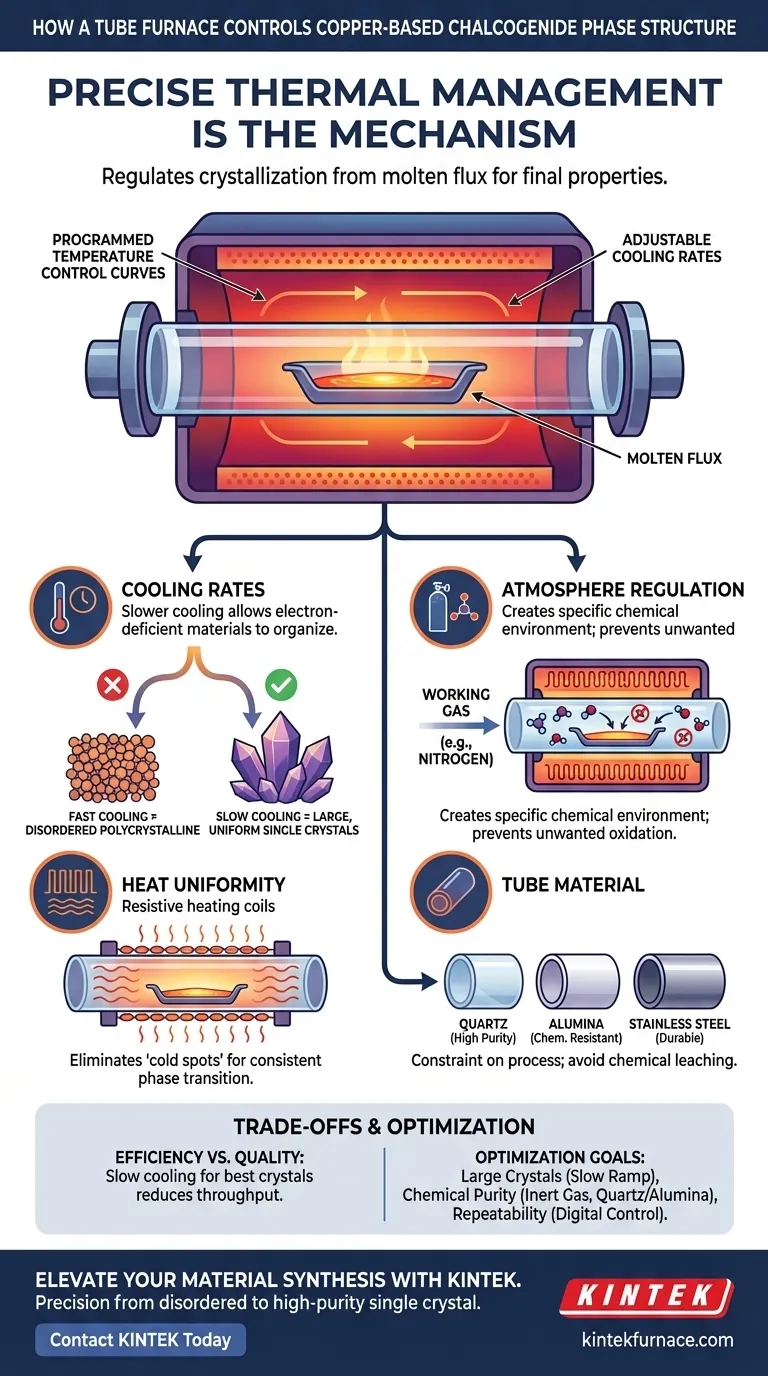
Precise thermal management is the mechanism by which a tube furnace defines the phase structure of copper-based chalcogenide materials. By strictly adhering to programmed temperature control curves and adjustable cooling rates, the furnace regulates the crystallization process from a molten flux to determine the final structural properties.
The core capability of the tube furnace lies in slowing the transition from liquid to solid; this controlled deceleration allows electron-deficient materials to organize into large, uniform single crystals rather than disordered polycrystalline structures.

Regulating Crystallization via Thermal Profiling
The fundamental lever for controlling phase structure is the temperature curve. A tube furnace allows you to define the exact thermal history of the material, which is critical when synthesizing chalcogenides from flux.
The Critical Role of Cooling Rates
The speed at which the furnace cools the sample is often more important than the maximum temperature reached. For electron-deficient copper chalcogenides, a rapid drop in temperature can freeze the material in a disordered state.
