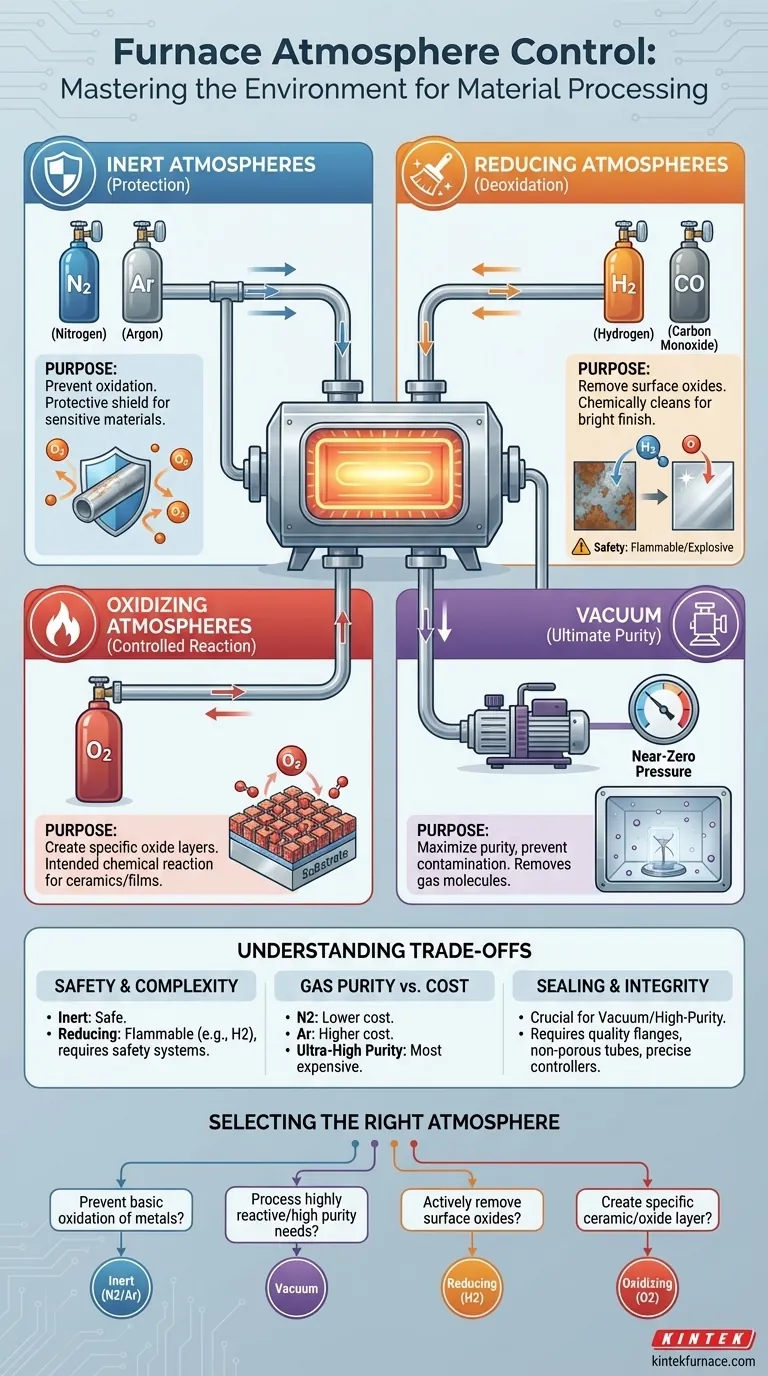
At its core, a horizontal electric furnace can control a wide range of atmospheres to suit specific material processing needs. These include inert atmospheres like argon and nitrogen, reducing atmospheres containing hydrogen or carbon monoxide, oxidizing atmospheres with controlled oxygen levels, and a vacuum environment for maximum purity.
The ability to precisely control the atmosphere is not a secondary feature; it is a fundamental tool that transforms a furnace from a simple heater into a sophisticated material processing instrument. The choice of atmosphere directly dictates whether you are protecting, cleaning, or intentionally reacting with your material.

The Purpose of Atmosphere Control
Controlling the environment inside a furnace is critical because at high temperatures, materials become significantly more reactive. The wrong atmosphere can lead to oxidation, contamination, or other unwanted chemical changes that ruin the sample.
