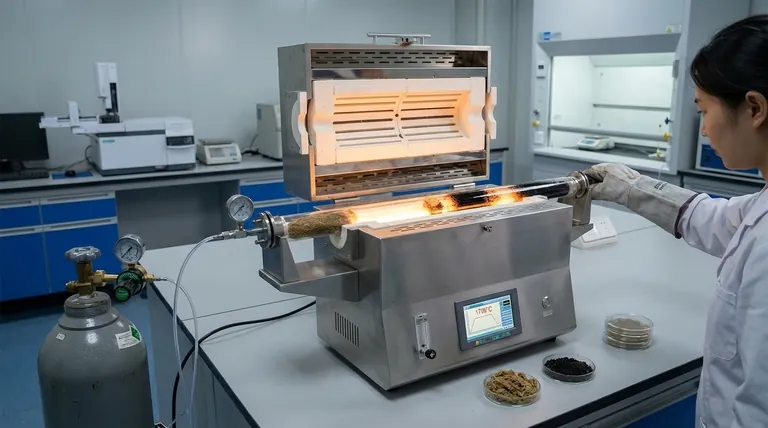
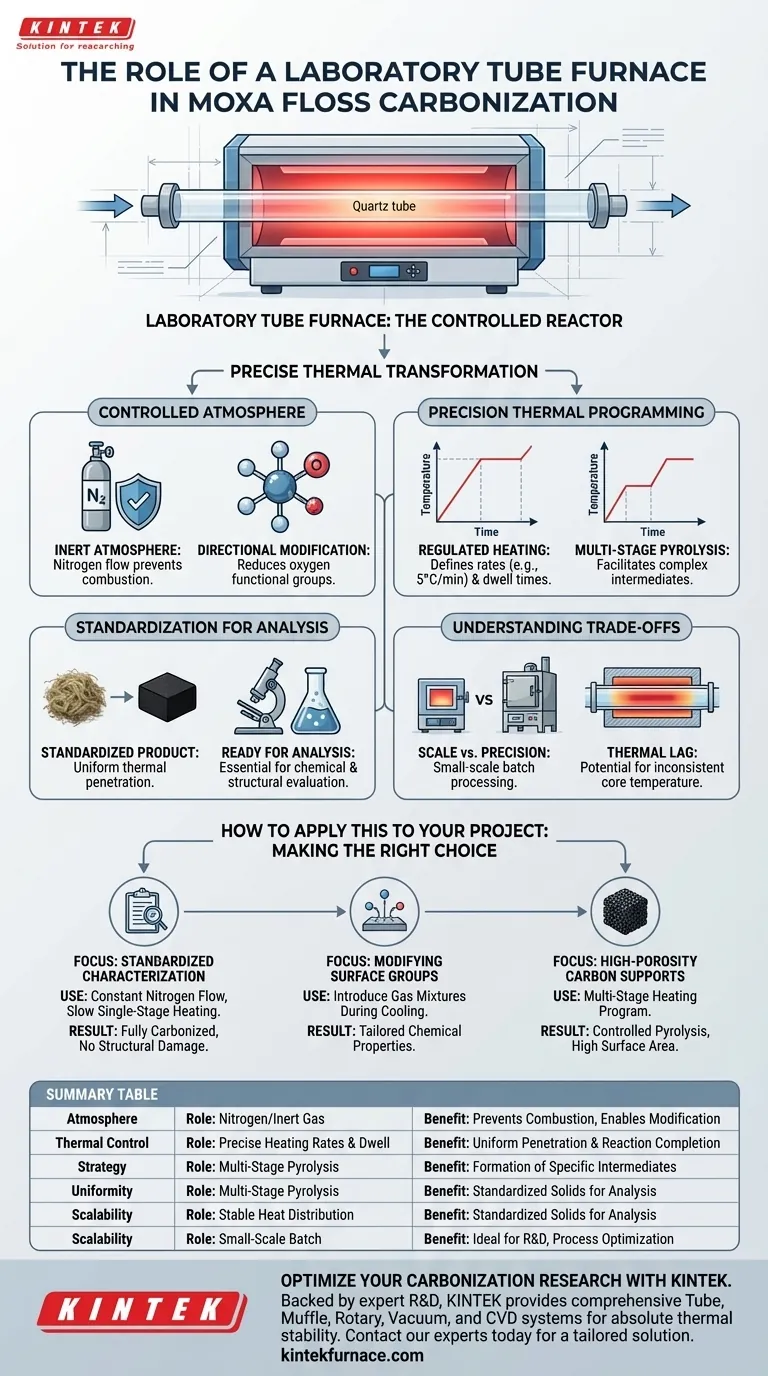
A laboratory tube furnace acts as the controlled reactor for the precise thermal transformation of moxa floss into carbonized material. It provides a sealed, large-volume environment that facilitates batch processing while maintaining strict control over heating rates, dwell times, and atmospheric composition, typically using nitrogen. This ensures the moxa floss biomass is converted into a standardized solid product suitable for rigorous chemical and structural analysis.
