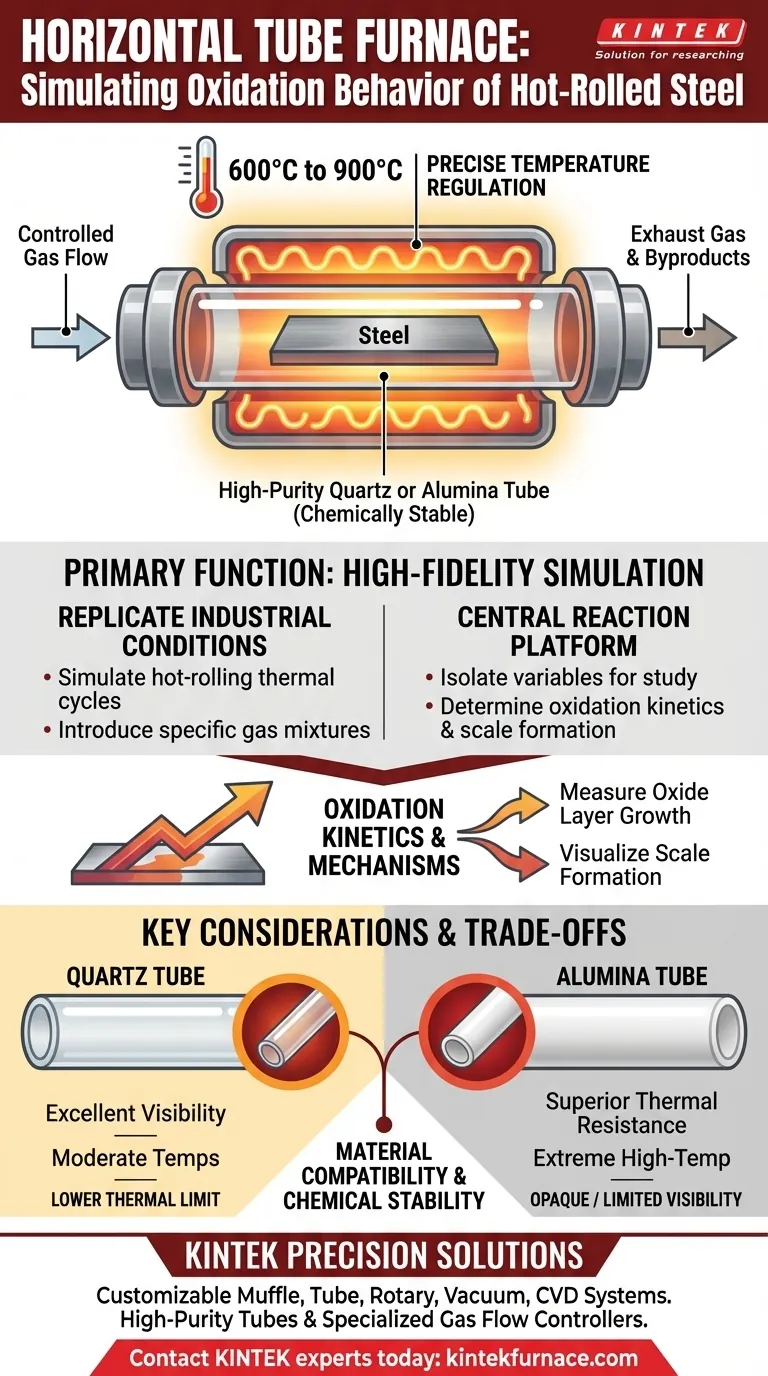
The primary function of a horizontal tube furnace is to replicate the specific environmental conditions of an industrial hot-rolling line within a controlled laboratory setting. By precisely regulating temperatures between 600°C and 900°C and introducing defined gas mixtures, the furnace serves as the central reaction platform for determining exactly how hot-rolled steel oxidizes and forms scale.
The furnace is not merely a heater; it is a simulation chamber. Its ability to simultaneously control thermal energy and atmospheric composition allows researchers to isolate specific variables, providing the data necessary to understand oxidation kinetics and scale formation mechanisms.
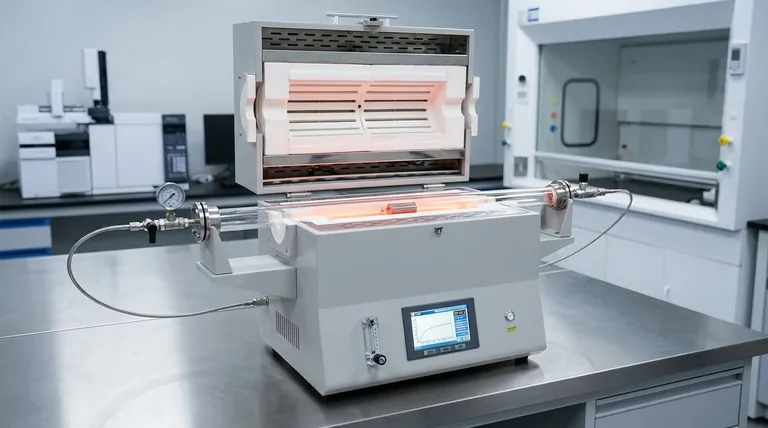

Creating a High-Fidelity Simulation Environment
To accurately model industrial processes, a furnace must do more than simply get hot. It must recreate the chemical reality of the production line.
