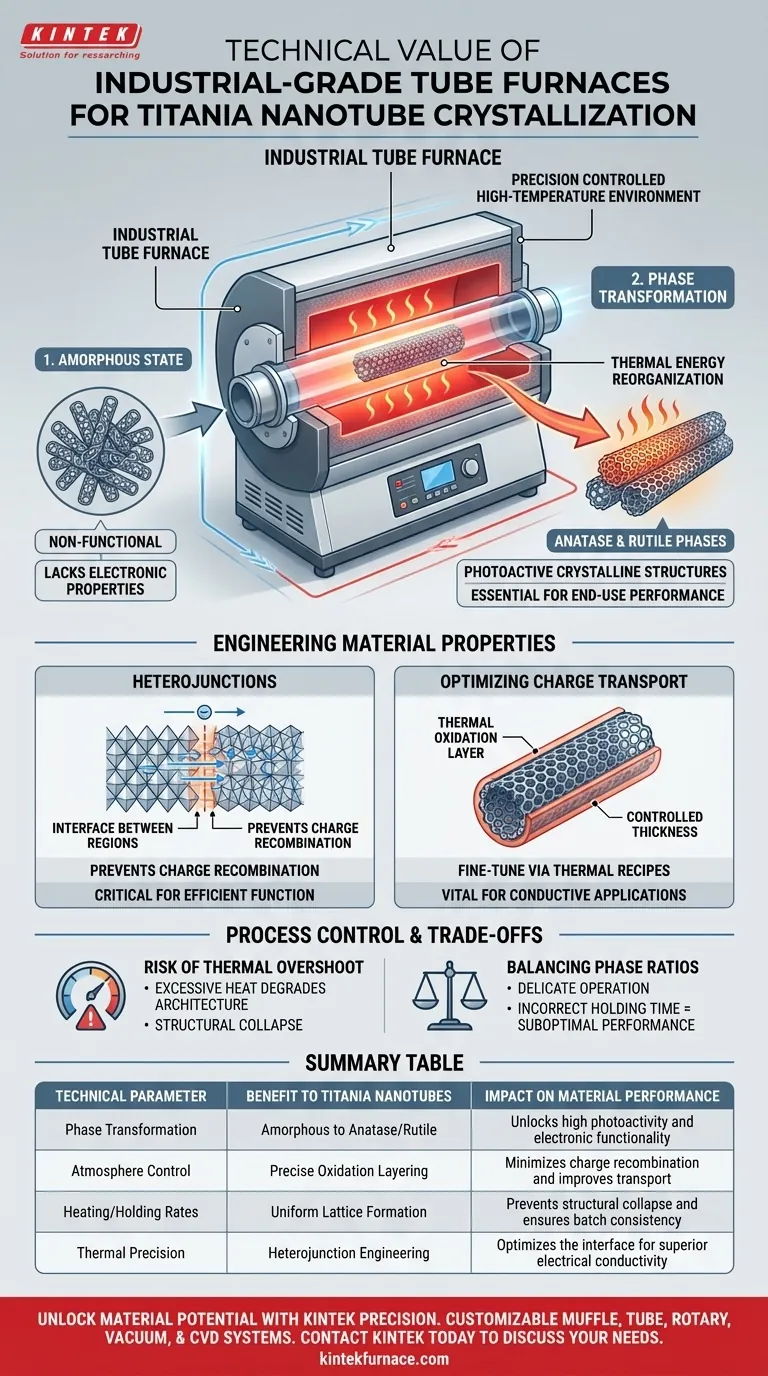
The distinct technical advantage of an industrial-grade tube furnace lies in its ability to facilitate the precise phase transformation of titania nanotubes from a non-functional amorphous state into highly photoactive crystalline structures. By providing a rigorously controlled high-temperature environment, this equipment enables the reliable conversion of raw nanotubes into specific anatase and rutile phases, which are essential for the material's end-use performance.
Beyond simple heating, the industrial tube furnace allows for the engineering of material properties; by manipulating heating rates and holding times, manufacturers can dictate the formation of heterojunctions and oxidation layers that define the material's charge transport capabilities.

The Mechanics of Phase Transformation
From Amorphous to Crystalline
In their initial state, titania nanotubes are typically amorphous and lack the electronic properties required for advanced applications. The tube furnace provides the thermal energy necessary to reorganize this atomic structure.