The laboratory tube furnace is the critical tool for standardized moxa floss carbonization, providing an oxygen-free, thermally stable environment. It enables researchers to manipulate heating profiles and gas flows to achieve consistent biomass conversion, which is essential for accurate downstream scientific evaluation.

Controlled Atmospheric Environments
Maintaining an Inert Atmosphere
The primary role of the tube furnace is to provide a well-sealed environment where air is displaced by a constant flow of protective gas. For moxa floss, a nitrogen flow is typically used to prevent the biomass from combusting when exposed to high temperatures.
Directional Chemical Modification
Beyond simple protection, the furnace atmosphere can be adjusted to influence the material's surface chemistry. While moxa carbonization usually relies on inert gases, the furnace's ability to introduce reducing gases allows for the directional removal of oxygen-containing functional groups if specific catalytic properties are required.
Precision Thermal Programming
Regulating Heating Rates and Dwell Times
The tube furnace allows researchers to define a precise heating rate, such as 5 °C per minute, to ensure uniform thermal penetration. Controlling the dwell time—the duration the moxa remains at a specific temperature—is vital for ensuring the carbonization reaction reaches completion without degrading the material's structure.
Multi-Stage Pyrolysis Strategies
Complex carbonization processes often require a two-stage heating strategy to form specific chemical intermediates. The furnace can be programmed to hold a lower temperature to allow for initial precursor pyrolysis before rising to a higher temperature to finalize the carbonized structure.
Ensuring Standardization for Analysis
Production of Standardized Solid Products
Because the tube furnace offers a stable and uniform heat distribution, it transforms raw moxa floss into a standardized solid. This consistency is mandatory for researchers who need to perform subsequent chemical and structural analysis on the carbonized samples.
Small-Scale Synthesis and Process Development
In research and development laboratories, the tube furnace serves as an efficient platform for small-scale material synthesis. It allows for the exploration of how different temperatures and atmospheres affect the final density of active sites and the specific surface area of the carbonized moxa.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Scale vs. Precision
While tube furnaces offer exceptional control over the thermal environment, they are generally limited to small-scale or batch processing. Researchers must balance the need for high-precision environmental control with the relatively low throughput compared to industrial-scale kilns.
Thermal Lag and Uniformity
In larger furnace tubes, a thermal gradient can exist between the heating elements and the center of the sample mass. If the moxa floss is packed too densely within the tube, the core may not reach the target temperature at the same rate as the exterior, leading to inconsistent carbonization across the batch.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
- If your primary focus is standardized chemical characterization: Use a constant nitrogen flow and a slow, single-stage heating ramp to ensure the moxa floss is fully carbonized without structural damage.
- If your primary focus is modifying surface functional groups: Utilize the furnace’s ability to introduce specific gas mixtures during the cooling phase to tailor the chemical properties of the carbonized surface.
- If your primary focus is developing high-porosity carbon supports: Implement a multi-stage heating program that allows for controlled pyrolysis of organic frameworks within the moxa at distinct temperature plateaus.
By mastering the thermal and atmospheric variables of the tube furnace, you transform a simple biomass into a sophisticated, scientifically viable carbon material.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Role in Moxa Carbonization | Benefit to Research |
|---|---|---|
| Atmosphere | Nitrogen flow/Inert gas environment | Prevents combustion; enables directional modification |
| Thermal Control | Precise heating rates & dwell times | Ensures uniform thermal penetration & reaction completion |
| Strategy | Multi-stage pyrolysis | Facilitates formation of specific chemical intermediates |
| Uniformity | Stable heat distribution | Produces standardized solids for structural analysis |
| Scalability | Small-scale batch processing | Ideal for R&D and process optimization |
Optimize Your Carbonization Research with KINTEK
Precision is non-negotiable when transforming delicate biomass like moxa floss into high-value carbon materials. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK provides a comprehensive range of Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed for absolute thermal stability.
Our lab high-temp furnaces are fully customizable to meet your unique atmospheric and programming needs, ensuring your research yields standardized, repeatable results every time.
Ready to elevate your material synthesis?
Contact our experts today for a tailored solution.
Visual Guide
References
- Yukun Feng, Zhaoyi Zhuang. Combustion Characteristics of Moxa Floss Under Nitrogen Atmosphere. DOI: 10.3390/fuels6020048
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a tube furnace contribute to the carbonization of biomass? Master Precise Pyrolysis for Superior Materials
- How does a lab tube furnace differ from a box furnace? A Guide to Choosing the Right Thermal Processing Tool
- What are the differences between solid and split tube furnaces? Choose the Right Furnace for Your Lab
- Why is a tube furnace equipped with a nitrogen environment necessary for biochar? Achieve Precise Pyrolysis Control
- What are the benefits of high yield and product concentration in a tube furnace? Boost Efficiency and Purity in Chemical Processes
- Why is a quartz tube furnace used for two-stage LiFePO4 coating? Master Oxidation Control and Conductivity
- How does a tube furnace control the phase structure of copper-based chalcogenides? Master Precise Thermal Management
- What industries commonly use High Temperature Tube Furnaces? Essential for Material Science, Electronics, and More



















