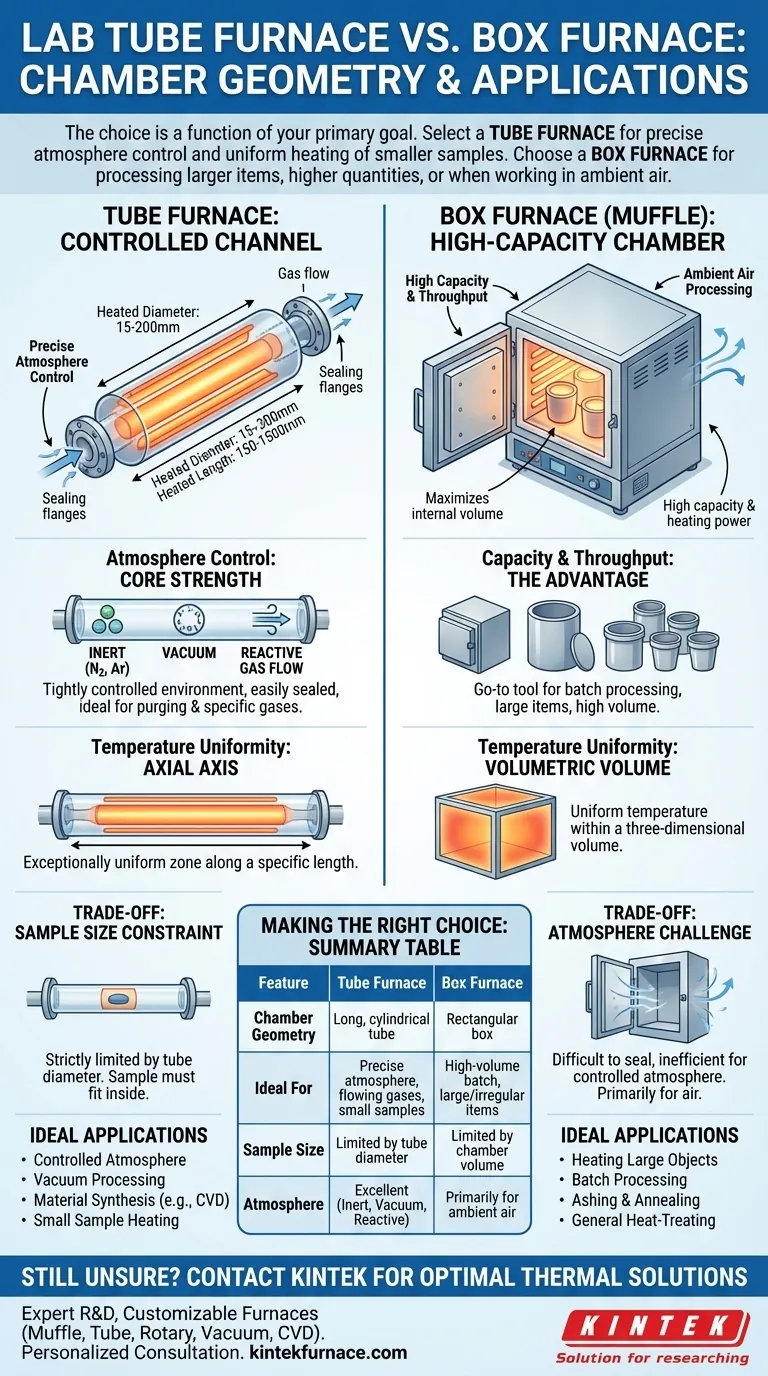
At its core, the fundamental difference between a lab tube furnace and a box furnace is the geometry of their heating chamber. A tube furnace uses a long, cylindrical tube for processing, whereas a box furnace uses a larger, rectangular chamber, a distinction that dictates their ideal applications.
The choice is a function of your primary goal. Select a tube furnace for precise atmosphere control and uniform heating of smaller samples. Choose a box furnace for processing larger items, higher quantities, or when working in ambient air.

The Defining Difference: Chamber Geometry
The shape of the heating chamber is not just a cosmetic detail; it is the single most important factor that determines the furnace's capabilities and limitations.
The Tube Furnace: A Controlled Channel
A tube furnace is defined by its long, narrow heating chamber. The material to be processed is placed inside this tube.
