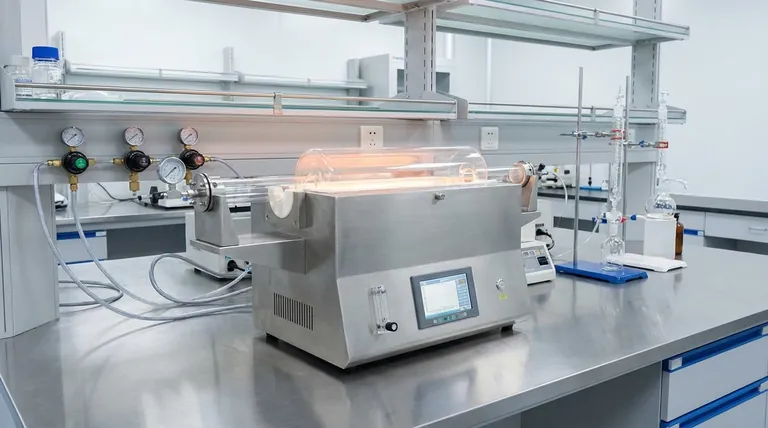
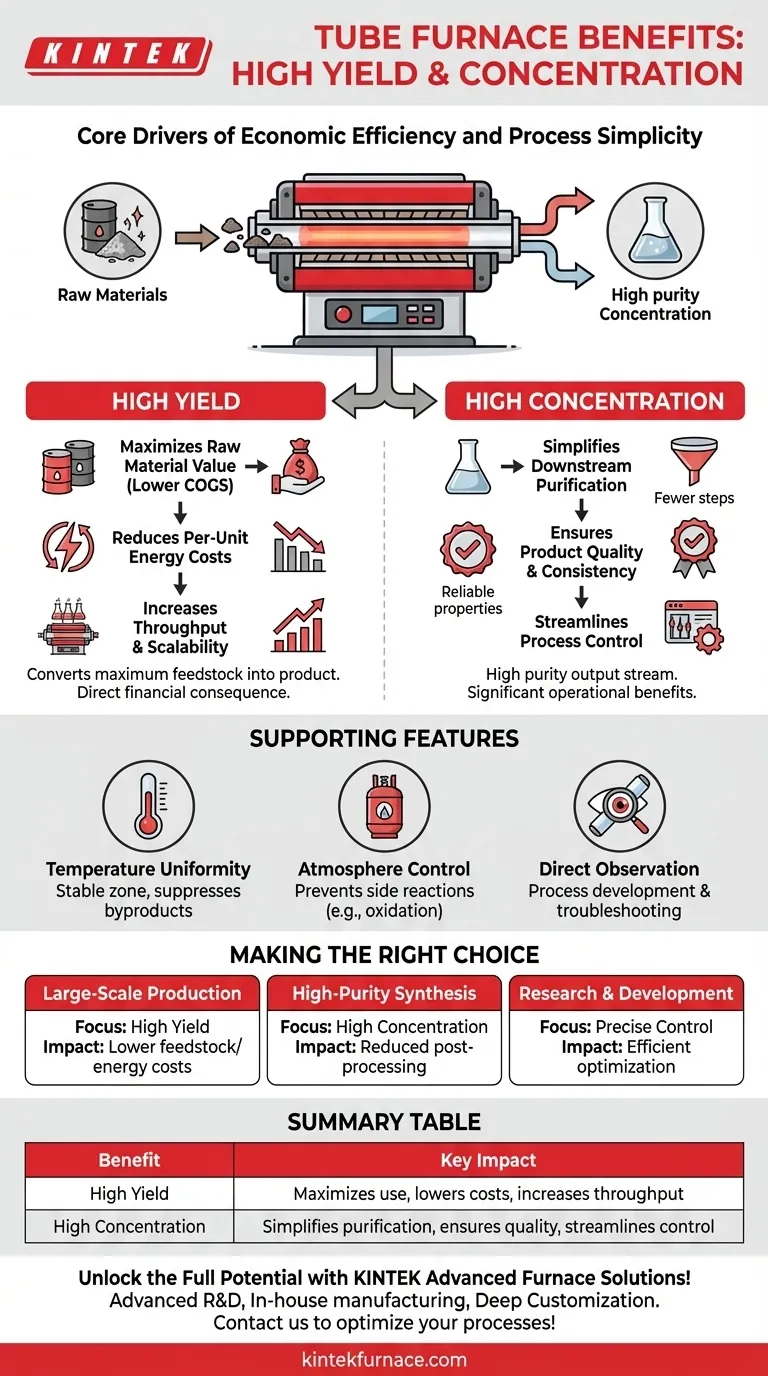
In chemical manufacturing, the high yield and high product concentration achieved in a tube furnace are not just minor advantages; they are core drivers of economic efficiency and process simplicity. High yield ensures you convert the maximum amount of raw material into your desired product, while high concentration means that product is purer, which significantly streamlines the entire production workflow.
