In short, high temperature tube furnaces are staples in advanced scientific and industrial fields. They are most commonly used in material science, chemistry, electronics, metallurgy, nanotechnology, and pharmaceuticals for both research and specialized production.
The true value of a high temperature tube furnace isn't just its ability to get hot, but its capacity to create a precisely controlled thermal environment. This control over temperature uniformity and atmosphere is why it's indispensable for creating the advanced materials that define modern technology.

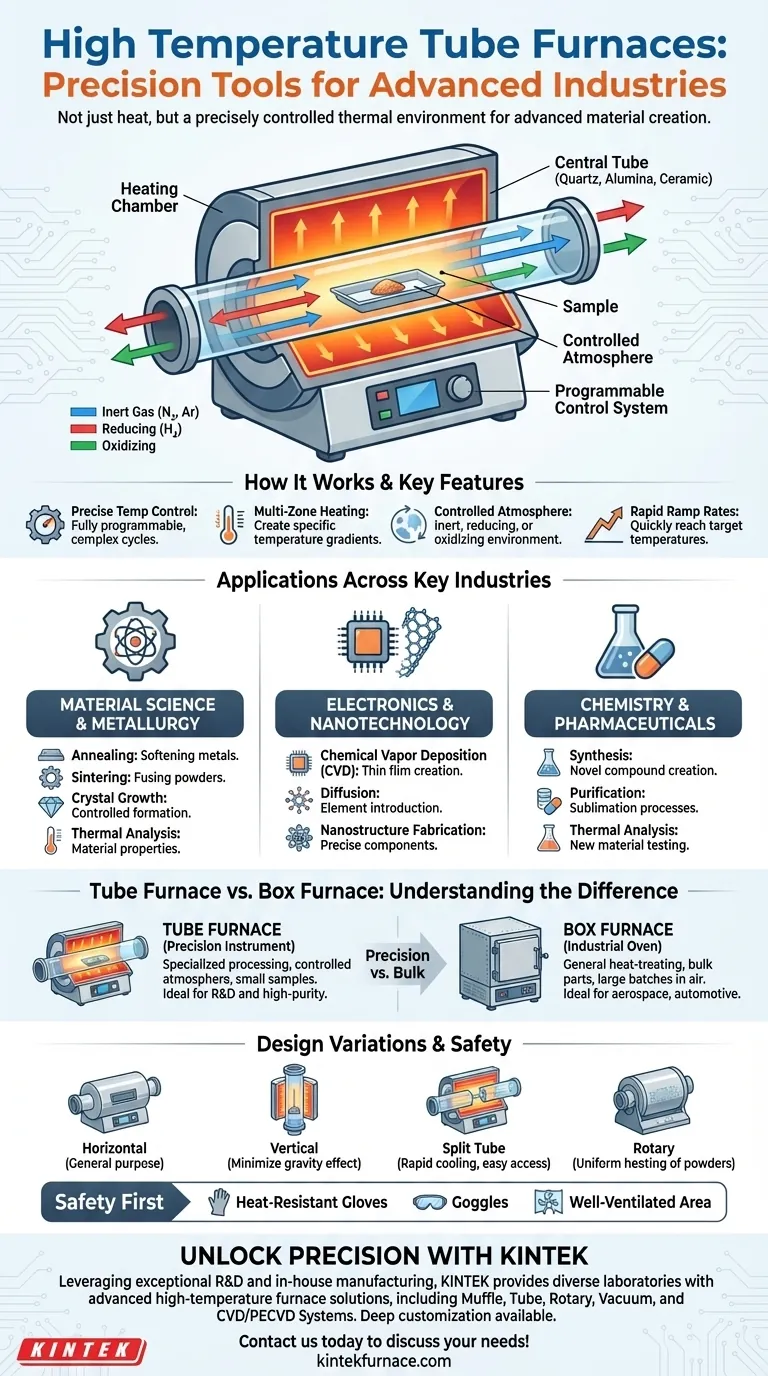
The Core Function: Precision in a Controlled Environment
A high temperature tube furnace is designed for one primary purpose: heating a sample to a precise temperature inside a contained, controlled atmosphere. This simple function is critical for a wide range of advanced processes.
