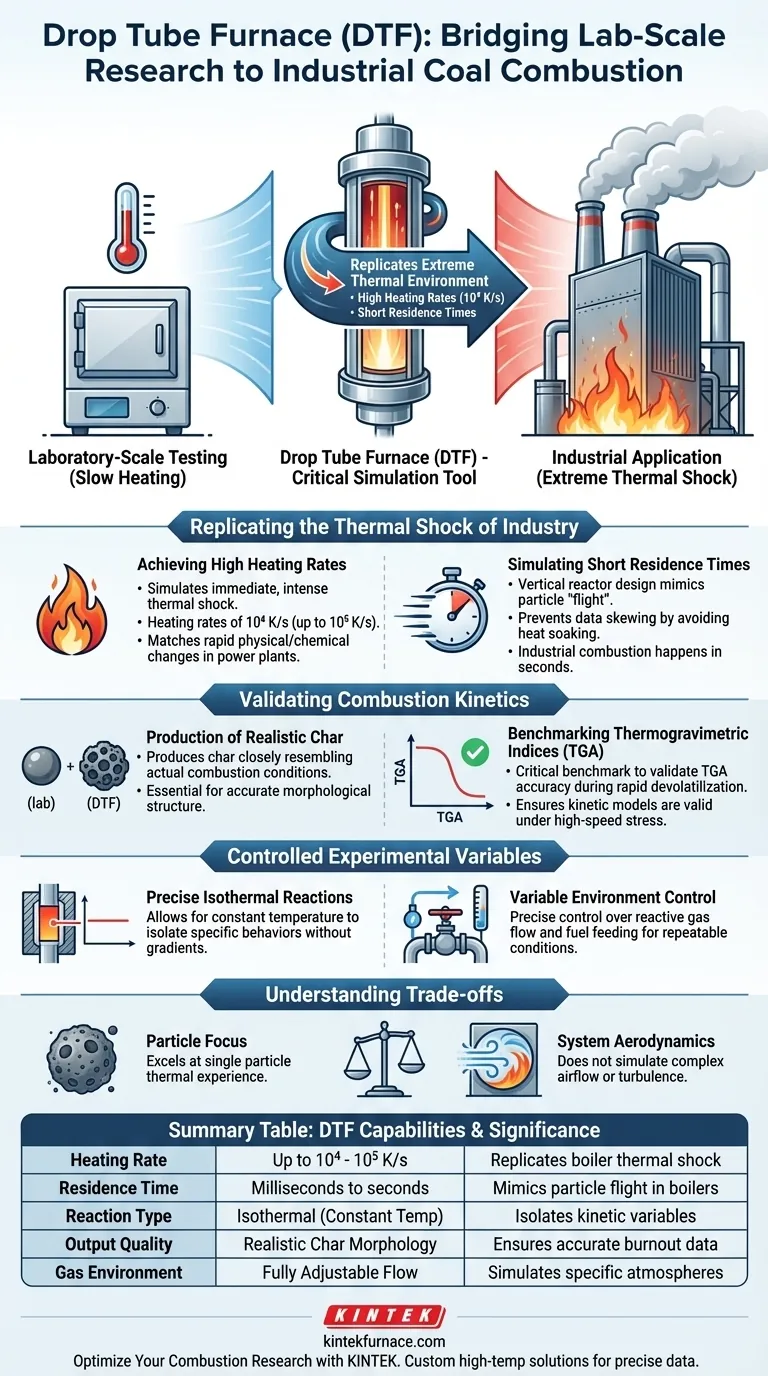
A Drop Tube Furnace (DTF) serves as a critical simulation tool that bridges the gap between laboratory-scale testing and full-scale industrial application. It replicates the extreme thermal environment of a power plant boiler by generating high heating rates (reaching 10⁴ K/s) and restricting particles to short residence times, ensuring the resulting data accurately reflects real-world pulverized coal combustion.
The Core Reality: Standard laboratory tests often heat fuel too slowly to predict industrial behavior accurately. The Drop Tube Furnace solves this by matching the rapid devolatilization phase of industrial boilers, serving as the essential benchmark for validating thermogravimetric indices and char characteristics.

Replicating the Thermal Shock of Industry
Achieving High Heating Rates
In an actual industrial boiler, pulverized coal is subjected to immediate, intense thermal shock. A DTF simulates this environment by achieving heating rates of 10⁴ K/s (and potentially up to 10⁵ K/s depending on configuration).