This process converts the material into photoactive crystalline phases, specifically anatase and rutile. Without this crystallization, the nanotubes cannot effectively participate in photochemical reactions.
Engineering Heterojunctions
The transition between different crystalline phases is not merely a side effect; it is a targetable outcome. The precise control offered by the furnace allows for the induction of specific heterojunctions.
These junctions—interfaces between different semiconductor regions—are critical for separating electrical charges. They prevent charge recombination, ensuring the material functions efficiently.
Optimizing Charge Transport
Controlling Thermal Oxidation Layers
A critical parameter in nanotube performance is the thickness of the thermal oxidation layer. The tube furnace allows operators to fine-tune this thickness through specific thermal recipes.
An optimized oxidation layer is vital for charge transport performance. If the layer is uncontrolled, it can impede the flow of electrons, rendering the nanotube ineffective for conductive applications.
Managing Heating Rates and Holding Times
The "how" of the heating process is just as important as the final temperature. The tube furnace offers granular control over heating rates and holding times.
These variables determine the final quality of the crystal lattice. Uniform heating ensures consistent performance across the entire batch of nanotubes, eliminating weak spots in the material structure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Risk of Thermal Overshoot
While high temperatures are necessary for crystallization, excessive heat or uncontrolled ramp rates can degrade the nanotube architecture. If the temperature exceeds the structural tolerance, the nanotubes may collapse or sinter together, destroying the high surface area that makes them valuable.
Balancing Phase Ratios
Achieving the right balance between anatase and rutile phases is a delicate operation. An incorrect holding time might result in a phase composition that is thermodynamically stable but electronically suboptimal for the intended application.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the value of your crystallization process, align your furnace parameters with your specific performance metrics.
- If your primary focus is photoactivity: Prioritize thermal profiles that favor the formation of the anatase phase, as it generally exhibits higher surface reactivity.
- If your primary focus is charge transport efficiency: Focus on optimizing the holding times to engineer robust heterojunctions and a controlled oxidation layer thickness.
Success in titania nanotube treatment relies not just on reaching high temperatures, but on the precise orchestration of that heat to engineer the material at the atomic level.
Summary Table:
| Technical Parameter | Benefit to Titania Nanotubes | Impact on Material Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Phase Transformation | Amorphous to Anatase/Rutile | Unlocks high photoactivity and electronic functionality |
| Atmosphere Control | Precise Oxidation Layering | Minimizes charge recombination and improves transport |
| Heating/Holding Rates | Uniform Lattice Formation | Prevents structural collapse and ensures batch consistency |
| Thermal Precision | Heterojunction Engineering | Optimizes the interface for superior electrical conductivity |
Unlock Material Potential with KINTEK Precision
Take full control of your material's phase transformation with KINTEK’s advanced thermal solutions. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet your specific research or industrial needs. Whether you are engineering titania nanotubes or developing next-generation semiconductors, our high-temp furnaces provide the uniformity and precision your lab demands.
Ready to optimize your crystallization process? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom furnace needs.
Visual Guide
References
- Younggon Son, Kiyoung Lee. Interfacial Charge Transfer Modulation via Phase Junctions and Defect Control in Spaced TiO <sub>2</sub> Nanotubes for Enhanced Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting. DOI: 10.1002/solr.202500334
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a two-zone tube furnace achieve stepwise control of precursors? Master CVD Heterostructure Growth
- Why is a tube furnace equipped with a nitrogen environment necessary for biochar? Achieve Precise Pyrolysis Control
- What is the purpose of using a high-temperature tube furnace during FePt annealing? Achieve the L1₀ Magnetic Phase
- What role does a tubular furnace play in the preparation of biochar? Master Precise Biochar Pyrolysis
- What is the necessity of annealing treatment for CuCo2O4@rGO? Optimize High-Crystallinity Synthesis in Tube Furnaces
- What are the possible configurations of heated sections in a High Temperature Tube Furnace? Choose the Right Setup for Your Process
- What is the advantage of a three-zone tube furnace? Achieve Larger, More Uniform Heating for Your Processes
- Why are quartz or alumina tubes used in tube furnaces? Key Benefits for High-Temp Processes



