How a Tube Furnace Works
The design consists of a heating chamber, or "furnace," built around a central tube. A sample is placed inside this tube, which can then be sealed and filled with a specific gas or held under a vacuum.
The tube itself is typically made from materials like quartz, alumina, ceramic, or specialized metal alloys, chosen based on the required temperature and chemical compatibility.
Why the "Tube" is Critical
The tubular geometry is the key to its function. It creates an isolated environment, ensuring the sample is heated uniformly and is not contaminated by outside air.
This allows for processes that require a specific atmosphere, such as inert (using nitrogen or argon), reducing (using hydrogen), or oxidizing.
Achieving Unmatched Precision
Modern tube furnaces offer features that enable exacting control over the heating process. Key features often include:
- Fully programmable control systems for complex temperature cycles.
- Multi-zone heating to create specific temperature gradients along the tube.
- Rapid ramp rates for quickly reaching a target temperature.
- Programmable cooling for controlled crystallization or annealing.
Applications Across Key Industries
The ability to control both temperature and atmosphere makes the tube furnace a cornerstone tool in several high-tech fields.
Material Science and Metallurgy
This is the most common domain for tube furnaces. They are used for processes like annealing (softening metals), sintering (fusing powders into a solid), and crystal growth. The ability to precisely manage heating and cooling rates is fundamental to determining a material's final properties.
Electronics and Nanotechnology
The manufacturing of semiconductors and nanostructures demands absolute purity and precision. Tube furnaces are used for creating thin films on wafers (chemical vapor deposition), diffusing elements into substrates, and fabricating components where even minor temperature fluctuations could ruin the product.
Chemistry and Pharmaceuticals
In chemical and pharmaceutical research, tube furnaces are used for synthesizing novel compounds, purification through sublimation, and performing thermal analysis on new materials. The controlled, inert atmosphere prevents unwanted side reactions and ensures the purity of the final product.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Variations
While powerful, a tube furnace is a specialized tool. Understanding its limitations and variations is key to using it effectively.
Tube Furnace vs. Box Furnace
A common point of confusion is the difference between a tube furnace and a box furnace. A box furnace is a larger chamber designed for heating bigger, bulkier items or large batches of parts in air.
Think of a box furnace as an industrial oven for general heat-treating, used heavily in aerospace, automotive, and mining. A tube furnace is a precision instrument for specialized material processing, not bulk production.
Key Design Variations
Not all tube furnaces are the same. The primary designs include:
- Horizontal: The most common configuration, suitable for general-purpose use.
- Vertical: Used to minimize the effect of gravity, ideal for crucible-based crystal growth or preventing samples from sagging at high temperatures.
- Split Tube: The furnace body opens like a clamshell, allowing for rapid cooling and easy access to the process tube and sample.
- Rotary: The tube slowly rotates during heating, ideal for tumbling powders to ensure every particle is heated uniformly.
Operational Considerations and Safety
Operating these devices requires training and strict safety protocols. This includes wearing heat-resistant gloves and goggles, ensuring the work area is well-ventilated, and never heating unknown materials that could release moisture or dangerous gases.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right thermal processing equipment depends entirely on your specific application and desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is high-purity synthesis, thin-film deposition, or atmospheric processing: A tube furnace is non-negotiable for its precise environmental control.
- If your primary focus is heat-treating bulk parts, large batches, or general-purpose heating in air: A box furnace is the more practical and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is research and development with diverse materials: A multi-zone split tube furnace offers the greatest flexibility for experimentation and rapid sample changes.
Ultimately, understanding the unique strengths of a tube furnace empowers you to select the right tool to achieve your material processing goals.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Key Applications |
|---|---|
| Material Science & Metallurgy | Annealing, sintering, crystal growth |
| Electronics & Nanotechnology | Chemical vapor deposition, diffusion, fabrication |
| Chemistry & Pharmaceuticals | Synthesis, purification, thermal analysis |
| General Notes | Controlled atmosphere, high precision, uniform heating |
Unlock Precision in Your Lab with KINTEK's High-Temperature Solutions
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in material science, electronics, or pharmaceuticals, our furnaces ensure precise temperature control and atmospheric management for superior results.
Contact us today to discuss how we can tailor a solution for your specific needs and enhance your research or production efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision



