Proper atmosphere control ensures the integrity of the material and achieves the desired outcome of the thermal process, whether that's annealing, sintering, or growing a crystal.
A Breakdown of Common Furnace Atmospheres
Each type of atmosphere serves a distinct technical purpose. The selection depends entirely on the material being processed and the desired final properties.
Inert Atmospheres: For Protection
An inert atmosphere is the most common choice for preventing unwanted reactions. By flooding the furnace tube with a non-reactive gas like nitrogen (N2) or argon (Ar), you displace the oxygen.
This protects the material from oxidation, which is especially important for metals and other sensitive compounds during high-temperature processing. Think of it as creating a protective shield around your sample.
Reducing Atmospheres: For Deoxidation
A reducing atmosphere goes a step further than an inert one. Gases like hydrogen (H2) or carbon monoxide (CO) not only prevent oxidation but can actively remove existing oxide layers from a material's surface.
This deoxidizing effect is crucial in applications like bright annealing of metals, where a clean, oxide-free surface is essential. It chemically "cleans" the material at high temperatures.
Oxidizing Atmospheres: For Controlled Reactions
While often avoided, oxidation is sometimes the desired outcome. An oxidizing atmosphere, which involves intentionally introducing oxygen (O2), is used to create specific oxide layers on a material.
This is common in the manufacturing of certain ceramics or for growing dielectric films on semiconductors. Here, the atmosphere is a reactant, not just a protective blanket.
Vacuum: For Ultimate Purity
Creating a vacuum provides the purest processing environment possible by removing nearly all gas molecules from the chamber. This is essential for highly sensitive materials that could be contaminated by even trace amounts of gas.
A vacuum is also necessary to prevent outgassing from interfering with the process and is often the first step before backfilling the furnace with a high-purity process gas.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing an atmosphere involves balancing cost, complexity, and safety. There is no single "best" option for all scenarios.
Safety and Equipment Complexity
Inert gases are relatively safe, but reducing gases like hydrogen are flammable and explosive. Using them requires specialized safety protocols, leak detectors, and ventilation systems, significantly increasing the complexity and cost of the setup.
Gas Purity vs. Cost
The cost of the gas itself is a factor. Nitrogen is generally less expensive than argon. For most applications, standard purity nitrogen is sufficient, but for highly sensitive materials, more expensive, ultra-high purity argon may be required to prevent even minute reactions.
Sealing and System Integrity
Maintaining a specific atmosphere, especially a high-purity one or a vacuum, depends on the quality of the furnace system. This requires excellent sealing flanges, a non-porous furnace tube (often quartz or high-purity alumina), and precise gas flow controllers. A leaky system will fail to maintain the desired atmosphere, compromising your results.
Selecting the Right Atmosphere for Your Application
Your choice should be driven by the technical goal of your thermal process.
- If your primary focus is preventing basic oxidation of most metals: An inert atmosphere of nitrogen or argon is your most practical and cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is processing highly reactive materials or ensuring maximum purity: A vacuum environment is necessary to eliminate potential contaminants.
- If your primary focus is actively removing surface oxides for a bright, clean finish: A reducing atmosphere containing hydrogen is the correct tool for the job.
- If your primary focus is creating a specific ceramic or oxide layer: A controlled oxidizing atmosphere is required to drive the intended chemical reaction.
Ultimately, viewing the furnace atmosphere as an active variable in your process is the key to achieving repeatable, high-quality results.
Summary Table:
| Atmosphere Type | Key Gases/Environment | Primary Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Inert | Nitrogen (N2), Argon (Ar) | Prevent oxidation and protect materials |
| Reducing | Hydrogen (H2), Carbon Monoxide (CO) | Remove oxides and clean surfaces |
| Oxidizing | Oxygen (O2) | Create oxide layers for specific reactions |
| Vacuum | Near-zero gas pressure | Ensure maximum purity and prevent contamination |
Ready to elevate your lab's capabilities with tailored high-temperature solutions? KINTEK specializes in advanced furnace systems, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With our strong R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs—ensuring precise atmosphere control for superior results. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your thermal processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis



