This rapid heating is distinct from standard lab ovens. It ensures the fuel particles undergo physical and chemical changes that match those occurring in a massive power plant.
Simulating Short Residence Times
Industrial combustion happens in seconds, not minutes. The DTF utilizes a vertical reactor design to ensure fuel particles fall through the heating zone quickly.
This mimics the "flight" of a particle through a boiler. It prevents the fuel from "soaking" in heat longer than it would in reality, which prevents skewed data regarding burnout and ash formation.
Validating Combustion Kinetics
Production of Realistic Char
The primary value of the DTF is its ability to produce char that closely resembles actual combustion conditions.
Slow-heating devices produce char with different morphological structures than fast-heating devices. By using a DTF, researchers generate char samples that are chemically and physically representative of industrial byproducts.
Benchmarking Thermogravimetric Indices
Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA) is a common method for studying fuel, but it typically operates at slower heating rates.
The DTF acts as a critical benchmark. It validates the accuracy of TGA indices specifically during the rapid devolatilization phase, ensuring that the kinetic models derived from simpler tests remain valid under high-speed thermal stress.
Controlled Experimental Variables
Precise Isothermal Reactions
Unlike the fluctuating zones in a massive boiler, a DTF allows for isothermal reactions (constant temperature).
This isolation allows researchers to observe specific behaviors—such as volatile release or char oxidation—without temperature gradients distorting the data.
Variable Environment Control
The device offers precise control over reactive gas flow and fuel feeding rates.
This enables the study of specific phenomena, such as ignition behavior and product formation characteristics, under highly repeatable conditions.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Particle Focus vs. System Aerodynamics
The DTF excels at simulating the thermal experience of a single particle. However, it is designed to study kinetics and chemistry, not the complex aerodynamics (like swirl or massive turbulence) of a full-scale utility boiler.
Complexity of Operation
Compared to static furnaces, the DTF requires rigorous control of feed rates and gas flows to maintain accuracy. It is a precision instrument designed for kinetic validation, not just bulk material heating.
Making the Right Choice for Your Research
If you are designing an experiment or interpreting combustion data, consider how the DTF fits into your methodology:
- If your primary focus is Kinetic Modeling: Use the DTF to derive reaction rates and char burnout data that accounts for high heating rates, which TGA alone cannot provide.
- If your primary focus is Fuel Comparison: Use the DTF to produce char samples under identical high-stress conditions to accurately compare how different coal types will behave in a specific boiler.
By simulating the speed and intensity of industrial heat, the Drop Tube Furnace translates theoretical laboratory data into actionable industrial insights.
Summary Table:
| Feature | DTF Simulation Capability | Industrial Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Rate | Up to 10⁴ - 10⁵ K/s | Replicates boiler thermal shock |
| Residence Time | Milliseconds to seconds | Mimics particle flight in boilers |
| Reaction Type | Isothermal (Constant Temp) | Isolates kinetic variables |
| Output Quality | Realistic Char Morphology | Ensures accurate burnout data |
| Gas Environment | Fully Adjustable Flow | Simulates specific atmospheres |
Optimize Your Combustion Research with KINTEK
Bridge the gap between lab-scale testing and industrial reality with high-precision thermal systems. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers customizable Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, including advanced furnace solutions tailored for pulverized coal and kinetic research.
Whether you need to replicate extreme thermal shock or ensure precise isothermal control, our team is ready to deliver the hardware your innovation demands.
Contact KINTEK Today to Customize Your High-Temp Solution
Visual Guide
References
- Krzysztof Czajka. Evaluation of the Reliability of Thermogravimetric Indices for Predicting Coal Performance in Utility Systems. DOI: 10.3390/en18133473
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
People Also Ask
- Why is a horizontal tube furnace used for CVD in catalyst synthesis? Achieve Precise Nano-Material Growth
- How does a tube furnace ensure uniform heating? Master Precise Temperature Control for Your Lab
- What is the purpose of using high-purity quartz tubes and vacuum sealing for Cu13Se52Bi35 alloy preparation?
- What is the specific role of a tube furnace in the pre-treatment of activated carbon catalysts? Precision Modification
- Why is a high-temperature tube furnace required for annealing repair after dry etching? Restoring Crystal Lattice
- Why is a high-temperature tube furnace with inert gas protection required for MAX phases? Ensure 1400°C Phase Purity
- What are the specifications for three-zone and three-phase horizontal tube furnace models? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Lab
- What is the primary function of a horizontal tube furnace in simulating the oxidation behavior of hot-rolled steel?



