Precise Temperature Regulation
The horizontal tube furnace is engineered to maintain a stable high-temperature environment.
For hot-rolled steel simulation, this typically involves a target range of 600°C to 900°C.
This stability is critical because even minor fluctuations in temperature can drastically alter the rate at which oxidation occurs.
Atmospheric Control
The defining characteristic of this apparatus is its ability to manage the gas environment.
By introducing mixed gases into the tube, the system simulates the specific combustion atmospheres found in industrial factories.
This allows researchers to move beyond simple air oxidation and study how steel reacts to the complex byproducts of industrial heating.
The Mechanics of the Experiment
The physical construction of the furnace is designed to ensure that the data collected is a result of the sample's reaction, not contamination from the equipment.
The Role of the Furnace Tube
The core component of the system is the tubular chamber where the sample resides.
This tube is constructed from high-temperature-resistant materials, most commonly quartz or alumina.
These materials are selected specifically for their chemical stability, ensuring they do not react with the sample or the gases even at extreme heat.
Studying Kinetics and Mechanisms
The ultimate goal of this setup is to facilitate the study of oxidation kinetics.
Researchers use this platform to measure how fast oxide layers grow and to visualize the mechanisms of scale formation.
This data helps engineers predict how steel will behave during actual manufacturing, leading to better quality control in hot-rolling lines.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While horizontal tube furnaces are powerful tools, reliable results depend on understanding the limitations of the materials involved.
Material Compatibility
The choice of tube material is a critical trade-off between cost and performance.
Quartz is excellent for visibility and moderate temperatures but has a lower thermal limit compared to other ceramics.
Alumina offers superior thermal resistance for higher-end experiments but is generally opaque, limiting visual observation during the process.
Chemical Stability Risks
If the tube material is not matched correctly to the experiment, the tube itself may degrade.
The supplementary references highlight that the tube must maintain chemical stability; failure to do so can contaminate the atmosphere and invalidate the simulation data.
Applying This to Your Research
To get the most out of a horizontal tube furnace, you must align your equipment choices with your specific experimental data requirements.
- If your primary focus is oxidation kinetics: Prioritize a furnace with high-precision gas flow controllers to ensure the atmospheric composition remains constant throughout the 600°C to 900°C cycle.
- If your primary focus is extreme high-temperature testing: Select a furnace tube made of alumina rather than quartz to ensure structural integrity and chemical inertness at the upper limits of the heating range.
By mastering the variables of temperature and atmosphere, you transform a standard lab instrument into a predictive model for industrial success.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Purpose in Oxidation Simulation | Key Specifications |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | Replicates hot-rolling thermal cycles | 600°C to 900°C |
| Atmospheric Control | Simulates industrial combustion gases | Mixed gas injection |
| Tube Material | Ensures chemical inertness/stability | Quartz or Alumina |
| Primary Goal | Measures oxidation kinetics/mechanisms | High-fidelity modeling |
Optimize Your Steel Research with KINTEK Precision
Precise simulation of oxidation kinetics requires absolute control over temperature and atmosphere. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all fully customizable for your unique metallurgical needs.
Whether you require high-purity alumina tubes for extreme heat or specialized gas flow controllers for industrial atmosphere replication, our high-temp lab furnaces provide the reliability your research demands.
Ready to elevate your lab's capabilities? Contact KINTEK experts today to design your custom furnace solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Seksan Singthanu, Thanasak Nilsonthi. A Comparative Study of the Oxidation Behavior of Hot-Rolled Steel established from Medium and Thin Slabs oxidized in 20% H2O-N2 at 600-900°C. DOI: 10.48084/etasr.6168
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
People Also Ask
- What are the disadvantages of quartz tube furnaces? Limitations in Durability and Temperature
- What is the technical value of using an industrial-grade tube furnace for titania nanotubes? Enhance Crystal Performance
- Why is controlling the residence time within a tube furnace critical for the synthesis of amorphous NiFe2O4 catalysts?
- What role does a tube annealing furnace play in the preparation of nanoporous NiPt catalysts? Vital Catalyst Activation
- What is the function of a tube furnace in catalyst annealing? Unlock L10 Ordered Structures for Peak Performance
- What is the purpose of using a tube resistance furnace with flowing oxygen for NMC synthesis? Achieve Pure Phase Purity
- Why is a specialized tube furnace with a steam inlet required for the steam activation of carbon materials?
- What are the advantages of a dual-zone tube furnace for Ti3C2Tx MXene? Master Precise Sulfurization Kinetics



















