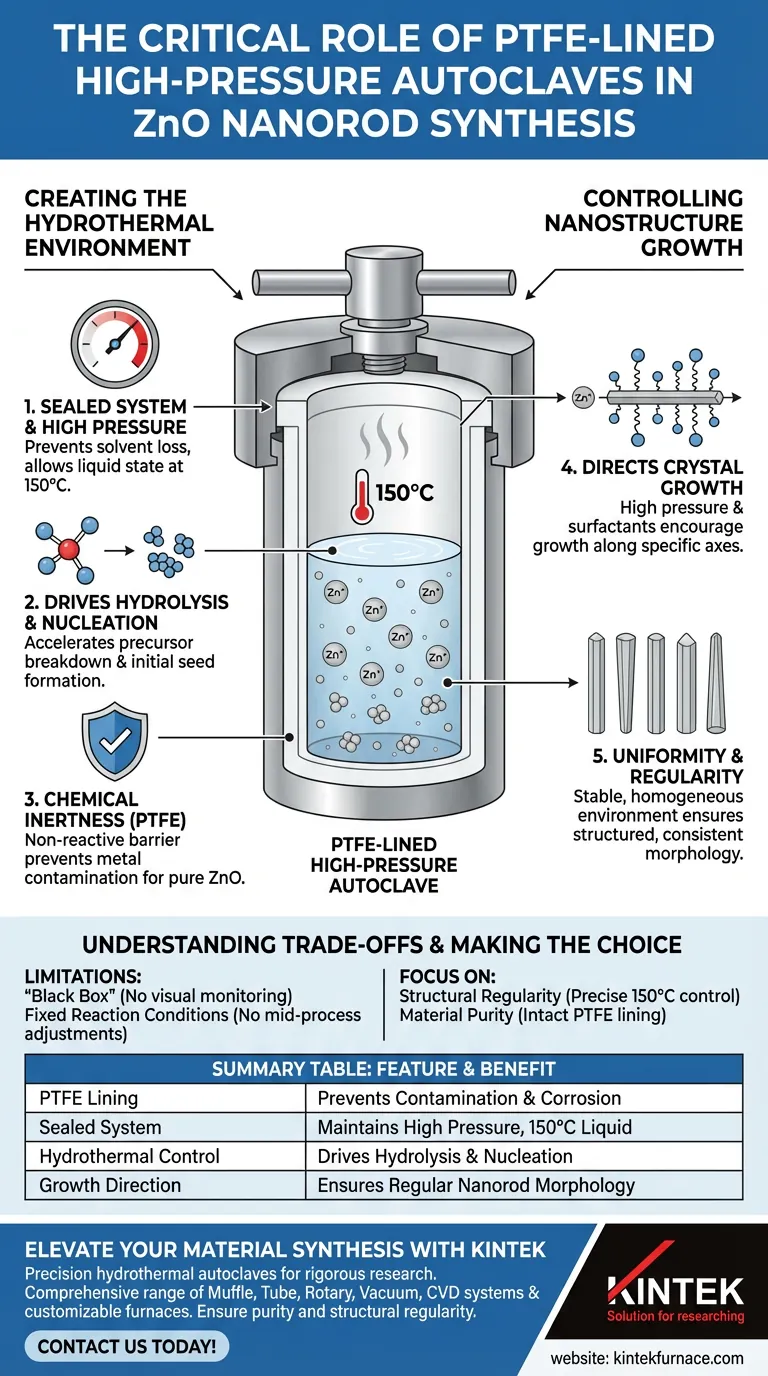
The PTFE-lined high-pressure autoclave serves as the critical reaction vessel for the hydrothermal synthesis of Zinc Oxide (ZnO) nanorods. It creates a sealed, corrosion-resistant environment that allows precursor solutions to be heated to 150°C while maintaining high pressure. This specific combination of heat and containment is required to drive the hydrolysis and nucleation of zinc ions effectively.
By establishing a high-pressure, high-temperature environment within a chemically inert chamber, the autoclave facilitates the precise conditions needed for ZnO to grow into structured, regular nanorods along specific crystal axes.
Creating the Hydrothermal Environment
The Necessity of High Pressure
The autoclave acts as a sealed system, which prevents solvents from escaping as vapor.
This generates high internal pressure, allowing the precursor solution to remain liquid at 150°C—temperatures that would otherwise cause the solution to boil away in an open container.
