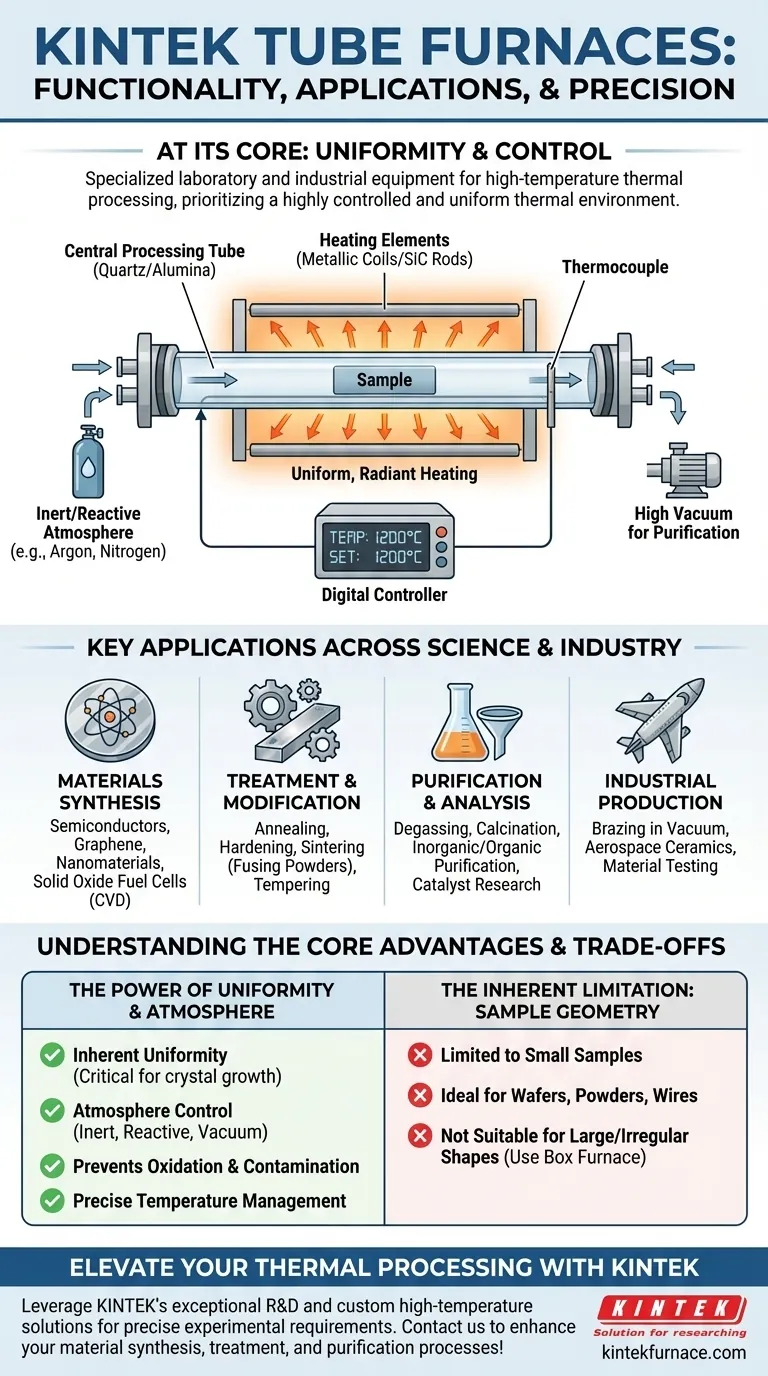
At its core, a tube furnace is a specialized piece of laboratory and industrial equipment designed for high-temperature thermal processing. It functions by heating a sample within a cylindrical tube, allowing for extremely precise temperature control and, most critically, the ability to manage the atmospheric environment around the sample.
The true value of a tube furnace is not just its ability to get hot, but its power to create a highly controlled and uniform thermal environment. This makes it an indispensable tool for processes where preventing contamination and ensuring consistent material properties are paramount.
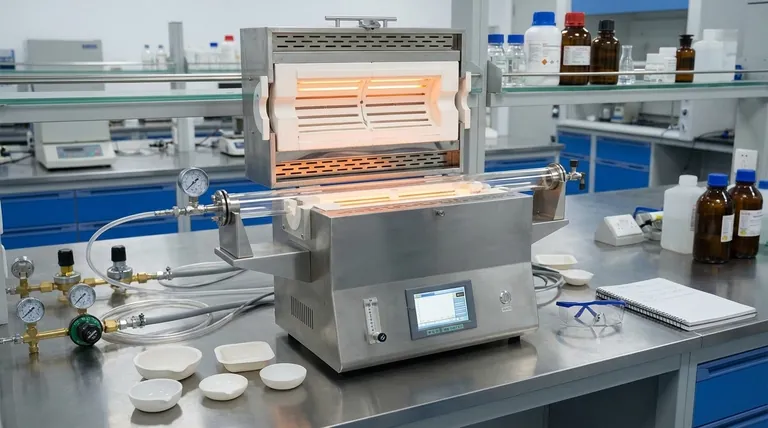

How a Tube Furnace Achieves Precision Control
A tube furnace's design is centered on providing exceptional thermal uniformity and atmospheric purity for sensitive processes. Its main components work in concert to create a highly repeatable and controlled environment.
