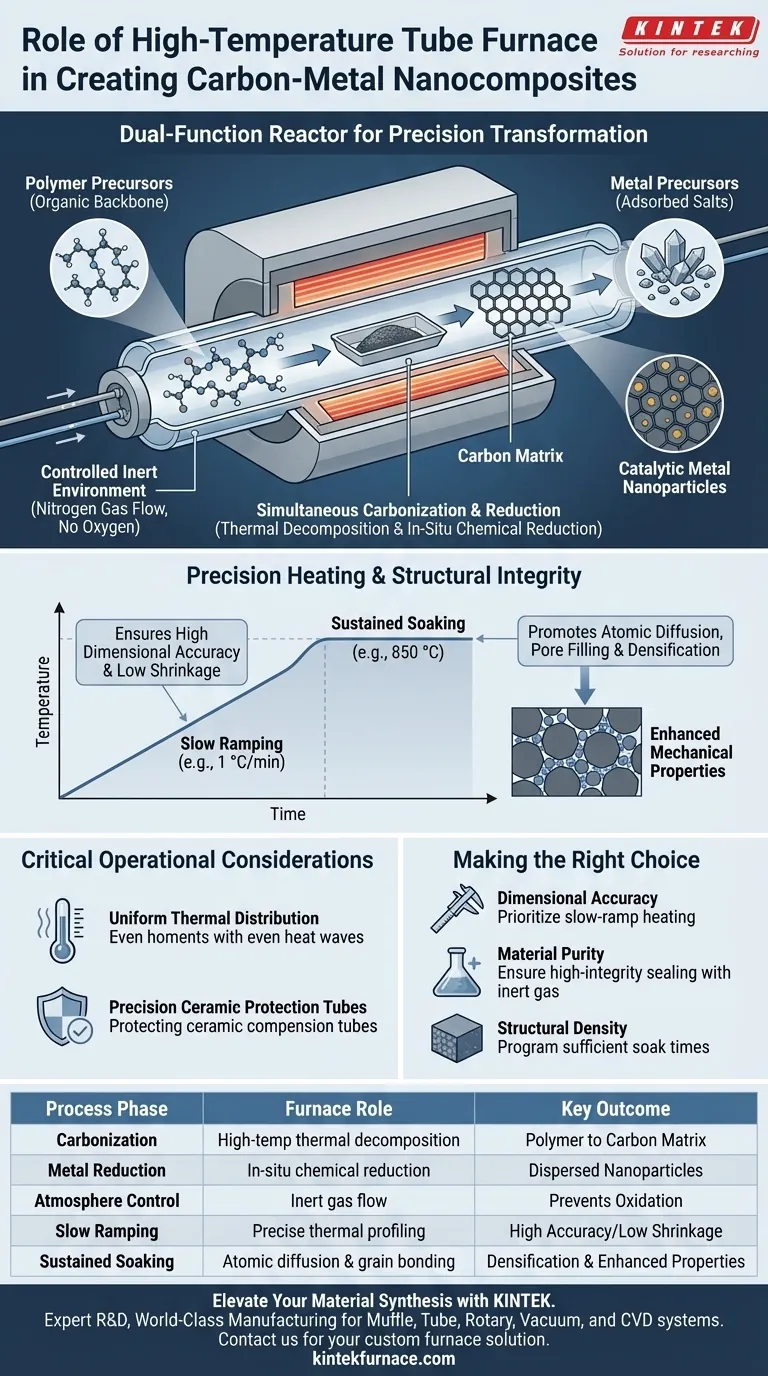
A high-temperature tube furnace serves as a dual-function reactor that facilitates both the thermal decomposition of polymers and the chemical reduction of metal precursors. It provides a sealed, inert environment—typically utilizing nitrogen gas—to convert a polymer backbone into a rigid carbon structure while simultaneously reducing adsorbed metal salts into highly dispersed catalytic nanoparticles.
Core Takeaway The tube furnace is not merely a heater but a precision instrument that orchestrates the delicate phase transformation of organic materials. Its ability to maintain a strictly controlled atmosphere and precise heating ramp is the defining factor in achieving carbon-metal nanocomposites with high dimensional accuracy and low shrinkage.

The Mechanism of Transformation
Simultaneous Carbonization and Reduction
The primary role of the furnace is to drive two chemical processes at once. As the temperature rises, the polymer backbone thermally decomposes to form a carbon matrix.
Simultaneously, the furnace environment facilitates the in-situ reduction of metal salts. This transforms the salts into metal nanoparticles that are highly dispersed throughout the newly formed carbon structure.