Driving Hydrolysis and Nucleation
The elevated temperature and pressure within the vessel significantly alter the physical properties of the solvent.
This environment accelerates hydrolysis, the chemical breakdown of the precursor materials. Simultaneously, it promotes nucleation, the initial step where zinc ions begin to cluster and form the fundamental seeds of the crystal structure.
Chemical Inertness via PTFE
The "PTFE-lined" aspect of the equipment is essential for maintaining the purity of the reaction.
PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) provides a non-reactive barrier between the corrosive precursor solutions and the metal shell of the autoclave. This ensures that the synthesized ZnO nanorods are not contaminated by metallic impurities from the vessel itself.
Controlling Nanostructure Growth
Directing Crystal Growth
The autoclave does not just facilitate a chemical reaction; it helps define the physical shape of the output.
When used in conjunction with surfactants, the high-pressure environment encourages the ZnO crystals to grow along specific crystal axes. This directional growth is what ultimately shapes the material into elongated nanorods rather than irregular particles.
Uniformity and Regularity
The sealed nature of the autoclave ensures a stable, homogeneous environment throughout the synthesis duration.
This stability allows the nanorods to develop a structured and regular morphology, ensuring consistency across the batch.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The "Black Box" Limitation
Because the autoclave must be sealed to generate high pressure, the reaction process is entirely enclosed.
You cannot visually monitor the growth of the nanorods or the color changes of the solution in real-time. The outcome is only visible after the reaction is complete and the vessel has cooled.
Fixed Reaction Conditions
Once the autoclave is sealed and heating begins, the chemical inputs cannot be altered.
Unlike open-beaker reactions, you cannot add reagents or adjust surfactant levels mid-process to correct for errors or change the growth trajectory dynamically.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The autoclave is a powerful tool, but its effectiveness depends on how you manipulate the variables it controls.
- If your primary focus is Structural Regularity: Ensure your temperature controls are precise at 150°C, as this thermal energy drives the specific axis growth facilitated by the pressure.
- If your primary focus is Material Purity: Rely on the integrity of the PTFE lining to prevent corrosion, but ensure the liner is inspected regularly for scratches or defects that could harbor contaminants.
Mastering the autoclave means mastering the balance between temperature, pressure, and time to dictate the final geometry of your nanorods.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in ZnO Nanorod Synthesis | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| PTFE Lining | Provides a chemically inert barrier | Prevents metallic contamination & corrosion |
| Sealed System | Maintains high internal pressure | Prevents solvent loss & allows 150°C liquid state |
| Hydrothermal Control | Drives hydrolysis & nucleation | Accelerates seed formation for crystal growth |
| Growth Direction | Focuses growth along specific axes | Ensures structured, regular nanorod morphology |
Elevate Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK
Precision is paramount when synthesizing ZnO nanorods. KINTEK provides industry-leading high-pressure hydrothermal autoclaves designed to meet the rigorous demands of your laboratory. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, along with customizable high-temp lab furnaces tailored to your unique research needs.
Ensure purity and structural regularity in your next project with our durable PTFE-lined solutions. Contact us today to find the perfect hydrothermal vessel for your lab!
Visual Guide
References
- Yanan Fan, Yongheng Zhu. Research on pH-responsive antibacterial materials using citral-modified zinc oxide nanoparticles. DOI: 10.1093/fqsafe/fyae010
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Spark Plasma Sintering SPS Furnace
People Also Ask
- What type of pump is used in water circulating vacuum pumps and how is it installed? Discover Robust Fluid-Based Vacuum Solutions
- What roles do ceramic crucibles play in 500 °C pre-calcination? Ensure Pure Layered Oxide Synthesis
- What are the technical functions of condensation units and gas collection bags? Optimize Your Reduction Experiments
- How do a three-stub tuner and a sliding short contribute to microwave carbothermic reduction? Maximize Energy Efficiency
- What is the function of an alumina boat during high-temperature activation of porous carbon? Durable Lab Solutions
- Why are high-purity quartz reaction tubes utilized in CVD reactions for preparing Ni-Co doped carbon nanotubes?
- What are the specific functions of high-purity graphite molds in SPS? Optimize Your Sintering Process
- What is the role of gold (Au), platinum (Pt), or platinum-iridium (Pt-Ir) foil in silicate melt experiments?



