Promoting Crystal Growth
A slow cooling rate facilitates the growth of large single crystals. This gradual reduction in thermal energy gives the atoms sufficient time to arrange themselves into specific, ordered orientations.
Ensuring Phase Uniformity
By maintaining a consistent temperature profile, the furnace ensures that the entire sample undergoes the same phase transition simultaneously. This prevents the formation of secondary phases or gradients within the material structure.
Controlling the Chemical Environment
Beyond temperature, the phase structure is heavily influenced by the atmosphere surrounding the sample during synthesis.
Atmosphere Regulation
The tube furnace allows for the introduction of working gases, such as nitrogen. Regulating the flow of these gases creates a specific chemical environment that prevents unwanted oxidation or side reactions that could alter the phase structure.
Uniform Heat Distribution
As noted in equipment specifications, resistive heating elements surround the work tube to provide uniform heat along its length. This hardware design ensures that the thermal logic programmed into the controller is applied evenly to the material, eliminating "cold spots" that could disrupt crystallization.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While tube furnaces offer precision, achieving the correct phase structure requires balancing conflicting variables.
The Efficiency vs. Quality Conflict
Extremely slow cooling rates yield the highest quality single crystals with the best phase uniformity. However, this dramatically increases the time required for each synthesis cycle, potentially limiting throughput in a research or production environment.
Tube Material Compatibility
The choice of the work tube (quartz, alumina, or stainless steel) creates a constraint on your process. For example, while quartz is excellent for high purity, it may not withstand the same chemical interactions as alumina or the mechanical stress of stainless steel. Using the wrong tube material can lead to chemical leaching, which introduces impurities and ruins the phase purity of the chalcogenide.
Optimizing Synthesis for Your Goals
To achieve the desired phase structure in copper-based chalcogenide materials, you must align the furnace parameters with your specific structural requirements.
- If your primary focus is Large Single Crystals: Prioritize an extended, slow cooling ramp to allow the flux to crystallize into specific, ordered orientations.
- If your primary focus is Chemical Purity: Utilize a high-purity quartz or alumina tube and maintain a strict flow of inert gas (like nitrogen) to isolate the reaction environment.
- If your primary focus is Process Repeatability: Rely on digital control systems to lock in the exact temperature curves and gas flow rates that yielded your baseline success.
By mastering the cooling rate and environmental controls, you transform the tube furnace from a simple heater into a precision instrument for material engineering.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Phase Structure | Optimization Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Cooling Rate | Determines crystal size and ordering | Slow cooling for large single crystals; fast for disordered states |
| Atmosphere | Prevents oxidation and side reactions | Use inert gases like Nitrogen to maintain chemical purity |
| Heat Uniformity | Ensures consistent phase transition | Utilize resistive heating elements to eliminate cold spots |
| Tube Material | Affects purity and chemical stability | Select Alumina or Quartz based on chemical compatibility |
Elevate Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK
Precision is the difference between a disordered polycrystalline structure and a high-purity single crystal. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all fully customizable to meet the rigorous demands of chalcogenide research.
Whether you need advanced thermal profiling or specialized gas environments, our laboratory high-temp furnaces provide the control you need for repeatable, world-class results. Contact us today to find the perfect furnace for your lab!
Visual Guide
References
- С.А. Новиков, Vladislav V. Klepov. Structural evolution and bonding features of electron deficient copper chalcogenides. DOI: 10.1039/d5ce00479a
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the key features of a quartz tube furnace? Discover High-Temp Precision for Your Lab
- What role do industrial tube furnaces play in the oxidation of NiCrAl alloys? Precise Stability for Reliable Data
- What materials are commonly used for the reaction tubes in a tube furnace? Choose the Best for Your Thermal Process
- How is the structure of a multi station vacuum tube furnace divided? Optimize Your Lab's Thermal Processing
- Why is a high-temperature tube furnace with inert protection needed for PCFC? Master Carbonization for Composites
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve energy efficiency? Key Design Features for Lower Energy Costs
- What role do high-performance box or tube furnaces play in LATP sintering? Master Densification & Ionic Conductivity
- How does a multi-channel thermocouple array assist in measuring REBCO tape temperature? Master Thermal Uniformity



