The Central Processing Tube
The heart of the furnace is a cylindrical tube, typically made from quartz, alumina, or another ceramic. The sample or material to be processed is placed inside this tube, which serves as the reaction chamber.
The Heating Elements
Heating elements, such as metallic coils or silicon carbide rods, are arranged around the outside of the processing tube. This configuration ensures uniform, radiant heating from all sides, minimizing temperature gradients and ensuring the entire sample experiences the same thermal conditions.
Precise Temperature Regulation
A thermocouple is used to measure the temperature inside or near the tube, feeding this data to a digital controller. This closed-loop system allows for precise management of heating rates, target temperatures, and cooling profiles.
Critical Atmosphere Control
The ends of the tube can be sealed, allowing for the introduction of specific gases or the creation of a vacuum. This is the furnace's key differentiator, enabling processes in inert atmospheres (like argon or nitrogen) to prevent oxidation, reactive atmospheres for chemical synthesis, or high vacuum for purification and degassing.
Key Applications Across Science and Industry
The combination of uniform heating and atmosphere control makes tube furnaces essential in a wide range of advanced fields. The applications can be broadly categorized by their primary goal.
Advanced Materials Synthesis
Tube furnaces are critical for creating materials with specific, engineered properties. This includes the production of semiconductors, graphene, nanomaterials, and components for solid oxide fuel cells. Processes like chemical vapor deposition (CVD) rely on the furnace's controlled environment to deposit thin films onto a substrate.
Material Treatment and Modification
These furnaces are widely used to alter the physical properties of existing materials. Applications like annealing (softening metals), hardening, sintering (fusing powders together), and tempering all require precise thermal cycles that a tube furnace provides.
Purification and Chemical Analysis
The ability to heat a sample in a vacuum or a controlled gas flow is ideal for purification. Processes like inorganic and organic purification, degassing, and calcination remove volatile impurities. It is also used for catalyst research and thermocouple calibration, where a stable, known temperature is required.
Industrial Production and Testing
In industrial settings, tube furnaces are used for specialized tasks like brazing components in a vacuum, developing advanced aerospace ceramics, and testing the properties of materials for the oil and gas industry.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Core Advantages
While incredibly versatile, a tube furnace is a specialized tool chosen for specific reasons. Understanding its primary advantage clarifies its role compared to other types of furnaces, like a box furnace.
The Power of Uniformity
The cylindrical heating chamber is inherently better at providing uniform temperature than a rectangular box. For applications like crystal growth or annealing sensitive components, any temperature variation can ruin the final product.
The Necessity of Atmosphere Control
Many advanced materials are highly reactive with oxygen at high temperatures. A tube furnace's ability to create a vacuum or inert atmosphere is not a luxury but a fundamental requirement to prevent unwanted oxidation and contamination.
The Inherent Limitation: Sample Geometry
The primary trade-off is sample size and shape. The cylindrical chamber is ideal for small samples, wafers, powders, or wires but is not suitable for large or irregularly shaped objects. For those, a box furnace is often a better, though less controlled, alternative.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a tube furnace depends entirely on whether your process demands the unique control it offers.
- If your primary focus is creating new materials (Synthesis): A tube furnace is essential for processes like chemical vapor deposition (CVD) or growing crystals where atmosphere and temperature uniformity are non-negotiable.
- If your primary focus is modifying existing materials (Treatment): A tube furnace provides the controlled, oxygen-free environment needed for annealing, sintering, or coating without contamination.
- If your primary focus is high-purity processing or analysis (Purification): A tube furnace's vacuum and gas-flow capabilities are necessary for degassing materials or testing chemical reactions under specific conditions.
Ultimately, a tube furnace is the definitive tool when the process environment is just as critical as the temperature itself.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | Heats samples in a cylindrical tube with uniform temperature and controlled atmosphere for high-precision thermal processing. |
| Key Components | Cylindrical tube, heating elements, thermocouple, digital controller, and gas/vacuum seals. |
| Applications | Materials synthesis (e.g., semiconductors, graphene), material treatment (e.g., annealing, sintering), purification, and industrial testing. |
| Advantages | Uniform heating, precise temperature control, atmosphere management (inert, reactive, vacuum), and contamination prevention. |
| Limitations | Limited to small or cylindrical samples; not ideal for large or irregular shapes. |
Ready to elevate your thermal processing with precision and reliability? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can enhance your material synthesis, treatment, and purification processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability



