This design is intentional. The constrained, cylindrical shape is perfect for creating a highly uniform temperature zone along its heated length and, most critically, for managing the internal atmosphere.
Key specifications for tube furnaces are their heated diameter (from 15 mm to 200 mm) and heated length (from 150 mm to 1500 mm), which define the usable processing area.
The Box Furnace: A High-Capacity Chamber
A box furnace, also known as a muffle furnace, has a chamber that is square or rectangular, resembling a box.
This geometry maximizes internal volume. Its primary advantage is the ability to accommodate larger, irregularly shaped items or multiple smaller samples at once.
These furnaces are typically characterized by their internal volume and are built for applications where high capacity and sheer heating power are more important than precise atmospheric control.
Key Functional Distinctions
Understanding the chamber geometry allows us to see how each furnace excels in different laboratory tasks.
Atmosphere Control: The Tube Furnace's Core Strength
This is the most critical distinction. The ends of a tube furnace can be easily sealed with flanges, allowing for a tightly controlled environment.
This design makes it simple to purge the air and introduce a specific gas, such as nitrogen or argon, to create an inert atmosphere. It is also ideal for creating a vacuum or flowing reactive gases over a sample.
Capacity and Throughput: The Box Furnace Advantage
The spacious chamber of a box furnace makes it the go-to tool for batch processing.
If you need to heat many crucibles, anneal a large component, or perform general heat-treating on bulky materials, the box furnace is far more efficient. They come in various sizes, from small benchtops to large, industrial-scale walk-in units.
Temperature Uniformity
While both furnace types can achieve high temperatures with excellent precision, their uniformity differs in character.
A tube furnace provides an exceptionally uniform temperature zone along a specific axis or length of the tube. A box furnace provides a uniform temperature within a three-dimensional volume.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing one furnace type means accepting the inherent limitations of its design.
The Constraint of Sample Size
A tube furnace's greatest strength—its controlled, narrow chamber—is also its primary weakness. You are strictly limited by the diameter of the process tube. Any sample you wish to heat must be able to fit inside.
The Challenge of Atmosphere
While a box furnace is excellent for heating in air, creating a controlled atmosphere within one is difficult and inefficient. Sealing a large door is far more complex than sealing the ends of a tube, and it requires a much higher volume of gas to purge the ambient air.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be based entirely on the demands of your specific process.
- If your primary focus is controlled atmosphere or vacuum: The sealed, efficient design of a tube furnace is the only logical choice.
- If your primary focus is heating large objects or multiple samples in air: The capacity and ease of access of a box furnace are superior.
- If your primary focus is material synthesis with reactive gases (e.g., CVD): A tube furnace is purpose-built for flowing gases over a substrate.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose ashing, annealing, or drying: A box furnace provides greater flexibility and throughput for common thermal processes.
Selecting the correct furnace is the first step toward reliable and repeatable results in your work.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Tube Furnace | Box Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Chamber Geometry | Long, cylindrical tube | Rectangular box |
| Ideal For | Precise atmosphere control, flowing gases, small samples | High-volume batch processing, large/irregular items |
| Sample Size Constraint | Limited by tube diameter | Limited by chamber volume |
| Atmosphere Control | Excellent (Inert, Vacuum, Reactive) | Primarily for ambient air |
Still Unsure Which Furnace is Right for Your Lab?
Selecting the correct furnace is critical for achieving reliable and repeatable results. The expert team at KINTEK is here to help you make the optimal choice for your specific thermal processing needs, whether they require the precise atmosphere control of a Tube Furnace or the high-capacity heating of a Box (Muffle) Furnace.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, CVD systems, and other lab high-temp furnaces, all customizable for unique needs.
Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation and let us provide the perfect heating solution to enhance your lab's efficiency and capability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- How does a tube heating furnace facilitate the carbon coating process? Boost Layered Oxide Conductivity
- What core process conditions does a tube furnace provide? Mastering Catalyst Precursor Treatment
- How do roller kilns and tube furnaces differ in their use of Alumina ceramic tubes? Compare Transport vs. Containment
- What are the material requirements for furnace tubes? Optimize Performance and Safety in High-Temperature Labs



