The true value of a tube furnace's performance is not just in producing more product, but in its cascading effect on the entire system—reducing waste, lowering energy costs, and minimizing the immense expense and complexity of downstream purification.

The Economic Impact of High Yield
High yield is the measure of how efficiently a process converts raw materials (feedstock) into the desired final product. In a commercial context, every percentage point of yield has a direct financial consequence.
Maximizing Raw Material Value
A higher yield means less of your expensive feedstock is wasted on unwanted byproducts or left unreacted. This directly lowers your cost of goods sold.
For processes like the cracking of hydrocarbons to produce ethylene and propylene, this efficiency is the foundation of profitability.
Reducing Per-Unit Energy Costs
A tube furnace consumes energy to maintain its high temperatures. By producing more product in a single run, high yield effectively lowers the amount of energy consumed per kilogram of product.
This improvement in thermal efficiency is critical for managing operational expenditures, especially in energy-intensive applications.
Increasing Throughput and Scalability
Because each furnace unit can produce more, achieving a target production volume requires less equipment and a smaller physical footprint.
Tube furnaces can also be combined for massive-scale production, and high-yield performance makes this scaling far more economically viable.
The Operational Advantage of High Concentration
Product concentration refers to the purity of the output stream. A high concentration of the desired substance, with minimal impurities, offers significant operational benefits.
Simplifying Downstream Purification
This is arguably the most significant benefit. A highly concentrated product stream requires fewer, less complex, and less energy-intensive separation steps, such as distillation or chromatography.
This simplification reduces both the initial capital investment in purification equipment and the long-term operational costs associated with running it.
Ensuring Product Quality and Consistency
A higher concentration of the target product inherently means a lower concentration of byproducts and contaminants.
This leads to a final product that is of higher quality and has more consistent, reliable properties from batch to batch, which is critical for high-spec applications.
Streamlining Process Control
Managing a process with a clean, concentrated output is far simpler than managing one with a complex mixture of byproducts.
The process is easier to monitor, analyze, and control, reducing the likelihood of operational errors and production deviations.
Understanding the Supporting Features
The high yield and concentration of a tube furnace don't happen in a vacuum. They are the result of several key design features working in concert.
The Role of Temperature Uniformity
Tube furnaces are designed to provide an exceptionally stable and uniform temperature zone in the center of the tube.
This precision is vital because it ensures all reactants experience the same thermal conditions, promoting the desired chemical reaction while suppressing the formation of unwanted byproducts that would lower both yield and concentration.
The Importance of Atmosphere Control
The ability to operate under a controlled atmosphere (using inert gases like argon) or a vacuum is essential.
This control prevents unwanted side reactions, such as oxidation, that would consume the product and create impurities, effectively destroying the yield.
The Value of Direct Observation
Many tube furnaces use a transparent quartz tube, allowing operators to see the process in real time.
This direct observation is invaluable for process development and troubleshooting, enabling researchers to quickly diagnose issues and optimize conditions to maximize both yield and purity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
The decision to use a tube furnace should be based on how its core benefits align with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is large-scale chemical production: The high yield is paramount for economic viability, as it directly lowers your feedstock and energy costs per unit of product.
- If your primary focus is high-purity material synthesis: The high product concentration is the key benefit, as it drastically reduces the cost and complexity of post-processing and purification.
- If your primary focus is research and development: The furnace's precise control, versatility, and observability are most important, allowing you to efficiently optimize new processes for both yield and concentration.
Ultimately, understanding how yield and concentration impact your entire workflow is the key to leveraging a tube furnace effectively for your goals.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Key Impact |
|---|---|
| High Yield | Maximizes raw material use, lowers energy costs, and increases throughput |
| High Concentration | Simplifies purification, ensures product quality, and streamlines process control |
Unlock the full potential of your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer a diverse product line—including Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—tailored to meet the unique needs of chemical manufacturers and research labs. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your experimental requirements, boosting efficiency, purity, and cost-effectiveness. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your processes and drive innovation together!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents



