Creating a Controlled Inert Environment
Successful conversion requires the total exclusion of oxygen. The tube furnace operates under a controlled inert atmosphere, usually flowing nitrogen gas.
This sealed environment is critical. It ensures that the carbonization process occurs without the material burning away, maintaining the structural integrity of the composite.
Precision Heating and Structural Integrity
The Importance of Slow Ramping
Achieving high-quality nanocomposites, such as carbon-based Joule heaters, requires exacting thermal control. The furnace is often programmed with a slow heating ramp, such as 1 °C per minute up to 800 °C.
This gradual increase is essential for dimensional accuracy. Rapid heating can cause uncontrolled shrinkage or warping, whereas a slow ramp allows for low shrinkage and a stable final shape.
Promoting Atomic Diffusion
At high temperatures (e.g., 500 °C to 850 °C), the furnace promotes atomic diffusion and grain boundary bonding.
During this phase, nanoparticles fill micropores within the matrix. This densification process eliminates residual stresses from earlier processing stages and significantly enhances the material's ultimate mechanical properties.
Critical Operational Considerations
Managing Thermal Gradients
A distinct advantage of the tube furnace design is its ability to deliver uniform thermal distribution along the length of the tube.
Minimizing temperature gradients is vital for experimental consistency. Any variation in temperature across the sample could lead to uneven carbonization or inconsistent nanoparticle distribution.
Protecting the Apparatus
High-temperature processing involves volatile byproducts and intense radiation. Precision ceramic protection tubes are often required to act as physical barriers.
These tubes shield sensitive internal components, such as induction coils and measurement systems, from melt volatiles and heat radiation, ensuring the system remains stable during prolonged exposure to extreme heat.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of a tube furnace for your specific application, consider the following:
- If your primary focus is dimensional accuracy: Prioritize a furnace controller that supports complex, slow-ramp heating profiles (e.g., 1 °C/min) to minimize shrinkage during the polymer-to-carbon transition.
- If your primary focus is material purity: Ensure the furnace utilizes a high-integrity sealing system with continuous inert gas flow (Nitrogen) to prevent oxidation of the carbon matrix.
- If your primary focus is structural density: Program sufficient soak times at peak temperatures (e.g., 850 °C) to allow for complete atomic diffusion and pore filling.
The success of converting polymer precursors lies in the precise synchronization of atmosphere control and thermal ramping.
Summary Table:
| Process Phase | Furnace Role | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Carbonization | High-temp thermal decomposition | Transformation of polymer to rigid carbon matrix |
| Metal Reduction | In-situ chemical reduction | Dispersion of catalytic metal nanoparticles |
| Atmosphere Control | Inert gas (N2) flow sealing | Prevents material oxidation and structural loss |
| Slow Ramping | Precise thermal profiling (e.g., 1°C/min) | High dimensional accuracy and low shrinkage |
| Sustained Soaking | Atomic diffusion & grain bonding | Matrix densification and enhanced mechanical properties |
Elevate Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK
Achieving the perfect carbon-metal nanocomposite requires more than just heat—it requires the precision of a KINTEK high-temperature tube furnace. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we provide high-integrity Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to maintain the strict inert atmospheres and gradual heating ramps your research demands.
Whether you need customized dimensions for specific polymer precursors or advanced controllers for complex thermal profiles, KINTEK delivers the reliability needed for low-shrinkage, high-purity results.
Ready to optimize your lab's high-temperature processes? Contact us today to find your custom furnace solution.
Visual Guide
References
- Paul N. Smith, Zhe Qiang. Transformative 3D Printing of Carbon‐metal Nanocomposites as Catalytic Joule Heaters for Enhanced Ammonia Decomposition. DOI: 10.1002/advs.202413149
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What function does the annealing treatment in a high-temperature quartz-tube furnace serve? Optimizing Glass Ceramics
- What role does a single-zone tube furnace play in synthesizing ZnPS3? Master the Thermal Profile for Layered Materials
- What types of atmospheres can a horizontal electric furnace control? Master Material Processing with Precision
- Why is the encapsulation of raw materials in a vacuum-sealed quartz tube necessary for crystal growth? Key to Purity
- What is a vertical tube furnace? Leverage Gravity for Superior Material Processing
- What materials are used for the chamber and insulation in three-zone split tube furnaces? Optimize Your High-Temp Processes
- How do tube furnaces function and where are they used? Discover Precision Heating Solutions
- How does a tube furnace facilitate the activation and shaping of NiCoO2 nanowires? Optimize Your Catalyst Performance



















